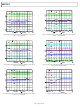
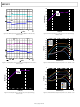
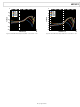
ADP5022 Analog Devices, ADP5022 Datasheet - Page 17

ADP5022
Manufacturer Part Number
ADP5022
Description
Dual 3 MHz, 600 mA Buck Regulator with 150 mA LDO
Manufacturer
Analog Devices
Datasheet
1.ADP5022.pdf
(28 pages)
Thermal Protection
In the event that the junction temperature rises above 150°C,
the thermal shutdown circuit turns off the converters and the
LDO. Extreme junction temperatures can be the result of high
current operation, poor circuit board design, or high ambient
temperature. A 20°C hysteresis is included so that when thermal
shutdown occurs, the bucks and LDO do not return to opera-
tion until the on-chip temperature drops below 130°C. When
coming out of thermal shutdown, soft start is initiated.
Undervoltage Lockout
To protect against battery discharge, undervoltage lockout
(UVLO) circuitry is integrated in the system. If the input
voltage on VDDA drops below a typical 2.15 V UVLO
threshold, all channels shut down. In the buck channels,
both the power switch and the synchronous rectifier turn
off. When the voltage on VDDA rises above the UVLO
threshold, the part is enabled once more.
Alternatively, the user can select device models with a UVLO
set at a higher level, suitable for USB applications. For these
models, the device hits the turn-off threshold when the input
supply drops to 3.65 V typical.
Enable/Shutdown
When all three enable pins are held low, the device is in
shutdown mode, and the input current remains below 2 μA.
BUCK SECTION
The two bucks use a fixed frequency and high speed current
mode architecture.
The bucks operate with an input voltage of 2.4 V to 5.5 V.
Control Scheme
The bucks operate with a fixed frequency, current mode PWM
control architecture at medium to high loads for high efficiency
but shift to a power save mode (PSM) control scheme at light
loads to lower the regulation power losses. When operating in
fixed frequency PWM mode, the duty cycle of the integrated
switches is adjusted and regulates the output voltage. When
operating in PSM at light loads, the output voltage is controlled
in a hysteretic manner, with higher output voltage ripple. During
part of this time, the converter is able to stop switching and
enters an idle mode, which improves conversion efficiency.
Rev. C | Page 17 of 28
PWM Mode
In PWM mode, the bucks operate at a fixed frequency of 3 MHz
set by an internal oscillator. At the start of each oscillator cycle,
the PFET switch is turned on, sending a positive voltage across
the inductor. Current in the inductor increases until the current
sense signal crosses the peak inductor current threshold that
turns off the PFET switch and turns on the NFET synchronous
rectifier. This sends a negative voltage across the inductor,
causing the inductor current to decrease. The synchronous
rectifier stays on for the rest of the cycle. The buck regulates the
output voltage by adjusting the peak inductor current threshold.
Power Save Mode (PSM)
The bucks smoothly transition to PSM operation when the
load current decreases below the PSM current threshold. When
either of the bucks enter power save mode, an offset is induced
in the PWM regulation level, which makes the output voltage
rise. When the output voltage reaches a level approximately
1.5% above the PWM regulation level, PWM operation is
turned off. At this point, both power switches are off, and the
buck enters an idle mode. The output capacitor discharges until
the output voltage falls to the PWM regulation voltage, at which
point the device drives the inductor to make the output voltage
rise again to the upper threshold. This process is repeated while
the load current is below the PSM current threshold.
PSM Current Threshold
The PSM current threshold is set to 100 mA. The bucks employ
a scheme that enables this current to remain accurately con-
trolled, independent of input and output voltage levels. This
scheme also ensures that there is very little hysteresis between
the PSM current threshold for entry to and exit from the PSM.
The PSM current threshold is optimized for excellent efficiency
over all load currents.
Oscillator/Phasing of Inductor Switching
The ADP5022 ensures that both bucks operate at the same
switching frequency when both bucks are in PWM mode.
Additionally, the ADP5022 ensures that when both bucks are
in PWM mode, they operate out-of-phase, whereby the Buck2
PFET starts conducting exactly half a clock period after the
Buck1 PFET starts conducting.
ADP5022