DSPIC33FJ128GP708-I/PT Microchip Technology, DSPIC33FJ128GP708-I/PT Datasheet - Page 13

DSPIC33FJ128GP708-I/PT
Manufacturer Part Number
DSPIC33FJ128GP708-I/PT
Description
IC DSPIC MCU/DSP 128K 80TQFP
Manufacturer
Microchip Technology
Series
dsPIC™ 33Fr
Datasheets
1.DSPIC33FJ12GP201-ISO.pdf
(90 pages)
2.DSPIC33FJ64GP206-IPT.pdf
(322 pages)
3.DSPIC33FJ64GP206-IPT.pdf
(28 pages)
4.DSPIC33FJ128MC506-IPT.pdf
(24 pages)
Specifications of DSPIC33FJ128GP708-I/PT
Program Memory Type
FLASH
Program Memory Size
128KB (128K x 8)
Package / Case
80-TFQFP
Core Processor
dsPIC
Core Size
16-Bit
Speed
40 MIPs
Connectivity
CAN, I²C, IrDA, LIN, SPI, UART/USART
Peripherals
AC'97, Brown-out Detect/Reset, DMA, I²S, POR, PWM, WDT
Number Of I /o
69
Ram Size
16K x 8
Voltage - Supply (vcc/vdd)
3 V ~ 3.6 V
Data Converters
A/D 24x10b/12b
Oscillator Type
Internal
Operating Temperature
-40°C ~ 85°C
Product
DSCs
Data Bus Width
16 bit
Processor Series
DSPIC33F
Core
dsPIC
Maximum Clock Frequency
40 MHz
Number Of Programmable I/os
69
Data Ram Size
16 KB
Maximum Operating Temperature
+ 85 C
Mounting Style
SMD/SMT
3rd Party Development Tools
52713-733, 52714-737, 53276-922, EWDSPIC
Development Tools By Supplier
PG164130, DV164035, DV244005, DV164005, PG164120, DM240001, DV164033
Minimum Operating Temperature
- 40 C
Lead Free Status / RoHS Status
Lead free / RoHS Compliant
For Use With
876-1001 - DSPIC33 BREAKOUT BOARDDM300024 - KIT DEMO DSPICDEM 1.1DV164033 - KIT START EXPLORER 16 MPLAB ICD2MA330012 - MODULE DSPIC33 100P TO 84QFPMA330011 - MODULE DSPIC33 100P TO 100QFPDM300019 - BOARD DEMO DSPICDEM 80L STARTERDM240001 - BOARD DEMO PIC24/DSPIC33/PIC32AC164328 - MODULE SKT FOR 80TQFPDV164005 - KIT ICD2 SIMPLE SUIT W/USB CABLE
Eeprom Size
-
Lead Free Status / Rohs Status
Lead free / RoHS Compliant
Available stocks
Company
Part Number
Manufacturer
Quantity
Price
Company:
Part Number:
DSPIC33FJ128GP708-I/PT
Manufacturer:
Microchip Technology
Quantity:
10 000
Part Number:
DSPIC33FJ128GP708-I/PT
Manufacturer:
MICROCHIP/微芯
Quantity:
20 000
3.3
The core has two data spaces, X and Y. These data
spaces can be considered either separate (for some
DSP instructions), or as one unified linear address
range (for MCU instructions). The data spaces are
accessed using two Address Generation Units (AGUs)
and separate data paths. This feature allows certain
instructions to concurrently fetch two words from RAM,
thereby enabling efficient execution of DSP algorithms
such as Finite Impulse Response (FIR) filtering and
Fast Fourier Transform (FFT).
3.3.1
The X data space is used by all instructions and
supports all addressing modes. There are separate
read and write data buses for X data space. The X read
data bus is the read data path for all instructions that
view data space as combined X and Y address space.
It is also the X data prefetch path for the dual operand
DSP instructions (MAC class).
The Y data space is used in concert with the X data
space by the MAC class of instructions (CLR, ED,
EDAC, MAC, MOVSAC, MPY, MPY.N and MSC) to
provide two concurrent data read paths.
Both the X and Y data spaces support Modulo
Addressing for all instructions, subject to addressing
mode restrictions. Bit-Reversed Addressing is only
supported for writes to X data space.
All data memory writes, including in DSP instructions,
view data space as combined X and Y address space.
The boundary between the X and Y data spaces is
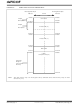
device-dependent (an example is shown in Figure 3-3)
and is not user-programmable.
All effective addresses are 16 bits wide and point to
bytes within the data space. Therefore, the data space
address range is 64 Kbytes or 32K words, though the
implemented memory locations vary from one device to
another.
3.3.2
Every dsPIC33F device contains 2 Kbytes of DMA RAM
located at the end of Y data space. Memory locations in
the DMA RAM space are accessible simultaneously by
the CPU and the DMA Controller module. DMA RAM is
utilized by the DMA Controller to store data to be
transferred to various peripherals using DMA, as well as
data transferred from various peripherals using DMA.
When the CPU and the DMA Controller attempt to
concurrently write to the same DMA RAM location, the
hardware ensures that the CPU is given precedence in
accessing the DMA RAM location. Therefore, the DMA
RAM provides a reliable means of transferring DMA
data without ever having to stall the CPU.
© 2005 Microchip Technology Inc.
Data Address Space
X AND Y DATA SPACES
DMA RAM
Preliminary
3.3.3
The core data width is 16 bits. All internal registers are
organized as 16-bit wide words. Data space memory is
organized in byte addressable, 16-bit wide blocks.
Figure 3-3 depicts a sample data space memory map
for the dsPIC33F device with 33 Kbytes of RAM.
3.3.4
To
PICmicro
usage efficiency, the dsPIC33F instruction set supports
both word and byte operations. Data is aligned in data
memory and registers as words, but all data space EAs
resolve to bytes. Data byte reads will read the complete
word which contains the byte, using the Least
Significant bit (LSb) of any EA to determine which byte
to select.
As a consequence of this byte accessibility, all effective
address calculations are internally scaled. For
example, the core would recognize that Post-Modified
Register Indirect Addressing mode, [Ws++], will result
in a value of Ws + 1 for byte operations and Ws + 2 for
word operations.
All word accesses must be aligned to an even address.
Misaligned word data fetches are not supported.
Should a misaligned read or write be attempted, a trap
will then be executed, allowing the system and/or user
to examine the machine state prior to execution of the
address Fault.
help
®
devices and improve data space memory
DATA SPACE WIDTH
DATA ALIGNMENT
maintain
backward
dsPIC33F
compatibility
DS70155C-page 11
with