MPC8313VRADDB Freescale Semiconductor, MPC8313VRADDB Datasheet - Page 19

MPC8313VRADDB
Manufacturer Part Number
MPC8313VRADDB
Description
MPU POWERQUICC II PRO 516-PBGA
Manufacturer
Freescale Semiconductor
Datasheet
1.MPC8313CZQAFFB.pdf
(100 pages)
Specifications of MPC8313VRADDB
Processor Type
MPC83xx PowerQUICC II Pro 32-Bit
Speed
267MHz
Voltage
0.95 V ~ 1.05 V
Mounting Type
Surface Mount
Package / Case
516-PBGA
Processor Series
MPC8xxx
Core
e300
Data Bus Width
32 bit
Development Tools By Supplier
MPC8313E-RDB
Maximum Clock Frequency
400 MHz
Operating Supply Voltage
- 0.3 V to + 1.26 V
Maximum Operating Temperature
+ 105 C
Mounting Style
SMD/SMT
Data Ram Size
16 KB
I/o Voltage
2.5 V
Interface Type
I2C, SPI, UART
Minimum Operating Temperature
- 40 C
Program Memory Type
EEPROM/Flash
Lead Free Status / RoHS Status
Lead free / RoHS Compliant
Features
-
Lead Free Status / Rohs Status
Lead free / RoHS Compliant
Available stocks
Company
Part Number
Manufacturer
Quantity
Price
Company:
Part Number:
MPC8313VRADDB
Manufacturer:
MOTOLOLA
Quantity:
885
Company:
Part Number:
MPC8313VRADDB
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor
Quantity:
10 000
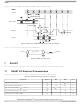
Figure 5
Freescale Semiconductor
Table 21. DDR and DDR2 SDRAM Output AC Timing Specifications for Silicon Rev 2.x or Later (continued)
MDQS preamble start
MDQS epilogue end
Notes:
1. The symbols used for timing specifications follow the pattern of t
2. All MCK/MCK referenced measurements are made from the crossing of the two signals ±0.1 V.
3. ADDR/CMD includes all DDR SDRAM output signals except MCK/MCK, MCS, and MDQ//MDM/MDQS.
4. Note that t
5. Determined by maximum possible skew between a data strobe (MDQS) and any corresponding bit of data (MDQ), ECC
6. All outputs are referenced to the rising edge of MCK[n] at the pins of the microprocessor. Note that t
from the rising edge of the MCK[n] clock (KH) until the MDQS signal is valid (MH). t
of the DQSS override bits in the TIMING_CFG_2 register. This is typically set to the same delay as the clock adjust in the
CLK_CNTL register. The timing parameters listed in the table assume that these 2 parameters have been set to the same
adjustment value. See the MPC8313E PowerQUICC™ II Pro Integrated Processor Family Reference Manual, for a
description and understanding of the timing modifications enabled by use of these bits.
inputs and t
(DD) from the rising or falling edge of the reference clock (KH or KL) until the output went invalid (AX or DX). For example,
t
outputs (A) are setup (S) or output valid time. Also, t
reference (K) goes low (L) until data outputs (D) are invalid (X) or data output hold time.
(MECC), or data mask (MDM). The data strobe should be centered inside of the data eye at the pins of the microprocessor.
symbol conventions described in note 1.
DDKHAS
shows the DDR SDRAM output timing for the MCK to MDQS skew measurement (t
symbolizes DDR timing (DD) for the time t
DDKHMH
(first two letters of functional block)(reference)(state)(signal)(state)
Parameter
For the ADDR/CMD setup and hold specifications in
assumed that the clock control register is set to adjust the memory clocks by
1/2 applied cycle.
follows the symbol conventions described in note 1. For example, t
MPC8313E PowerQUICC
MCK[ n ]
MCK[ n ]
MDQS
MDQS
Figure 5. Timing Diagram for t
™
Symbol
t
t
DDKHMP
DDKHME
II Pro Processor Hardware Specifications, Rev. 3
MCK
DDKLDX
t
DDKHMH
t
DDKHMH
1
memory clock reference (K) goes from the high (H) state until
t
NOTE
MCK
symbolizes DDR timing (DD) for the time t
–0.5 × t
(min) = –0.6 ns
(max) = 0.6 ns
(first two letters of functional block)(signal)(state)(reference)(state)
for outputs. Output hold time can be read as DDR timing
–0.6
Min
MCK
– 0.6
DDKHMH
Table
–0.5 × t
DDKHMH
DDKHMH
21, it is
Max
0.6
MCK
can be modified through control
describes the DDR timing (DD)
+ 0.6
DDKHMP
DDR and DDR2 SDRAM
MCK
Unit
ns
ns
memory clock
follows the
DDKHMH
Notes
for
6
6
19
).