HCPL-0738-500 Avago Technologies US Inc., HCPL-0738-500 Datasheet - Page 7

HCPL-0738-500
Manufacturer Part Number
HCPL-0738-500
Description
OPTOCOUPLER 15MBD 2CH 8-SOIC
Manufacturer
Avago Technologies US Inc.
Datasheet
1.HCPL-0738-500.pdf
(8 pages)
Specifications of HCPL-0738-500
Package / Case
8-SOIC (0.154", 3.90mm Width)
Voltage - Isolation
3750Vrms
Number Of Channels
2, Unidirectional
Current - Output / Channel
2mA
Data Rate
15MBd
Propagation Delay High - Low @ If
35ns @ 12mA
Current - Dc Forward (if)
20mA
Input Type
DC
Output Type
Open Collector
Mounting Type
Surface Mount
Isolation Voltage
3750 Vrms
Maximum Continuous Output Current
2 mA
Maximum Fall Time
25 ns
Maximum Forward Diode Current
20 mA
Maximum Rise Time
20 ns
Minimum Forward Diode Voltage
1.3 V
Output Device
Logic Gate Photo IC
Configuration
2 Channel
Maximum Baud Rate
15 MBps
Maximum Forward Diode Voltage
1.8 V
Maximum Operating Temperature
+ 100 C
Minimum Operating Temperature
- 40 C
Lead Free Status / RoHS Status
Contains lead / RoHS non-compliant
Available stocks
Company
Part Number
Manufacturer
Quantity
Price
Company:
Part Number:
HCPL-0738-500E
Manufacturer:
AVAGO
Quantity:
300
Propagation Delay, Pulse-Width
Distortion, and Propagation Delay Skew
Propagation delay is a figure of merit which describes how
quickly a logic signal propagates through a system. The
propagation delay from low to high (t
of time required for an input signal to propagate to the
output, causing the output to change from low to high.
Similarly, the propagation delay from high to low
(t
put signal to propagate to the output, causing the
output to change from high to low (see Figure 7).
Pulse-width distortion (PWD) results when t
t
between t
mum data rate capability of a transmission system. PWD
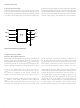
Figure 6. Recommended printed circuit board layout.
7
Application Information
Bypassing and PC Board Layout
The HCPL-0738 optocoupler is extremely easy to use. No
external interface circuitry is required because the HCPL-
0738 uses high-speed CMOS IC technology allowing CMOS
logic to be connected directly to the inputs and outputs.
PHL
GND 1
GND 1
PHL
I
I
F1
F2
differ in value. PWD is defined as the difference
) is the amount of time required for the in-
PLH
and t
1
2
3
4
PHL
and often determines the maxi-
7
6
8
5
PLH
) is the amount
GND 2
C
PLH
V
V
V
DD
O
O
and
1
2
As shown in Figure 6, the only external component required
for proper operation is the bypass capacitor. Capacitor values
should be between 0.01 µF and 0.1 µF. For each capacitor,
the total lead length between both ends of the capacitor
and the power-supply pins should not exceed 20 mm.
can be expressed in percent by dividing the PWD (in ns)
by the minimum pulse width (in ns) being transmitted.
Typically, PWD on the order of 20-30% of the minimum
pulse width is tolerable; the exact figure depends on
the particular application (RS232, RS422, T-1, etc.).
Propagation delay skew, t
to con-sider in parallel data applications where synchro-
nization of signals on parallel data lines is a concern. If
the parallel data is being sent through a group of op-
tocouplers, differences in propagation delays will cause
the data to arrive at the outputs of the optocouplers at
different times. If this difference in propagation delays
is large enough, it will determine the maximum rate at
which parallel data can be sent through the optocouplers.
PSK
, is an important parameter