MPC8358E_11 FREESCALE [Freescale Semiconductor, Inc], MPC8358E_11 Datasheet

MPC8358E_11
Related parts for MPC8358E_11
MPC8358E_11 Summary of contents
Page 1
Freescale Semiconductor Technical Data MPC8358E PowerQUICC II Pro Processor Revision 2.1 PBGA Silicon Hardware Specifications This document provides an overview of the MPC8358E PowerQUICC II Pro processor revision 2.1 PBGA features, including a block diagram showing the major functional components. ...
Page 2
Overview 1 Overview This section describes a high-level overview including features and general operation of the MPC8358E PowerQUICC II Pro processor. A major component of this device is the e300 core, which includes 32 Kbytes of instruction and data cache ...
Page 3
Lockable portion of L1 cache — Dynamic power management — Software-compatible with the Freescale processor families implementing the Power Architecture™ technology • QUICC Engine unit — Two 32-bit RISC controllers for flexible ...
Page 4
Overview – ATM (AAL2/AAL5) to Ethernet (IP) interworking in accordance with RFC2684 including bridging of ATM ports to Ethernet ports – Extensive support for ATM statistics and Ethernet RMON/MIB statistics – AAL2 protocol rate CPS at OC-3/STM-1 ...
Page 5
Advanced encryption standard unit (AESU) — Implements the Rinjdael symmetric key cipher — Key lengths of 128, 192, and 256 bits, two key – ECB, CBC, CCM, and counter modes — ARC four execution unit (AFEU) – Implements a ...
Page 6
Overview — Data bus widths: – Single 32-bit data PCI interface that operates MHz — PCI 3.3-V compatible (not 5-V compatible) — PCI host bridge capabilities on both interfaces — PCI agent mode supported on PCI ...
Page 7
Multiple master support 2 — Master or slave I C mode support — On-chip digital filtering rejects spikes on the bus — System initialization data is optionally loaded from I embedded hardware • DMA controller — Four independent virtual ...
Page 8
Electrical Characteristics 2.1 Overall DC Electrical Characteristics This section covers the ratings, conditions, and other characteristics. 2.1.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings Table 1 provides the absolute maximum ratings. Characteristic Core supply voltage PLL supply voltage DDR and DDR2 DRAM I/O voltage ...
Page 9
Power Supply Voltage Specification Table 2 provides the recommended operating conditions for the device. Note that the values in the recommended and tested operating conditions. Proper device operation outside of these conditions is not guaranteed. Table 2. Recommended Operating ...
Page 10
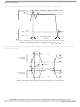
Electrical Characteristics Figure 2 shows the undershoot and overshoot voltages at the interfaces of the device. G/L/OV + 20% DD G/L/OV DD G/L/ GND – 0 GND – 0.7 V Note: 1. Note that t ...
Page 11
Output Driver Characteristics Table 3 provides information on the characteristics of the output driver strengths. The values are preliminary estimates. Driver Type Local bus interface utilities signals PCI signals PCI output clocks (including PCI_SYNC_OUT) DDR signal DDR2 signal 10/100/1000 ...
Page 12
Power Characteristics Voltage 90% I/O voltage supplies ( another. 2.2.2 Power-Down Sequencing The MPC8358E does not require the core supply voltage and I/O supply voltages to be powered down in any particular order. 3 Power Characteristics The ...
Page 13
Table 5 shows the estimated typical I/O power dissipation for the device. Table 5. Estimated Typical I/O Power Dissipation Interface Parameter DDR I/O 200 MHz, 1x32 bits 65% utilization 200 MHz, 1x64 bits 2 Ω R 200 ...
Page 14
Clock Input Timing 4.1 DC Electrical Characteristics Table 6 provides the clock input (CLKIN/PCI_SYNC_IN) DC timing specifications for the device. Table 6. CLKIN DC Electrical Characteristics Parameter Input high voltage Input low voltage CLKIN input current PCI_SYNC_IN input current PCI_SYNC_IN ...
Page 15
Gigabit Reference Clock Input Timing Table 8 provides the Gigabit reference clocks (GTX_CLK125) AC timing specifications. Table 8. GTX_CLK125 AC Timing Specifications At recommended operating conditions with LV Parameter/Condition GTX_CLK125 frequency GTX_CLK125 cycle time GTX_CLK rise and fall time ...
