DSP56100 MOTOROLA [Motorola, Inc], DSP56100 Datasheet

DSP56100
Related parts for DSP56100
DSP56100 Summary of contents
Page 1
... This parallelism greatly increases the effective processing speed of the DSP56166. The MPU-style programming model and instruction set allow straightforward generation of efficient, compact code. The basic architectures and development tools of the DSP56100 family, DSP56000 family, and DSP96002 are so similar that learning to design and program one greatly reduces the time needed to learn the others. ...
Page 2
ADDRESS GENERATION PORT B UNIT OR HOST ON-CHIP 15 PERIPHERALS HOST, RSSI0, 7+10 RSSI1, TIMER GPI/O, CODEC CODEC, PORT C INTERNAL DATA AND/OR BUS SWITCH RSSI0, AND BIT RSSI1, MANIPULATION UNIT TIMER PROGRAM CONTROL UNIT EXTAL CLOCK SXFC AND PLL ...
Page 3
... INTRODUCTION This data sheet is intended to be used with the DSP56100 Fam- ily Manual and the DSP56166 User’s Manual . The DSP56100 Family Manual provides a description of the components of the DSP5616 core processor that are common to all DSP56100 fam- ily processors and includes a detailed description of the basic DSP56100 family instruction set. The DSP56166 User’ ...
Page 4
T0 CLKO BS A0-A15 PS/DS R D0-D15 CLKO BS PS/DS A0-A15 R D0-D15 MOTOROLA Data In Bus Operation (Read-Write- 0WT ...
Page 5
Interrupt MODA/IRQA and Mode MODB/IRQB Control MODC/IRQC RESET EXTAL Clock CLKO and PLL SXFC VddS GNDS A0-A15 D0-D15 Vdd Add/Data Vss Add/Data BS External PS/DS Bus PEREN 56 pins WR (42 func. RD 5Vdd;9Vss) R Vdd ...
Page 6
CLKO ...
Page 7
BB pin is sampled high. This pin becomes an input if the bus arbitration mode bit in the OMR register is set (Master Mode). It ...
Page 8
HOST INTERFACE (15 PINS) H0-H7 (Host Data Bus) — This bidirectional data bus is used to transfer data between the host processor and the DSP. This bus is an input unless enabled by a host processor read. H0-H7 may be ...
Page 9
ON-CHIP EMULATION (4 PINS) DSI/OS0 (Debug Serial Input/Chip Status 0) — The DSI/OS0 pin, when an input, is the pin through which serial data or commands are provided to the OnCE controller. The data received on the DSI pin will ...
Page 10
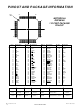
PINOUT AND PACKAGE INFORMATION 112 PIN 1 IDENT PIN # FUNCTION PIN # 1 GND4 VDD3 GND5 GND6 ...
Page 11
The preliminary DC/AC electrical specifications are generated from design simulations. These specifications may not be fully tested or guaranteed at this early stage of the product life cycle. Finalized specifications will be published after complete characterization and de- vice qualifications ...
Page 12
Thermal Characteristics — CQFP Package Characteristics Thermal Resistance — Ceramic Junction to Ambient Junction to Case (estimated) Thermal Characteristics — PQFP Package Characteristics Thermal Resistance — Plastic Junction to Ambient Junction to Case (estimated) This device contains protective circuitry against ...
Page 13
Power Considerations The average chip junction temperature (PD Where Ambient Temperature Package Thermal Resistance, Junction-to-Ambient, C INT I/O PINT ...
Page 14
Layout Practices Each DSP56166 Vdd pin should be provided with a low-impedance path volts. Each DSP56166 Vss pin should likewise be provided with a low-impedance path to ground. The power supply pins drive six dis- tinct groups ...
Page 15
Power Dissipation (Vdd = 5.0 Vdc +/- 10 -40 to +125 TTL Load). The DC electrical characteristics of this device are shown below. Conditions Digital Vdd with Codec & PLL disabled ...
Page 16
Analog I/O Characteristics (VddA = 5.0 Vdc +/- 10 -40 to +125 C). The Analog I/O characteristics of this device are shown below. Characteristic Input Impedance on Mic & Aux Input Capacitance on Mic and Aux Peak Input ...
Page 17
Analog I/O Figure 1. describes the recommended analog I/O and power supply configurations. The two analog inputs are electrically identical. When one is not used, it can be left floating. When used coupling capacitor is required. The value ...
