AT89LP51ED2 Atmel Corporation, AT89LP51ED2 Datasheet - Page 217

AT89LP51ED2
Manufacturer Part Number
AT89LP51ED2
Description
Manufacturer
Atmel Corporation
Specifications of AT89LP51ED2
Flash (kbytes)
64 Kbytes
Max. Operating Frequency
20 MHz
Cpu
8051-1C
Max I/o Pins
42
Spi
1
Twi (i2c)
1
Uart
1
Adc Channels
7
Adc Resolution (bits)
10
Adc Speed (ksps)
153.8
Sram (kbytes)
2.25
Eeprom (bytes)
4096
Self Program Memory
API
Operating Voltage (vcc)
2.4 to 5.5
Timers
4
Isp
SPI/OCD/UART
Watchdog
Yes
Available stocks
Company
Part Number
Manufacturer
Quantity
Price
- Current page: 217 of 254
- Download datasheet (8Mb)
24.6.2
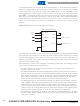
Figure 24-19. Command Sequence Flow Chart
3714A–MICRO–7/11
Command Format
Programming commands consist of two preamble bytes, an opcode byte, two address bytes,
and zero or more data bytes.
mand sequence.
A sample command packet is shown in
packet frame. SS must be brought low before the first byte in a command is sent and brought
back high after the final byte in the command has been sent. The command is not complete until
SS returns high. Command bytes are issued serially on MOSI. Data output bytes are received
serially on MISO. Packets of variable length are supported by returning SS high when the final
required byte has been transmitted. In some cases command bytes have a don’t care value.
Don’t care bytes in the middle of a packet must be transmitted. Don’t care bytes at the end of a
packet may be ignored.
Page oriented instructions always include a full 16-bit address. The higher order bits select the
page and the lower order bits select the byte within that page. The AT89LP51RD2/ED2/ID2 allo-
cates 6 bits for byte address, 1 bit for low/high half page selection and 9 bits for page address.
The half page to be accessed is always fixed by the page address and half select as transmitted.
The byte address specifies the starting address for the first data byte. After each data byte has
been transmitted, the byte address is incremented to point to the next data byte. This allows a
page command to linearly sweep the bytes within a page. If the byte address is incremented
past the last byte in the half page, the byte address will roll over to the first byte in the same half
page. While loading bytes into the page buffer, overwriting previously loaded bytes will result in
data corruption.
For a summary of available commands, see
Input Preamble 1
Input Preamble 2
Input Address
Input Address
Input Opcode
Input/Output
High Byte
Low Byte
(AAh)
(55h)
Data
AT89LP51RD2/ED2/ID2 Preliminary
Figure 24-19 on page 217
Figure 24-20 on page
Address +1
Table 24-20 on page
shows a simplified flow chart of a com-
218. The SS pin defines the
219.
217
Related parts for AT89LP51ED2
Image
Part Number
Description
Manufacturer
Datasheet
Request
R

Part Number:
Description:
8-Bit Microcontroller with 4K Bytes Flash
Manufacturer:
ATMEL Corporation
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
INTERVAL AND WIPE/WASH WIPER CONTROL IC WITH DELAY
Manufacturer:
ATMEL Corporation
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Low-Voltage Voice-Switched IC for Hands-Free Operation
Manufacturer:
ATMEL Corporation
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
MONOLITHIC INTEGRATED FEATUREPHONE CIRCUIT
Manufacturer:
ATMEL Corporation
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
AM-FM Receiver IC U4255BM-M
Manufacturer:
ATMEL Corporation
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Monolithic Integrated Feature Phone Circuit
Manufacturer:
ATMEL Corporation
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Multistandard Video-IF and Quasi Parallel Sound Processing
Manufacturer:
ATMEL Corporation
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
High-performance EE PLD
Manufacturer:
ATMEL Corporation
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
8-bit Flash Microcontroller
Manufacturer:
ATMEL Corporation
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
2-Wire Serial EEPROM
Manufacturer:
ATMEL Corporation
Datasheet: