LTC2414 LINER [Linear Technology], LTC2414 Datasheet - Page 42

LTC2414
Manufacturer Part Number
LTC2414
Description
8-/16-Channel 24-Bit No Latency TM ADCs
Manufacturer
LINER [Linear Technology]
Datasheet
1.LTC2414.pdf
(48 pages)
Available stocks
Company
Part Number
Manufacturer
Quantity
Price
Part Number:
LTC2414CGN
Manufacturer:
LTNEAR
Quantity:
20 000
LTC2414/LTC2418
APPLICATIO S I FOR ATIO
Multichannel Bridge Digitizer and Digital Cold
Junction Compensation
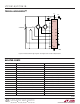
The bridge application as shown in Figures 41, 42, and 43
can be expanded to multiple bridge transducers. Figure 54
shows the expansion for simple bridge measurement.
Also included is the temperature measurement.
In Figure 54, CH0 to CH13 are configured as differential to
measure up to seven bridge transducers using the LTC2418.
CH14 and CH15 are configured as single-ended. CH14
measures the thermocouple while CH15 measures the
output of the cold junction sensor (diode, thermistor,
etc.). The measured cold junction sensor output is then
used to compensate the thermocouple output to find the
absolute temperature. The final temperature value may
then be used to compensate the temperature effects of the
bridge transducers.
Sample Driver for LTC2414/LTC2418 SPI Interface
The LTC2414/LTC2418 have a simple 4-wire serial inter-
face and it is easy to program microprocessors and
microcontrollers to control the device.
42
Figure 48. Measurement of a Ladder of Sensors Using
100Ω
100Ω
100Ω
0.1%
RTD
RTD
RTD
PT1
PT2
PT8
25k
R1
•
•
•
+
U
10µF
Differential Mode
11
12
21
22
23
24
7
8
U
REF
REF
CH0
CH1
CH2
CH3
CH14
CH15
•
•
•
LTC2418
+
–
9
GND
V
5V
CC
15
SDO
SCK
SDI
CS
F
O
W
0.1µF
20
18
17
16
19
2418 F48
U
4-WIRE
SPI
Figure 49 shows the 4-wire SPI connection between the
LTC2414/LTC2418 and a PIC16F84 microcontroller. The
sample program for CC5X compiler in Figure 50 can be
used to program the PIC16F84 to control the LTC2414/
LTC2418. It uses PORT B to interface with the device.
The program begins by declaring variables and allocating
four memory locations to store the 32-bit conversion
result. In execution, it first initiates the PORT B to the
proper SPI configuration and prepares channel address.
The LTC2414/LTC2418 is activated by setting the CS low.
Then the microcontroller waits until a logic LOW is de-
tected on the data line, signifying end-of-conversion. After
a LOW is detected, a subroutine is called to exchange data
between the LTC2414/LTC2418 and the microcontroller.
The main loop ends by setting CS high, ending the data
output state.
The performance of the LTC2414/LTC2418 can be verified
using the demonstration board DC434A, see Figure 51 for
the schematic. This circuit uses the computer’s serial port
to generate power and the SPI digital signals necessary for
starting a conversion and reading the result. It includes a
LabVIEW
which graphically captures the conversion results. It can
be used to determine noise performance, stability and with
an external source linearity. As exemplified in the sche-
matic, the LTC2414/LTC2418 is extremely easy to use.
This demonstration board and associated software is
available by contacting Linear Technology.
TM
Figure 49. Connecting the LTC2414/LTC2418 to
a PIC16F84 MCU Using the SPI Serial Interface
LTC2414/
LTC2418
application software program (see Figure 52)
SDO
SCK
SDI
CS
18
20
17
16
10
11
8
9
RB2
RB3
RB4
RB5
PIC16F84
2414/18 F49
241418fa