PCA9922PW,112 NXP Semiconductors, PCA9922PW,112 Datasheet
PCA9922PW,112
Specifications of PCA9922PW,112
Related parts for PCA9922PW,112
PCA9922PW,112 Summary of contents
Page 1
PCA9922 8-channel constant current LED driver with output error detection Rev. 2 — 6 April 2011 1. General description The PCA9922 is an 8-channel constant current LED driver designed for LED signage and display applications. The output current is adjustable ...
Page 2
... NXP Semiconductors Packages offered: DIP16, TSSOP16, HVQFN20 3. Applications Full color, multi-color, monochrome LED signs LED billboard displays Traffic display signs Transportation and commercial LED signs 4. Ordering information Table 1. Ordering information Type number Package Name Description PCA9922N DIP16 plastic dual in-line package; 16 leads (300 mil) ...
Page 3
... NXP Semiconductors 5. Block diagram Fig 1. PCA9922 Product data sheet 8-channel constant current LED driver with output error detection LED0 LED1 V DD R_EXT CURRENT REGULATOR OUTPUT ENABLE LE 8× DATA LATCH V SS SDI 8× SHIFT REGISTER CLK ERROR CONTROL Block diagram of PCA9922 All information provided in this document is subject to legal disclaimers. Rev. 2 — ...
Page 4
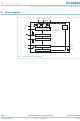
... NXP Semiconductors 6. Pinning information 6.1 Pinning Fig 2. Fig 4. PCA9922 Product data sheet 8-channel constant current LED driver with output error detection SDI 2 15 R_EXT 3 14 CLK SDO LE/DM1 4 13 OE/DM2 PCA9922N LED0 5 12 LED7 6 11 LED1 LED6 LED2 7 10 LED5 8 9 LED3 ...
Page 5
... NXP Semiconductors 6.2 Pin description Table input output. Symbol V SS SDI CLK LE/DM1 LED0 LED1 LED2 LED3 LED4 LED5 LED6 LED7 OE/DM2 SDO R_EXT V DD n.c. [1] HVQFN20 package die supply ground is connected to both V be connected to supply ground for proper device operation. For enhanced thermal, electrical, and board ...
Page 6
... NXP Semiconductors 7. Functional description The PCA9922 is an 8-channel constant current LED driver with built-in LED output error detection. The PCA9922 contains an 8-bit shift register and data latches, which convert serial input data into parallel output data. At the output stage, 8 regulated current sinks are designed to provide constant and ...
Page 7
... NXP Semiconductors Fig 5. 7.2 LED output error detection The PCA9922 has built-in circuitry for detecting LED open-circuit and output short conditions. A predefined set of signal sequence on the input control lines must be initiated to perform the output error detection. Once the error data is captured by this sequence, error status can be read out of the device via the serial interface ...
Page 8
... NXP Semiconductors Table 4. State of output port off on [1] I th(det) 7.2.2 Short-circuit detection principle The LED short-circuit detection compares the effective voltage level (V shorted-load detection threshold voltages V V th(det)sc V th(norm error status code in the Special mode. For short-circuit error detection, a channel must be on. ...
Page 9
... NXP Semiconductors 7.2.4 Setting the outputs to test Before the Capture Fault sequence may be performed, the outputs must be set up. A logic HIGH must be sent to the output control register for all eight bits. This is done after the Enter Error Detect sequence is performed as a normal data load sequence as seen in Figure 5 ...
Page 10
... NXP Semiconductors 7.2.6 Exit error detect mode The ‘Exit error detect mode’ sequence is used to exit the error detect mode of operation and resume normal mode. This is a 5-clock timing sequence using CLK, OE and LE. This sequence consists of LE being held inactive for all five clocks active in the second clock for one and only one clock ...
Page 11
CLK SDI shift_reg[n-1:0] SDO previous serial data shifting out OE LE fault_load fault_data[n-1:0] error_detect_mode Lower-case signal names are internal signals shown to aid understanding of timing. Fig 9. Timing for a complete error detection sequence at ...
Page 12
... NXP Semiconductors 8. Application design-in information Fig 10. Typical application V DD Fig 11. The PCA9922 in a typical multi-device architecture PCA9922 Product data sheet 8-channel constant current LED driver with output error detection C 10 μF LED0 LED1 R_EXT SDI CLK MICROCONTROLLER scan OE CLK CPU PCA9922 ...
Page 13
... NXP Semiconductors 9. Limiting values Table 6. In accordance with the Absolute Maximum Rating System (IEC 60134). Symbol O(LED) V O(SDO O(LEDn) f clk T stg tot 10. Recommended operating conditions Table 7. Symbol O(LED) I O(LEDn) V O(SDO) P tot T oper 11. Thermal characteristics Table 8. Symbol R th(j-a) PCA9922 Product data sheet ...