Page 18
Analog I/O Figure 2. shows three possible single-ended output configurations. Configuration (a) is highly recommended. For configuration (b) and (c), since the load resistor is tied to VssA coupling capacitor is required. Vref VddA 47K + 47K - ...
Page 19
A/D and D/A Performances (VddA = 5.0 Vdc +/- 10 -40 to +125 C). The A/D and D/A performances of the codec section are given below. Characteristic Analog to Digital Section Signal to Noise plus Distortion Ratio (S/N+T) ...
Page 20
Other On-Chip Codec Characteristics (VddA = 5.0 Vdc +/- 10 -40 to +125 TTL Load). The Analog I/O characteristics of this device are shown below. Characteristic Codec Master Clock Codec Sampling ...
Page 21
DC Electrical Characteristics (VSS = 0 Vdc) (Vdd = 5.0 Vdc +/- 10 -40 to +125 TTL Load). The DC electrical characteristics of this device are shown below. Characteristic Input High ...
Page 22
AC Electrical Characteristics (VSS = 0 Vdc) The timing waveforms in the AC Electrical Characteristics are tested with a VIL maximum of 0.5 V and a VIH minimum of 2.4 V for all pins, except EXTAL, RESET, MODA, MODB and ...
Page 23
Clock Figure 1. External Clock Timing AC Electrical Characteristics — Other Clock and PLL Operation Timing Characteristics PLL Output frequency EXTAL Input Clock Amplitude a. Maximum DSP operating frequency. See Operating Conditions coupling capacitor is required on ...
Page 24
AC Electrical Characteristics — Reset, Stop, Wait, Mode Select, and Interrupt Timing (Vdd = 5.0 Vdc +/- 10 -40 to +125 TTL Load). cyc = Clock cycle = 1/2 instruction cycle ...
Page 25
AC Electrical Characteristics — Reset, Stop, Wait, Mode Select, and Interrupt Timing (Continued) (Vdd = 5.0 Vdc +/- 10 -40 to +125 TTL Load). Num 21 Delay from General-Purpose Out- put ...
Page 26
When using fast interrupts and IRQA and IRQB are defined as level-sensitive, then timings 20 & 21 apply to prevent multiple interrupt service. To avoid these timing restrictions, the negative edge- triggered mode is recommended when using fast interrupt. ...
Page 27
IRQA, IRQB, IRQC Interrupt Figure 4. External Interrupt Timing (Negative Edge-Triggered) A0-A15 PS/DS BS, R/W PEREN 18 IRQA IRQB, IRQC General Purpose I/O 19 IRQA IRQB, IRQC Interrupt Figure 5. External Level-Sensitive Fast Interrupt Timing 17 DSP56166 Technical Data Sheet ...
Page 28
CLKO IRQA, IRQB, IRQC A0-A15, PD/DS BS,R/W,PEREN Wait and Stop 1. Synchronous Interrupt from Wait State Timing IRQA A0-A15, PD/DS BS,R/W,PEREN Recovery from STOP State using Asynchronous Interrupt Timing IRQA A0-A15, PD/DS BS,R/W,PEREN Recovery from Stop State Using IRQA Interrupt ...
Page 29
AC Electrical Characteristics — Wait and Stop Timings (Continued) Num 30 DR Asserted to CLK low (Setup Time for Synchronous Recovery from Wait State) 31 CLK low to DSO (ACK) Valid (Enter Debug Mode) After Syn- chronous Recovery from Wait ...
Page 30
DR (input) DSO (output) Recovery from WAIT/STOP State Using DR Pin— Asynchronous Timing MOTOROLA DSP56166 Technical Data Sheet PRELIMINARY - 6/15/ Wait and Stop 5. 20 ...
Page 31
Capacitance Derating —External Bus Synchronous Timing VCC = 5.0 Vdc +/- 10 -40 to +125˚ TTL Load. J The DSP56166 External Bus Timing Specifications are designed and tested at the maximum ...
Page 32
Num 34 CLK in (EXTAL) High to CLKO High 35 CLKO High to a. A0-A15 Valid b. PS/DS, PEREN Assertion, R/W Valid c. BS Assertion d. RD Assertion 36 BS Width Deassertion 37 CLKO High to WR Assertion Low 38 ...
Page 33
EXTAL (Input) CLKO 34 (Output) A0-A15, PS/DS,R/W PEREN Note (Output) WR (Output) RD (Output) TA (Input) D0-D15 (Output) D0-D15 (Input) External Bus Figure 1. External Bus Synchronous Timing — No Wait States Note 1: During Read-Modify-Write instructions ...