Page 16
RESET Initialization Table 9. RESET Pins DC Electrical Characteristics (continued) Characteristic Output low voltage Notes: 1. This table applies for pins PORESET, HRESET, SRESET, and QUIESCE. 2. HRESET and SRESET are open drain pins, thus V 5.2 RESET AC Electrical ...
Page 17
Table 11 provides the PLL and DLL lock times. Parameter/Condition PLL lock times DLL lock times Notes: 1. DLL lock times are a function of the ratio between the output clock and the coherency system bus clock (csb_clk). A 2:1 ...
Page 18
DDR and DDR2 SDRAM Table 12. QUICC Engine Block Operating Frequency Limitations (continued) Interface UART/async HDLC BISYNC USB Notes: 1. The QUICC Engine module needs to run at a frequency higher than or equal to what is listed in this ...
Page 19
Table 13. DDR2 SDRAM DC Electrical Characteristics for GV Parameter/Condition Input current (0 V ≤V ≤ Notes expected to be within the DRAM expected to equal 0.5 ...
Page 20
DDR and DDR2 SDRAM Table 16 provides the DDR capacitance when GV Table 16. DDR SDRAM Capacitance for GV Parameter/Condition Input/output capacitance: DQ, DQS Delta input/output capacitance: DQ, DQS Note: 1. This parameter is sampled 6.2 DDR and ...
Page 21
Table 19. DDR and DDR2 SDRAM Input AC Timing Specifications Mode At recommended operating conditions with GV Parameter MDQS—MDQ/MECC input skew per byte Notes timing values are based on the DDR data rate, which is twice the DDR ...
Page 22
DDR and DDR2 SDRAM Table 20. DDR and DDR2 SDRAM Output AC Timing Specifications for Source At recommended operating conditions with GV 8 Parameter ADDR/CMD output setup with respect to MCK ADDR/CMD output hold with respect to MCK MCS(n) output ...
Page 23
Table 20. DDR and DDR2 SDRAM Output AC Timing Specifications for Source At recommended operating conditions with GV 8 Parameter MDQS epilogue end Notes: 1. The symbols used for timing specifications follow the pattern of t inputs and t (first ...
Page 24
DDR and DDR2 SDRAM Figure 7 provides the AC test load for the DDR bus. Output Table 21. DDR and DDR2 SDRAM Measurement Conditions Symbol OUT Notes: 1. Data input threshold measurement point. 2. Data output ...
Page 25
DUART This section describes the DC and AC electrical specifications for the DUART interface of the MPC8358E. 7.1 DUART DC Electrical Characteristics Table 22 provides the DC electrical characteristics for the DUART interface of the device. Table 22. DUART ...
Page 26
UCC Ethernet Controller: Three-Speed Ethernet, MII Management 8.1 Three-Speed Ethernet Controller (10/100/1000 Mbps)— GMII/MII/RMII/TBI/RGMII/RTBI Electrical Characteristics The electrical characteristics specified here apply to all GMII (gigabit media independent interface), MII (media independent interface), RMII (reduced media independent interface), TBI (ten-bit ...
Page 27
Table 25. RGMII/RTBI DC Electrical Characteristics (when operating at 2.5 V) Parameters Supply voltage 2.5 V Output high voltage Output low voltage Input high voltage Input low voltage Input current 8.2 GMII, MII, RMII, TBI, RGMII, and RTBI AC Timing ...
Page 28
UCC Ethernet Controller: Three-Speed Ethernet, MII Management Figure 9 shows the GMII transmit AC timing diagram. GTX_CLK TXD[7:0] TX_EN TX_ER 8.2.1.2 GMII Receive AC Timing Specifications Table 27 provides the GMII receive AC timing specifications. Table 27. GMII Receive AC ...
Page 29
Figure 10 shows the GMII receive AC timing diagram. RX_CLK RXD[7:0] RX_DV RX_ER 8.2.2 MII AC Timing Specifications This section describes the MII transmit and receive AC timing specifications. 8.2.2.1 MII Transmit AC Timing Specifications Table 28 provides the MII ...
