EPF10K100 ALTERA [Altera Corporation], EPF10K100 Datasheet - Page 25

EPF10K100
Manufacturer Part Number
EPF10K100
Description
Embedded Programmable Logic Device Family
Manufacturer
ALTERA [Altera Corporation]
Datasheet
1.EPF10K100.pdf
(128 pages)
Available stocks
Company
Part Number
Manufacturer
Quantity
Price
Company:
Part Number:
EPF10K100A3NBC356
Manufacturer:
ALTERA
Quantity:
21
Company:
Part Number:
EPF10K100ABC356-1
Manufacturer:
ALTERA
Quantity:
8 831
Company:
Part Number:
EPF10K100ABC356-1
Manufacturer:
ALTERA30
Quantity:
205
Company:
Part Number:
EPF10K100ABC356-1N
Manufacturer:
ST
Quantity:
230
FLEX 10K Embedded Programmable Logic Device Family Data Sheet
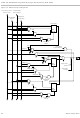
FastTrack Interconnect
In the FLEX 10K architecture, connections between LEs and device I/O
pins are provided by the FastTrack Interconnect, which is a series of
continuous horizontal and vertical routing channels that traverse the
device. This global routing structure provides predictable performance,
even in complex designs. In contrast, the segmented routing in FPGAs
requires switch matrices to connect a variable number of routing paths,
increasing the delays between logic resources and reducing performance.
The FastTrack Interconnect consists of row and column interconnect
channels that span the entire device. Each row of LABs is served by a
dedicated row interconnect. The row interconnect can drive I/O pins and
feed other LABs in the device. The column interconnect routes signals
between rows and can drive I/O pins.
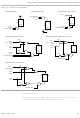
A row channel can be driven by an LE or by one of three column channels.
These four signals feed dual 4-to-1 multiplexers that connect to two
specific row channels. These multiplexers, which are connected to each
LE, allow column channels to drive row channels even when all eight LEs
in an LAB drive the row interconnect.
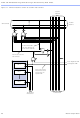
Each column of LABs is served by a dedicated column interconnect. The
column interconnect can then drive I/O pins or another row’s
interconnect to route the signals to other LABs in the device. A signal from
the column interconnect, which can be either the output of an LE or an
input from an I/O pin, must be routed to the row interconnect before it
can enter an LAB or EAB. Each row channel that is driven by an IOE or
EAB can drive one specific column channel.
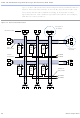
Access to row and column channels can be switched between LEs in
adjacent pairs of LABs. For example, an LE in one LAB can drive the row
and column channels normally driven by a particular LE in the adjacent
LAB in the same row, and vice versa. This routing flexibility enables
routing resources to be used more efficiently. See
Figure
11.
Altera Corporation
25