ISL6596 Intersil Corporation, ISL6596 Datasheet - Page 6

ISL6596
Manufacturer Part Number
ISL6596
Description
Synchronous Rectified MOSFET Driver
Manufacturer
Intersil Corporation
Datasheet
1.ISL6596.pdf
(10 pages)
Available stocks
Company
Part Number
Manufacturer
Quantity
Price
Company:
Part Number:
ISL6596CRZ
Manufacturer:
Intersil
Quantity:
900
Part Number:
ISL6596CRZ-T
Manufacturer:
INTERSIL
Quantity:
20 000
Part Number:
ISL6596IBZ-T
Manufacturer:
INTERSIL
Quantity:
20 000
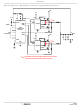
Operation and Adaptive Shoot-Through Protection
Designed for high speed switching, the ISL6596 MOSFET
driver controls both high-side and low-side N-Channel FETs
from one externally provided PWM signal.
A rising transition on PWM initiates the turn-off of the lower
MOSFET (see Timing Diagram). After a short propagation
delay [t
[t
shoot-through circuitry monitors the LGATE voltage and turns
on the upper gate following a short delay time [t
the LGATE voltage drops below ~1V. The upper gate drive
then begins to rise [t
A falling transition on PWM indicates the turn-off of the upper
MOSFET and the turn-on of the lower MOSFET. A short
propagation delay [t
begins to fall [t
monitors the UGATE-PHASE voltage and turns on the lower
MOSFET a short delay time, t
gate voltage drops below 1V. The lower gate then rises [t
turning on the lower MOSFET. These methods prevent both the
lower and upper MOSFETs from conducting simultaneously
(shoot-through), while adapting the dead time to the gate
charge characteristics of the MOSFETs being used.
This driver is optimized for voltage regulators with large step
down ratio. The lower MOSFET is usually sized larger
compared to the upper MOSFET because the lower
MOSFET conducts for a longer time during a switching
period. The lower gate driver is therefore sized much larger
to meet this application requirement. The 0.4Ω on-resistance
and 4A sink current capability enable the lower gate driver to
absorb the current injected into the lower gate through the
drain-to-gate capacitor of the lower MOSFET and help
prevent shoot through caused by the self turn-on of the lower
MOSFET due to high dV/dt of the switching node.
PWM Input and Threshold Control
A unique feature of the ISL6596 is the programmable PWM
logic threshold set by the control pin (VCTRL) voltage. The
VCTRL pin should connect to the VCC of the controller, thus
the PWM logic threshold follows with the voltage level of the
controller. For 5V applications, this pin can tie to the driver
VCC and simplify the routing.
The ISL6596 also features the adaptable tri-state PWM input.
Once the PWM signal enters the shutdown window, either
MOSFET previously conducting is turned off. If the PWM signal
remains within the shutdown window for longer than the gate
turn-off propagation delay of the previously conducting
MOSFET, the output drivers are disabled and both MOSFET
gates are pulled and held low. The shutdown state is removed
when the PWM signal moves outside the shutdown window.
The PWM rising and falling thresholds outlined in the Electrical
Specifications determine when the lower and upper gates are
enabled. During normal operation in a typical application, the
PWM rise and fall times through the shutdown window should
FL
] are provided in the Electrical Specifications. Adaptive
PDLL
], the lower gate begins to fall. Typical fall times
FU
]. The adaptive shoot-through circuitry
PDLU
RU
] and the upper MOSFET turns on.
] is encountered before the upper gate
PDHL
6
, after the upper MOSFET’s
PDHU
] after
RL
],
ISL6596
not exceed either output’s turn-off propagation delay plus the
MOSFET gate discharge time to ~1V. Abnormally long PWM
signal transition times through the shutdown window will simply
introduce additional dead time between turn off and turn on of
the synchronous bridge’s MOSFETs. For optimal performance,
no more than 50pF parasitic capacitive load should be present
on the PWM line of ISL6596 (assuming an Intersil PWM
controller is used).
Bootstrap Considerations
This driver features an internal bootstrap diode. Simply
adding an external capacitor across the BOOT and PHASE
pins completes the bootstrap circuit.
The following equation helps select a proper bootstrap
capacitor size:
where Q
at V
control MOSFETs. The ∆V
allowable droop in the rail of the upper gate drive.
As an example, suppose two IRLR7821 FETs are chosen as
the upper MOSFETs. The gate charge, Q
sheet is 10nC at 4.5V (V
Q
assume a 200mV droop in drive voltage over the PWM
cycle. We find that a bootstrap capacitance of at least
0.110µF is required. The next larger standard value
capacitance is 0.22µF. A good quality ceramic capacitor is
recommended.
C
Q
GATE
BOOT_CAP
GATE
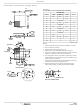
FIGURE 2. BOOTSTRAP CAPACITANCE vs BOOT RIPPLE
GS1
2.0
1.8
1.6
1.4
1.2
1.0
0.8
0.6
0.4
0.2
0.0
=
is calculated to be 22nC at VCC level. We will
G1
gate-source voltage and N
0.0
Q
------------------------------ - N
20nC
G1
is the amount of gate charge per upper MOSFET
V
≥
0.1
GS1
------------------------------------- -
∆V
•
VOLTAGE
VCC
BOOT_CAP
Q
0.2
GATE
Q
GATE
•
0.3
Q1
GS
= 100nC
BOOT_CAP
) gate-source voltage. Then the
∆V
0.4
BOOT_CAP
0.5
Q1
0.6
term is defined as the
is the number of
(V)
G
0.7
, from the data
0.8
November 2, 2005
0.9
FN9240.0
(EQ. 1)
1.0