Page 14
... NXP Semiconductors 12. Static characteristics Table 9. Static characteristics ° 5 unless otherwise specified. DD amb Symbol Parameter V short-circuit detection threshold th(det)sc voltage V normal mode threshold voltage th(norm) Control interface (OE, LE, CLK, SDI, SDO) V HIGH-level input voltage IH V LOW-level input voltage IL V LOW-level output voltage ...
Page 15
... NXP Semiconductors 13. Dynamic characteristics Table 10. Dynamic characteristics Symbol Parameter t LE pulse width w(LE pulse width w(OE) t SDI set-up time su(SDI) t SDI hold time h(SDI) f frequency on pin CLK CLK δ clock duty cycle t CLK HIGH pulse width w(CLKH) t CLK LOW pulse width ...
Page 16
... NXP Semiconductors [2] OE must be held active LOW for at least the duration of the rise/fall time of the LEDn pins. This pulse width does not apply to active LOW times for executing error detect sequences. [3] Timing required for signaling of error detection sequences. Not necessary for ‘normal’ operation. ...
Page 17
... NXP Semiconductors Fig 14. Timing 2 PCA9922 Product data sheet 8-channel constant current LED driver with output error detection t w(OE PD(OE-LEDH) t PD(OE-LEDL) LEDn w(LE PD(LEH-LEDH) t PD(LEH-LEDL) LEDn 50 % CLK PD(CLKH-LEDH) t PD(CLKH-LEDL) LEDn 50 % All information provided in this document is subject to legal disclaimers. Rev. 2 — 6 April 2011 ...
Page 18
... NXP Semiconductors 14. Package outline DIP16: plastic dual in-line package; 16 leads (300 mil pin 1 index 1 DIMENSIONS (inch dimensions are derived from the original mm dimensions UNIT max. min. max. mm 4.2 0.51 3.2 inches 0.17 0.02 0.13 Note 1. Plastic or metal protrusions of 0.25 mm (0.01 inch) maximum per side are not included. ...
Page 19
... NXP Semiconductors TSSOP16: plastic thin shrink small outline package; 16 leads; body width 4 pin 1 index 1 DIMENSIONS (mm are the original dimensions) A UNIT max. 0.15 0.95 mm 1.1 0.25 0.05 0.80 Notes 1. Plastic or metal protrusions of 0.15 mm maximum per side are not included. 2. Plastic interlead protrusions of 0.25 mm maximum per side are not included. ...
Page 20
... NXP Semiconductors HVQFN20: plastic thermal enhanced very thin quad flat package; no leads; 20 terminals; body 0.85 mm terminal 1 index area terminal 1 20 index area DIMENSIONS (mm are the original dimensions) (1) A UNIT max. 0.05 0. 0.2 0.00 0.23 Note 1. Plastic or metal protrusions of 0.075 mm maximum per side are not included. ...
Page 21
... NXP Semiconductors 15. Handling information All input and output pins are protected against ElectroStatic Discharge (ESD) under normal handling. When handling ensure that the appropriate precautions are taken as described in JESD625-A or equivalent standards. 16. Soldering of SMD packages This text provides a very brief insight into a complex technology. A more in-depth account of soldering ICs can be found in Application Note AN10365 “ ...
Page 22
... NXP Semiconductors • Process issues, such as application of adhesive and flux, clinching of leads, board transport, the solder wave parameters, and the time during which components are exposed to the wave • Solder bath specifications, including temperature and impurities 16.4 Reflow soldering Key characteristics in reflow soldering are: • ...
Page 23
... NXP Semiconductors Fig 18. Temperature profiles for large and small components For further information on temperature profiles, refer to Application Note AN10365 “Surface mount reflow soldering description”. 17. Soldering of through-hole mount packages 17.1 Introduction to soldering through-hole mount packages This text gives a very brief insight into wave, dip and manual soldering. ...
Page 24
... NXP Semiconductors 17.4 Package related soldering information Table 13. Package CPGA, HCPGA DBS, DIP, HDIP, RDBS, SDIP, SIL [2] PMFP [1] For SDIP packages, the longitudinal axis must be parallel to the transport direction of the printed-circuit board. [2] For PMFP packages hot bar soldering or manual soldering is suitable. ...
Page 25
... In no event shall NXP Semiconductors be liable for any indirect, incidental, punitive, special or consequential damages (including - without limitation - lost profits, lost savings, business interruption, costs related to the removal or ...
Page 26
... LED driver with output error detection NXP Semiconductors’ specifications such use shall be solely at customer’s own risk, and (c) customer fully indemnifies NXP Semiconductors for any liability, damages or failed product claims resulting from customer design and use of the product for automotive applications beyond NXP Semiconductors’ ...
Page 27
... NXP Semiconductors 22. Contents 1 General description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1 2 Features and benefits . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1 3 Applications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2 4 Ordering information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2 4.1 Ordering options . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2 5 Block diagram . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3 6 Pinning information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4 6.1 Pinning . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4 6.2 Pin description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5 7 Functional description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6 7.1 System interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6 7.2 LED output error detection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7 7.2.1 Open-circuit detection principle . . . . . . . . . . . . 7 7 ...