ISL6556BCR-T Intersil, ISL6556BCR-T Datasheet - Page 19

ISL6556BCR-T
Manufacturer Part Number
ISL6556BCR-T
Description
IC CTRLR MULTIPHASE VRM10 32-QFN
Manufacturer
Intersil
Datasheet
1.ISL6556BCBZ-T.pdf
(24 pages)
Specifications of ISL6556BCR-T
Applications
Controller, Intel VR10X
Voltage - Input
3 ~ 12 V
Number Of Outputs
4
Voltage - Output
0.84 ~ 1.6 V
Operating Temperature
0°C ~ 70°C
Mounting Type
Surface Mount
Package / Case
32-VQFN Exposed Pad, 32-HVQFN, 32-SQFN, 32-DHVQFN
Lead Free Status / RoHS Status
Contains lead / RoHS non-compliant
Available stocks
Company
Part Number
Manufacturer
Quantity
Price
Company:
Part Number:
ISL6556BCR-T
Manufacturer:
INTESIL
Quantity:
6 645
Company:
Part Number:
ISL6556BCR-T
Manufacturer:
AGERE
Quantity:
2 646
Part Number:
ISL6556BCR-T
Manufacturer:
INTERSIL
Quantity:
20 000
Current Sensing
The ISEN pins are denoted ISEN1, ISEN2, ISEN3 and
ISEN4. The resistors connected between these pins and the
respective phase nodes determine the gains in the load-line
regulation loop and the channel-current balance loop as well
as setting the overcurrent trip point. Select values for these
resistors based on the room temperature r
lower MOSFETs; the full-load operating current, I
number of phases, N using Equation 18 (see also Figure 3).
In certain circumstances, it may be necessary to adjust the
value of one or more ISEN resistor. When the components of
one or more channels are inhibited from effectively dissipating
their heat so that the affected channels run hotter than
desired, choose new, smaller values of R
phases (see the section entitled Channel-Current Balance).
Choose R
temperature rise in order to cause proportionally less current
to flow in the hotter phase.
In Equation 19, make sure that ∆T
rise above the ambient temperature, and ∆T
temperature rise above the ambient temperature. While a
single adjustment according to Equation 19 is usually
sufficient, it may occasionally be necessary to adjust R
two or more times to achieve optimal thermal balance
between all channels.
Load-Line Regulation Resistor
The load-line regulation resistor is labeled R
Its value depends on the desired full-load droop voltage
(V
ISEN resistor, the load-line regulation resistor is as shown
in Equation 20.
If one or more of the ISEN resistors is adjusted for thermal
balance, as in Equation 20, the load-line regulation resistor
should be selected according to Equation 21 where I
full-load operating current and R
connected to the n
Compensation
The two opposing goals of compensating the voltage
regulator are stability and speed. Depending on whether the
R
R
R
R
ISEN
ISEN 2 ,
FB
FB
DROOP
=
=
=
V
------------------------ -
--------------------------------
I
70 10
FL
V
=
DROOP
---------------------- -
70 10
r
ISEN,2
DROOP
DS ON
in Figure 5). If Equation 19 is used to select each
×
r
R
DS ON
×
ISEN
(
–
(
6
–
6
)
in proportion to the desired decrease in
∆T
----------
∆T
)
I
------- -
th
FL
N
∑
n
2
1
ISEN pin.
R
ISEN n ( )
19
ISEN(n)
2
is the desired temperature
ISEN
is the ISEN resistor
DS(ON)
1
is the measured
FB
for the affected
in Figure 5.
FL
of the
; and the
FL
(EQ. 18)
(EQ. 19)
(EQ. 20)
(EQ. 21)
ISEN
is the
ISL6556B
regulator employs the optional load-line regulation as
described in Load-Line Regulation.
COMPENSATING LOAD-LINE REGULATED
CONVERTER
The load-line regulated converter behaves in a similar
manner to a peak-current mode controller because the two
poles at the output-filter L-C resonant frequency split with
the introduction of current information into the control loop.
The final location of these poles is determined by the system
function, the gain of the current signal, and the value of the
compensation components, R
Since the system poles and zero are effected by the values
of the components that are meant to compensate them, the
solution to the system equation becomes fairly complicated.
Fortunately there is a simple approximation that comes very
close to an optimal solution. Treating the system as though it
were a voltage-mode regulator by compensating the L-C
poles and the ESR zero of the voltage-mode approximation
yields a solution that is always stable with very close to ideal
transient performance.
The feedback resistor, R
outlined in Load-Line Regulation Resistor. Select a target
bandwidth for the compensated system, f
bandwidth must be large enough to assure adequate
transient performance, but smaller than 1/3 of the per-
channel switching frequency. The values of the
compensation components depend on the relationships of f
to the L-C pole frequency and the ESR zero frequency. For
each of the following three, there is a separate set of
equations for the compensation components.
Case 1:
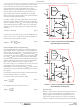
FIGURE 12. COMPENSATION CONFIGURATION FOR
R
FB
LOAD-LINE REGULATED ISL6556B CIRCUIT
V
R
C
+
-------------------
2π LC
-
DROOP
R
C
C
C
1
=
=
C
FB
R
2
----------------------------------- -
2πV
C
>
(OPTIONAL)
FB
, has already been chosen as
C
0.75V
f
0
PP
2πf
----------------------------------- -
C
0.75V
R
and C
0
IN
FB
V
COMP
VDIFF
pp
f
0
FB
IN
C
LC
.
0
. The target
December 28, 2004
FN9097.4
0