Page 30
UCC Ethernet Controller: Three-Speed Ethernet, MII Management Figure 11 shows the MII transmit AC timing diagram. TX_CLK TXD[3:0] TX_EN TX_ER 8.2.2.2 MII Receive AC Timing Specifications Table 29 provides the MII receive AC timing specifications. Table 29. MII Receive AC ...
Page 31
Figure 13 shows the MII receive AC timing diagram. RX_CLK RXD[3:0] RX_DV RX_ER 8.2.3 RMII AC Timing Specifications This section describes the RMII transmit and receive AC timing specifications. 8.2.3.1 RMII Transmit AC Timing Specifications Table 30 provides the RMII ...
Page 32
UCC Ethernet Controller: Three-Speed Ethernet, MII Management Figure 14 shows the RMII transmit AC timing diagram. REF_CLK TXD[1:0] TX_EN Figure 14. RMII Transmit AC Timing Diagram 8.2.3.2 RMII Receive AC Timing Specifications Table 31 provides the RMII receive AC timing ...
Page 33
Figure 16 shows the RMII receive AC timing diagram. REF_CLK RXD[1:0] CRS_DV RX_ER 8.2.4 TBI AC Timing Specifications This section describes the TBI transmit and receive AC timing specifications. 8.2.4.1 TBI Transmit AC Timing Specifications Table 32 provides the TBI ...
Page 34
UCC Ethernet Controller: Three-Speed Ethernet, MII Management Figure 17 shows the TBI transmit AC timing diagram. GTX_CLK TXD[7:0] TX_EN TX_ER 8.2.4.2 TBI Receive AC Timing Specifications Table 33 provides the TBI receive AC timing specifications. Table 33. TBI Receive AC ...
Page 35
Figure 18 shows the TBI receive AC timing diagram. PMA_RX_CLK1 RCG[9:0] PMA_RX_CLK0 8.2.5 RGMII and RTBI AC Timing Table 34 presents the RGMII and RTBI AC timing specifications. Table 34. RGMII and RTBI AC Timing Specifications At recommended operating conditions ...
Page 36
UCC Ethernet Controller: Three-Speed Ethernet, MII Management Table 34. RGMII and RTBI AC Timing Specifications (continued) At recommended operating conditions with LV Parameter/Condition GTX_CLK125 reference clock duty cycle Notes: 1. Note that, in general, the clock reference symbol representation for ...
Page 37
Ethernet Management Interface Electrical Characteristics The electrical characteristics specified here apply to MII management interface signals MDIO (management data input/output) and MDC (management data clock). The electrical characteristics for GMII, RGMII, TBI, and RTBI are specified in (10/100/1000 Mbps)— ...
Page 38
UCC Ethernet Controller: Three-Speed Ethernet, MII Management Table 36. MII Management AC Timing Specifications (continued) At recommended operating conditions with LV Parameter/Condition MDC fall time Notes: 1. The symbols used for timing specifications follow the pattern of t inputs and ...
Page 39
Table 37. IEEE 1588 Timer AC Specifications (continued) Parameter Timer alarm to output valid Notes: 1. The timer can operate on rtc_clock or tmr_clock. These clocks get muxed and any one of them can be selected. The minimum and maximum ...
Page 40
Local Bus Table 39. Local Bus General Timing Parameters—DLL Enabled (continued) Parameter Local bus clock to LALE rise Local bus clock to output valid (except LAD/LDP and LALE) Local bus clock to data valid for LAD/LDP Local bus clock to ...
Page 41
Table 40. Local Bus General Timing Parameters—DLL Bypass Mode (continued) Parameter Local bus clock to output high impedance for LAD/LDP Notes: 1. The symbols used for timing specifications follow the pattern of t inputs and t (first two letters of ...
Page 42
Local Bus Figure 22 through Figure 27 show the local bus signals. LSYNC_IN Input Signals: LAD[0:31]/LDP[0:3] Output Signals: LSDA10/LSDWE/LSDRAS/ LSDCAS/LSDDQM[0:3] LA[27:31]/LBCTL/LBCKE/LOE/ Output (Data) Signals: LAD[0:31]/LDP[0:3] Output (Address) Signal: LAD[0:31] LALE Figure 22. Local Bus Signals, Nonspecial Signals Only (DLL Enabled) ...