Page 34
T0 T1 EXTAL (Input) CLKO 34 (Output) 35 A0-A15, PS/DS,R/W PEREN (Outputs (Output (Output (Output (Input) 43 D0-D15 (Output) 50 D0-D15 (Input) External Bus Figure 2. External Bus Synchronous Timing – Two ...
Page 35
External Bus Asynchronous Timing VCC = 5.0 Vdc +/- 10 -40 to +125˚ TTL Load. J cyc = Clock cycle = 1/2 instruction cycle = 2 T cycles WS = Number ...
Page 36
A0-A15, PS/DS, R/W PEREN D0-D15 Note: 1. During Read-Modify-Write instructions and internal instructions, the address lines do not change state. External Bus Figure 3. External Bus Asynchronous Timing MOTOROLA DSP56166 Technical Data Sheet PRELIMINARY ...
Page 37
AC Electrical Characteristics — Bus Arbitration Timing — Slave Mode VCC = 5.0 Vdc +/- 10 -40 to +125˚ TTL Load. J cyc = Clock cycle = 1/2 instruction cycle = ...
Page 38
Num Characteristics 83 BR Assertion to BB Deassertion 84 BR Assertion to Addr/Data/Control Three-state NOTES: 1. With no external access from the DSP56166 2. During external read or write access 3. During external read-modify-write access 4. During STOP mode — ...
Page 39
CLKO (Output) BR (Input) BG (Output) BB (I/O) A0-A15, PS/DS R/W PEREN D0-D15 External Bus Figure 4. Bus Arbitration Timing — Slave Mode — Bus Release. 29 DSP56166 Technical Data Sheet PRELIMINARY - 6/15/ ...
Page 40
CLKO (Output (Input) BG (Output) BB (I/O) A0-A15, PS/DS R/W PEREN Bus Arbitration Timing — Slave Mode — Bus Acquisition. MOTOROLA DSP56166 Technical Data Sheet PRELIMINARY - 6/15/ External Bus Figure 5. 80 ...
Page 41
AC Electrical Characteristics — Bus Arbitration Timing — Master Mode VCC = 5.0 Vdc +/- 10 -40 to +125˚ TTL Load. J Num 85 CLKO high to BR Output Valid 86 ...
Page 42
CLKO (Output (Output) BG (Input) BB (I/O) A0-A15, PS/DS R/W PEREN Bus Arbitration Timing — Master Mode — Bus Acquisition. MOTOROLA DSP56166 Technical Data Sheet PRELIMINARY - 6/15/ Three-state External Bus Figure 6. ...
Page 43
CLKO (Output) BR (Output (Input) Output BB (I/O) A0-A15, D0-D15, PS/DS, BS, R/W, RD, WR, PEREN Bus Arbitration Timing — Master Mode — Bus Release. 33 DSP56166 Technical Data Sheet PRELIMINARY - 6/15/ ...
Page 44
HOST PORT USAGE CONSIDERATIONS Careful synchronization is required when reading multibit registers that are written by another asynchronous system. This is a common problem when two asynchronous systems are connected. The situation exists in the Host port. The considerations for ...
Page 45
AC Electrical Characteristics — Host I/O Timing (VCC = 5.0 Vdc +/- 10 -40 to +125 TTL Load, see Host Figures 1 through Icyc / 4 cyc=Clock cycle ...
Page 46
AC Electrical Characteristics — Host I/O Timing (Continued) Num 110 HR/W Low Setup Time Before HEN Asser- tion 111 HR/W Low Hold Time After HEN Deasser- tion 112 HR/W High Setup Time to HEN Assertion 113 HR/W High Hold Time ...
Page 47
EXTERNAL INTERNAL Host Figure 1. Host Synchronization Delay HREQ (OUTPUT) HACK (INPUT) HR/W (INPUT) 106 H0-H7 (OUTPUT) Host Figure 2. Host Interrupt Vector Register (IVR) Read 37 DSP56166 Technical Data Sheet PRELIMINARY - 6/15/93 100 100 103 101 102 112 ...
Page 48
HREQ (OUTPUT) HEN (INPUT) HA2-HA0 (INPUT) HR/W (INPUT) H0-H7 (OUTPUT) Host Figure 3. Host Read Cycle (Non-DMA Mode) HREQ (OUTPUT) HEN (INPUT) HA2-HA0 (INPUT) HR/W (INPUT) H0-H7 (INPUT) Host Figure 4. Host Write Cycle (Non-DMA Mode) MOTOROLA DSP56166 Technical Data ...
