OPF794 Optek, OPF794 Datasheet - Page 30

OPF794
Manufacturer Part Number
OPF794
Description
Photodiodes Pin Photodiode
Manufacturer
Optek
Datasheet
1.OPF794.pdf
(135 pages)
Specifications of OPF794
Maximum Reverse Voltage
100 V
Maximum Rise Time
6 ns
Mounting Style
SMD/SMT
Product
Photodiode
Lead Free Status / RoHS Status
Lead free / RoHS Compliant
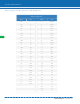
Available stocks
Company
Part Number
Manufacturer
Quantity
Price
Hall-effect (Magnetic)
T
U
Page B—10
Product Definitions
HE
NPRECEDENTED
OPTEK Technology produces temperature-compensated Hall-effect magnetic sensing devices. The Magnetologic® and Hallogic®
Hall-effect Sensors are superior products that meet the demands of motion sensing in extremely harsh environments such as
under-the-hood automotive and heavy industrial machinery applications, including robotics.
Hallogic® refers to the combination of a Hall element magnetic field sensor with highly refined integrated circuitry on a single,
monolithic bipolar silicon chip. Incorporated on the Hallogic® sensor chip are:
The basic Hall element relies on a magnetic field in order to sense
motion. The principle is based on the Hall-effect, discovered more than
100 years ago by the American physicist, Edwin Herbert Hall. The Hall-
effect is the small electrical potential created when a stationary magnetic
field is placed perpendicular to a current-carrying conductor.
Most available Hall elements hold current constant and measure voltage,
which is then correlated with magnetic field strength. The superior
performance of the OPTEK device is due in part to the fundamental
design change which instead provides a constant bias voltage and
measures the Hall current. This method proves more accurate for
sensing magnetic field strengths when temperature varies. It also
provides a better way to interface the Hall element with the complex
integrated circuitry of the Hallogic® sensor.
The OPTEK element then is basically a block of semiconductor material
with four contact points. Two contacts are used to supply a constant
bias voltage to the element; the other two are used for the varying
current output. If voltage is held constant across the device while a
perpendicular magnetic field is applied, the Hall current can be sensed
across the output connections. The Hall current is proportional to the
strength of the applied magnetic field.
Temperature coefficients have been optimized to insure stable electrical characteristics over the temperature range of –55°C to
+150°C. Other design aspects of the Hallogic® sensor that enable it to meet OPTEK’s demanding temperature stability objectives
are two important circuit areas on the chip, the bandgap regulator and the threshold amplifier.
1.Bandgap Voltage Regulator:
In addition to maintaining a constant output voltage level (no matter what changes occur in input voltage or output current), the
OPTEK Hallogic® bandgap voltage regulator also serves as an extremely good temperature compensated voltage source to bias
the Hall supply voltage ranging from 4.5 to 24 volts DC, with virtually no drift in magnetic sensitivity (i.e., in the magnetic trigger
point).
1.Threshold Amplifier
The amplifier/detector circuit is a constant-gain type, designed with temperature-compensated trip points at the input to the
voltage comparator. The Schmitt trigger output then drives an open-collector transistor with a 50 mA current sinking capability.
This open-collector transistor enables the device output to drive up to ten TTL loads directly.
H
ALL
A Hall element
A bandgap voltage regulator
Threshold amplifier including a linear amplifier and Schmitt trigger
An open-collector output transistor that can drive ten TTL loads
E
LEMENT
T
EMPERATURE
S
TABILITY
Issue A.1 2005
OPTEK Technology Inc. www.optekinc.com