Page 43
LSYNC_IN T1 T3 GPCM Mode Output Signals: LCS[0:3]/LWE UPM Mode Input Signal: LUPWAIT Input Signals: LAD[0:31]/LDP[0:3] UPM Mode Output Signals: LCS[0:3]/LBS[0:3]/LGPL[0:5] Figure 24. Local Bus Signals, GPCM/UPM Signals for LCRR[CLKDIV (DLL Enabled) LCLK T1 T3 GPCM Mode Output ...
Page 44
Local Bus LCLK GPCM Mode Output Signals: LCS[0:3]/LWE UPM Mode Input Signal: LUPWAIT Input Signals: LAD[0:31]/LDP[0:3] (DLL Bypass Mode) UPM Mode Output Signals: LCS[0:3]/LBS[0:3]/LGPL[0:5] Figure 26. Local Bus Signals, GPCM/UPM Signals for LCRR[CLKDIV (DLL ...
Page 45
LSYNC_IN GPCM Mode Output Signals: LCS[0:3]/LWE UPM Mode Input Signal: LUPWAIT Input Signals: LAD[0:31]/LDP[0:3] UPM Mode Output Signals: LCS[0:3]/LBS[0:3]/LGPL[0:5] Figure 27. Local Bus Signals, GPCM/UPM Signals for LCRR[CLKDIV (DLL Enabled) 10 JTAG This section ...
Page 46
JTAG 10.2 JTAG AC Electrical Characteristics This section describes the AC electrical specifications for the IEEE 1149.1 (JTAG) interface of the device. Table 42 provides the JTAG AC timing specifications as defined in Table 42. JTAG AC Timing Specifications (Independent ...
Page 47
Figure 28 provides the AC test load for TDO and the boundary-scan outputs of the device. Output Figure 28. AC Test Load for the JTAG Interface Figure 29 provides the JTAG clock input timing diagram. JTAG External Clock Figure 29. ...
Page 48
JTAG Figure 32 provides the test access port timing diagram. JTAG External Clock TDI, TMS t JTKLOX TDO TDO Output Data Valid Figure 32. Test Access Port Timing Diagram MPC8358E PowerQUICC II Pro Processor Revision 2.1 PBGA Silicon Hardware Specifications, ...
Page 49
I C This section describes the DC and AC electrical characteristics for the Electrical Characteristics Table 43 provides the DC electrical characteristics for the I At recommended operating conditions with OV Parameter ...
Page 50
I C Table 44. I All values refer to V (min) and V (max) levels (see IH IL Parameter Data hold time: Rise time of both SDA and SCL signals Fall time of both SDA and SCL signals Set-up ...
Page 51
PCI This section describes the DC and AC electrical specifications for the PCI bus of the MPC8358E. 12.1 PCI DC Electrical Characteristics Table 45 provides the DC electrical characteristics for the PCI interface of the device. Parameter High-level input ...
Page 52
PCI Table 47. PCI AC Timing Specifications at 33 MHz Parameter Clock to output valid Output hold from clock Clock to output high impedance Input setup to clock Input hold from clock Notes: 1. The symbols used for timing specifications ...
Page 53
Figure 37 shows the PCI output AC timing conditions. CLK Output Delay High-Impedance Output Figure 37. PCI Output AC Timing Measurement Condition 13 Timers This section describes the DC and AC electrical specifications for the timers of the MPC8358E. 13.1 ...
Page 54
GPIO Figure 38 provides the AC test load for the timers. Output 14 GPIO This section describes the DC and AC electrical specifications for the GPIO of the MPC8358E. 14.1 GPIO DC Electrical Characteristics Table 50 provides the DC electrical ...
Page 55
Figure 39 provides the AC test load for the GPIO. Output 15 IPIC This section describes the DC and AC electrical specifications for the external interrupt pins of the MPC8358E. 15.1 IPIC DC Electrical Characteristics Table 52 provides the DC ...
Page 56
SPI 16.1 SPI DC Electrical Characteristics Table 54 provides the DC electrical characteristics for the device SPI. Characteristic Output high voltage Output low voltage Output low voltage Input high voltage Input low voltage Input current 16.2 SPI AC Timing Specifications ...