Page 49
HREQ (OUTPUT) HACK (INPUT) H0-H7 (OUTPUT) Host Figure 5. Host DMA Read Cycle HREQ (OUTPUT) HACK (INPUT) H0-H7 (INPUT) Host Figure 6. Host DMA Write Cycle 39 DSP56166 Technical Data Sheet PRELIMINARY - 6/15/93 117 116 101 102 RXH Read ...
Page 50
AC Electrical Characteristics — RSSI Timing (VCC = 5.0 Vdc +/- 10 - 125 TTL Load, see RSSI Figure 1 and Icyc / 4 SCK Pin ...
Page 51
AC Electrical Characteristics — RSSI Timing (Continued) Num 140 SCK Rising Edge to SFS Out (bl) High 141 SCK Rising Edge to SFS Out (wl) High 142 SCK Rising Edge to SFS Out Low 143 SCK Rising Edge to Data ...
Page 52
SCK Continuous (Output) SCK Gated (Output) 134 SFS(Bit Early) (Input) 136 SFS (Word Early) (Input) SFS(Bit ) (Input) SFS (Word ) (Input) 143 STD (Output) 144 SRD (Input) 138 140 SFS(Bit Early) (Output) 141 SFS (Word Early) (Output) ...
Page 53
AC Electrical Characteristics — RSSI Timing (Continued) Num 150 SCK Clock Cycle (see Note 1) 151 SCK Clock High Period 152 SCK Clock Low Period 153 SCK Clock Rise/Fall Time 154 SCK Rising Edge to SFS Out (bl) High 155 ...
Page 54
SCK Continuous (Input) SCK Gated (Input) 154 SFS(Bit Early) (Output) 156 SFS (Word Early) (Output) SFS(Bit ) (Output) SFS (Word ) (Output) 163 STD (Output) 164 SRD (Input) 158 160 SFS(Bit Early) (Input) 161 SFS (Word Early) (Input) ...
Page 55
AC Electrical Characteristics — Timer Timing (VCC = 5.0 Vdc +/- 10 -40 to +125 TTL Load). Num 170 TIN Valid to CLKO low (Setup time) 171 CLKO Low to TIN ...
Page 56
AC Electrical Characteristics — OnCE Timing VCC = 5.0 Vdc +/- 10 -40 to +125 TTL Load). Num Characteristic 180 DSCK High to DSO Valid 181 DSI Valid to DSCK Low ...
Page 57
DSCK (Input) OnCE Figure 1. OnCE Serial Clock Timing DR (Input) DSO (Output) OnCE Figure 2. OnCE Acknowledge Timing DSCK (Input) 180 DSO (Output) DSI (Input) 181 Note 1: Three-state, external pull-down resistor OnCE Figure 3. OnCE Data I/O To ...
Page 58
OS1 (Output) (Note 1) DSO 191 (Output) OS0 (Output) 189 Note 1: Three-state, external pull-down resistor OnCE Figure 4. OnCE Data I/O To Status Timing CLKO (Output) OS0-1 (Output) OnCE Figure 5. OnCE CLK To Status Timing DSCK (Input) ...
Page 59
AC Electrical Characteristics — General Purpose I/O (GPIO) Timing (VCC = 5.0 Vdc +/- 10 -40 to +125 TTL Load). Num 201 CLKO Edge to GPIO Out Valid (GPIO Out Delay ...
Page 60
... This parallelism greatly increases the effective processing speed of the DSP56166ROM. The MPU-style program- ming model and instruction set allow straightforward generation of efficient, compact code. The basic architectures and development tools of the DSP56100, DSP56000, and DSP96000 families are so similar that learning to design and program one greatly reduces the time needed to learn the others. ...
Page 61
OnCE is a trademark of Motorola, Inc. All product and brand names appearing herein are trademarks or registered trademarks of their respective holders. Motorola reserves the right to make changes without further notice to any products herein. Motorola makes no ...
Page 62
ADDRESS GENERATION PORT B UNIT OR HOST ON-CHIP 15 PERIPHERALS HOST, RSSI0, 7+10 RSSI1, TIMER GPI/O, CODEC CODEC, PORT C INTERNAL DATA AND/OR BUS SWITCH RSSI0, AND BIT RSSI1, MANIPULATION UNIT TIMER EXTAL CLOCK SXFC AND PLL PROGRAM CLKO ADDRESS ...
Page 63
Corrections to the DSP56166 Data Sheet Dated 6/15/93 1. Remove the entry for the BIAS pin (page 9 of the 6/15/93 data sheet) ...