ISL6564 Intersil Corporation, ISL6564 Datasheet - Page 26

ISL6564
Manufacturer Part Number
ISL6564
Description
Multiphase PWM Controller
Manufacturer
Intersil Corporation
Datasheet
1.ISL6564.pdf
(27 pages)
Available stocks
Company
Part Number
Manufacturer
Quantity
Price
Company:
Part Number:
ISL6564CRZ-T
Manufacturer:
REELDATE
Quantity:
67 500
Company:
Part Number:
ISL6564CRZ-T
Manufacturer:
INTERSIL/PB-FREE
Quantity:
4 000
and off. Select low ESL ceramic capacitors and place one as
close as possible to each upper MOSFET drain to minimize
board parasitic impedances and maximize suppression.
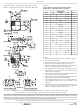
MULTI-PHASE RMS IMPROVEMENT
Figure 24 is provided as a reference to demonstrate the
dramatic reductions in input-capacitor RMS current upon the
implementation of the multi-phase topology. For example,
compare the input rms current requirements of a two-phase
converter versus that of a single phase. Assume both
converters have a duty cycle of 0.25, maximum sustained
output current of 40A, and a ratio of I
single phase converter would require 17.3 Arms current
capacity while the two-phase converter would only require
10.9 Arms. The advantages become even more pronounced
when output current is increased and additional phases are
added to keep the component cost down relative to the
single phase approach.
FIGURE 24. NORMALIZED INPUT-CAPACITOR RMS
FIGURE 23. NORMALIZED INPUT-CAPACITOR RMS CURRENT
0.3
0.2
0.1
0.6
0.4
0.2
0
0
0
0
I
I
L,PP
L,PP
= 0
= 0.25 I
vs DUTY CYCLE FOR 4-PHASE CONVERTER
I
I
I
CURRENT vs DUTY CYCLE FOR SINGLE-PHASE
CONVERTER
L,PP
L,PP
L,PP
0.2
0.2
O
= 0
= 0.5 I
= 0.75 I
DUTY CYCLE (V
O
DUTY CYCLE (V
O
0.4
0.4
26
I
I
L,PP
L,PP
= 0.5 I
= 0.75 I
0.6
0.6
O/
O/
L,PP
V
V
O
IN
IN
O
)
)
to I
O
0.8
0.8
of 0.5. The
1.0
1.0
ISL6564
Layout Considerations
The following layout strategies are intended to minimize the
impact of board parasitic impedances on converter
performance and to optimize the heat-dissipating capabilities
of the printed-circuit board. These sections highlight some
important practices which should not be overlooked during the
layout process.
Component Placement
Within the allotted implementation area, orient the switching
components first. The switching components are the most
critical because they carry large amounts of energy and tend
to generate high levels of noise. Switching component
placement should take into account power dissipation. Align
the output inductors and MOSFETs such that space between
the components is minimized while creating the PHASE
plane. Place the Intersil MOSFET driver IC as close as
possible to the MOSFETs they control to reduce the parasitic
impedances due to trace length between critical driver input
and output signals. If possible, duplicate the same
placement of these components for each phase.
Next, place the input and output capacitors. Position one
high-frequency ceramic input capacitor next to each upper
MOSFET drain. Place the bulk input capacitors as close to
the upper MOSFET drains as dictated by the component
size and dimensions. Long distances between input
capacitors and MOSFET drains result in too much trace
inductance and a reduction in capacitor performance. Locate
the output capacitors between the inductors and the load,
while keeping them in close proximity to the microprocessor
socket.
The ISL6564 can be placed off to one side or centered
relative to the individual phase switching components.
Routing of sense lines and PWM signals will guide final
placement. Critical small signal components to place close
to the controller include the ISEN resistors, R
feedback resistor, and compensation components.
Bypass capacitors for the ISL6564 and ISL66XX driver bias
supplies must be placed next to their respective pins. Trace
parasitic impedances will reduce their effectiveness.
Plane Allocation and Routing
Dedicate one solid layer, usually a middle layer, for a ground
plane. Make all critical component ground connections with
vias to this plane. Dedicate one additional layer for power
planes; breaking the plane up into smaller islands of
common voltage. Use the remaining layers for signal wiring.
Route phase planes of copper filled polygons on the top and
bottom once the switching component placement is set. Size
the trace width between the driver gate pins and the
MOSFET gates to carry 4A of current. When routing
components in the switching path, use short wide traces to
reduce the associated parasitic impedances.
T
December 27, 2004
resistor,
FN9156.2