ADP5022 Analog Devices, ADP5022 Datasheet - Page 19

ADP5022
Manufacturer Part Number
ADP5022
Description
Dual 3 MHz, 600 mA Buck Regulator with 150 mA LDO
Manufacturer
Analog Devices
Datasheet
1.ADP5022.pdf
(28 pages)
APPLICATIONS INFORMATION
BUCK EXTERNAL COMPONENT SELECTION
Trade-offs between performance parameters such as efficiency
and transient response can be made by varying the choice of
external components in the applications circuit, as shown in
Figure 1.
Inductor
The high switching frequency of the ADP5022 bucks allows for
the selection of small chip inductors. For best performance, use
inductor values between 0.7 μH and 3 μH. Suggested inductors
are shown in Table 7.
The peak-to-peak inductor current ripple is calculated using
the following equation:
where:
f
L is the inductor value.
The minimum dc current rating of the inductor must be greater
than the inductor peak current. The inductor peak current is
calculated using the following equation:
Inductor conduction losses are caused by the flow of current
through the inductor, which has an associated internal dc
resistance (DCR). Larger sized inductors have smaller DCR,
which may decrease inductor conduction losses. Inductor core
losses are related to the magnetic permeability of the core material.
Because the bucks are high switching frequency dc-to-dc
converters, shielded ferrite core material is recommended for
its low core losses and low EMI.
Table 7. Suggested 1.0 μH Inductors
Vendor
Murata
Murata
Taiyo Yuden
Coilcraft
TDK
Coilcraft
Toko
SW
is the switching frequency.
I
I
RIPPLE
PEAK
=
=
I
LOAD
Model
LQM2MPN1R0NG0B
LQM18FN1R0M00B
CBMF1608T1R0M
EPL2014-102ML
GLFR1608T1R0M-LR
0603LS-102
MDT2520-CN
V
OUT
V
(
MAX
IN
×
(
×
V
)
f
IN
+
SW
I
−
RIPPLE
×
V
2
L
OUT
)
Dimensions
(mm)
2.0 × 1.6 × 0.9
1.6 × 0.8 × 0.8
1.6 × 0.8 × 0.8
2.0 × 2.0 × 1.4
1.6 × 0.8 × 0.8
1.8 × 1.69 × 1.1
2.5 × 2.0 × 1.2
I
(mA)
1400
150
290
900
230
400
1350
SAT
Rev. C | Page 19 of 28
DCR
(mΩ)
85
26
90
59
80
81
85
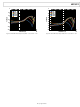
Output Capacitor
Higher output capacitor values reduce the output voltage ripple
and improve load transient response. When choosing this value,
it is also important to account for the loss of capacitance due to
output voltage dc bias.
Ceramic capacitors are manufactured with a variety of dielec-
trics, each with a different behavior over temperature and
applied voltage. Capacitors must have a dielectric adequate
to ensure the minimum capacitance over the necessary
temperature range and dc bias conditions. X5R or X7R
dielectrics with a voltage rating of 6.3 V or 10 V are recom-
mended for best performance. Y5V and Z5U dielectrics are
not recommended for use with any dc-to-dc converter because
of their poor temperature and dc bias characteristics.
The worst-case capacitance accounting for capacitor variation
over temperature, component tolerance, and voltage is calcu-
lated using the following equation:
where:
C
TEMPCO is the worst-case capacitor temperature coefficient.
TOL is the worst-case component tolerance.
In this example, the worst-case temperature coefficient
(TEMPCO) over −40°C to +85°C is assumed to be 15% for an
X5R dielectric. The tolerance of the capacitor (TOL) is assumed
to be 10%, and C
Substituting these values in the equation yields
To guarantee the performance of the bucks, it is imperative
that the effects of dc bias, temperature, and tolerances on the
behavior of the capacitors be evaluated for each application.
EFF
is the effective capacitance at the operating voltage.
C
C
EFF
EFF
12
10
8
6
4
2
0
= C
= 9.2481 μF × (1 − 0.15) × (1 − 0.1) = 7.0747 μF
0
OUT
Figure 49. Typical Capacitor Performance
× (1 − TEMPCO) × (1 − TOL)
OUT
1
is 9.2481 μF at 1.8 V, as shown in Figure 49.
2
DC BIAS VOLTAGE (V)
3
4
5
ADP5022
6