Page 57
Figure 41 and Figure 42 represent the AC timing from generally reference the rising edge of the clock, these AC timing diagrams also apply when the falling edge is the active edge. Figure 41 shows the SPI timing in slave ...
Page 58
TDM/SI Table 56. TDM/SI DC Electrical Characteristics (continued) Characteristic Input low voltage Input current 17.2 TDM/SI AC Timing Specifications Table 57 provides the TDM/SI input and output AC timing specifications. Table 57. TDM/SI AC Timing Specifications Characteristic TDM/SI outputs—External clock ...
Page 59
Figure 44 shows the TDM/SI timing with external clock. TDM/SICLK (Input) t SEIVKH Input Signals: TDM/SI (See Note) Output Signals: TDM/SI (See Note) Note: The clock edge is selectable on TDM/SI Figure 44. TDM/SI AC Timing (External Clock) Diagram 18 ...
Page 60
UTOPIA/POS Table 59. UTOPIA AC Timing Specifications Characteristic UTOPIA inputs—External clock input setup time UTOPIA inputs—Internal clock input hold time UTOPIA inputs—External clock input hold time Notes: 1. Output specifications are measured from the 50% level of the rising edge ...
Page 61
Figure 47 shows the UTOPIA timing with internal clock. UtopiaCLK (Output) Input Signals: UTOPIA Output Signals: UTOPIA Figure 47. UTOPIA AC Timing (Internal Clock) Diagram 19 HDLC, BISYNC, Transparent, and Synchronous UART This section describes the DC and AC electrical ...
Page 62
HDLC, BISYNC, Transparent, and Synchronous UART 19.2 HDLC, BISYNC, Transparent, and Synchronous UART AC Timing Specifications Table 61 and Table 62 provide the input and output AC timing specifications for HDLC, BISYNC, transparent, and synchronous UART protocols. Table 61. HDLC, ...
Page 63
Figure 48 provides the AC test load. Output 19.3 AC Test Load Figure 49 and Figure 50 represent the AC timing from specifications generally reference the rising edge of the clock, these AC timing diagrams also apply when the falling ...
Page 64
USB 20 USB This section provides the AC and DC electrical specifications for the USB interface of the MPC8358E. 20.1 USB DC Electrical Characteristics Table 63 provides the DC electrical characteristics for the USB interface. Parameter High-level input voltage Low-level ...
Page 65
Package and Pin Listings This section details package parameters, pin assignments, and dimensions. The MPC8358E is available in a plastic ball grid array (PBGA), see Section 21.2, “Mechanical Dimensions of the PBGA 21.1 Package Parameters for the PBGA Package ...
Page 66
Package and Pin Listings 21.2 Mechanical Dimensions of the PBGA Package Figure 52 depicts the mechanical dimensions and bottom surface nomenclature of the 668-PBGA package. Figure 52. Mechanical Dimensions and Bottom Surface Nomenclature of the PBGA Package Notes: 1. All ...
Page 67
Datum A, the seating plane, is determined by the spherical crowns of the solder balls. 5. Parallelism measurement must exclude any effect of mark on top surface of package. 6. Distance from the seating plane to the encapsulant material. ...
Page 68
Package and Pin Listings Table 65. MPC8358E PBGA Pinout Listing (continued) Signal PCI_PAR/ PF[11] PCI_FRAME/ PF[12] PCI_TRDY/ PF[13] PCI_IRDY/ PF[14] PCI_STOP/ PF[15] PCI_DEVSEL/ PF[16] PCI_IDSEL/ PF[17] PCI_SERR/ PF[18] PCI_PERR/ PF[19] PCI_REQ[0:2]/ PF[20:22] PCI_GNT[0:2]/ PF[23:25] PCI_MODE M66EN/ CE_PF[4] LAD[0:31] LDP[0:3] LA[27:31] ...
Page 69
Table 65. MPC8358E PBGA Pinout Listing (continued) Signal LGPL2/ LSDRAS/ LOE LGPL3/ LSDCAS/ cfg_reset_source2 LGPL4/ LGTA/ LUPWAIT/ LPBSE LGPL5/ cfg_clkin_div LCKE LCLK[0] LCLK[1]/ LCS[6] LCLK[2]/ LCS[7] LSYNC_OUT LSYNC_IN MCP_OUT IRQ0/ MCP_IN IRQ[1:2] IRQ[3]/ CORE_SRESET IRQ[4:5] IRQ[6:7] UART1_SOUT UART1_SIN UART1_CTS UART1_RTS ...
Page 70
Package and Pin Listings Table 65. MPC8358E PBGA Pinout Listing (continued) Signal CE_PA[1:2] CE_PA[3:7] CE_PA[8] CE_PA[9:12] CE_PA[13:14] CE_PA[15] CE_PA[16] CE_PA[17:21] CE_PA[22] CE_PA[23:26] CE_PA[27:28] CE_PA[29] CE_PA[30] CE_PA[31] CE_PB[0:27] CE_PC[0:1] CE_PC[2:3] CE_PC[4:6] CE_PC[7] CE_PC[8:9] CE_PC[10:30] CE_PD[0:27] CE_PE[0:31] CE_PF[0:3] PCI_CLK[0]/ PF[26] PCI_CLK[1:2]/ PF[27:28] ...
Page 71
Table 65. MPC8358E PBGA Pinout Listing (continued) Signal TDI TDO TMS TRST TEST TEST_SEL QUIESCE PORESET HRESET SRESET THERM0 THERM1 GND MPC8358E PowerQUICC II Pro Processor Revision 2.1 ...
Page 72
Package and Pin Listings Table 65. MPC8358E PBGA Pinout Listing (continued) Signal MVREF1 MVREF2 NC Notes: 1. This pin is an open drain signal. A ...
Page 73
Clocking Figure 53 shows the internal distribution of clocks within the MPC8358E. MPC8358E ce_clk to QUICC Engine Block QUICC Engine PLL CFG_CLKIN_DIV CLKIN The primary clock source for the device can be one of two inputs, CLKIN or PCI_CLK, ...
Page 74
Clocking input selects whether CLKIN or CLKIN/2 is driven out on the PCI_SYNC_OUT signal. The OCCR[PCIOENn] parameters enable the PCI_CLK_OUTn, respectively. PCI_SYNC_OUT is connected externally to PCI_SYNC_IN to allow the internal clock subystem to synchronize to the system PCI clocks. ...
Page 75
Note that lb_clk is not the external local bus or DDRC2 frequency; lb_clk passes through the a LB clock divider to create the external local bus clock outputs (LSYNC_OUT and LCLK[0:2]). The LB clock divider ratio is controlled by LCRR[CLKDIV]. ...
Page 76
Clocking 22.1 System PLL Configuration The system PLL is controlled by the RCWL[SPMF] and RCWL[SVCOD] parameters. multiplication factor encodings for the system PLL. The RCWL[SVCOD] denotes the system PLL VCO internal frequency as shown in The VCO divider must be ...
Page 77
The system VCO frequency is derived from the following equations: • csb_clk = {PCI_SYNC_IN × CFG_CLKIN_DIV)} × SPMF • System VCO Frequency = csb_clk × VCO divider (if both RCWL[DDRCM] and RCWL[LBCM] are cleared) OR System VCO frequency ...
Page 78
Clocking Table 70. CSB Frequency Options (continued) CFG_CLKIN_DIV SPMF 1 at Reset High 0110 High 0111 High 1000 High 1001 High 1010 High 1011 High 1100 High 1101 High 1110 High 1111 High 0000 1 CFG_CLKIN_DIV is only used for ...
Page 79
Table 71. e300 Core PLL Configuration (continued) RCWL[COREPLL] 0– Core VCO frequency = Core frequency × VCO divider. The VCO divider (RCWL[COREPLL[0:1]]) must be set properly so ...
Page 80
Clocking Table 72. QUICC Engine Block PLL Multiplication Factors (continued) RCWL[CEPMF] RCWL[CEPDF] 00101 00110 00111 01000 01001 01010 01011 01100 01101 01110 01111 10000 10001 10010 10011 10100 10101 10110 10111 11000 11001 11010 11011 11100 11101 11110 11111 00011 ...
Page 81
Table 72. QUICC Engine Block PLL Multiplication Factors (continued) RCWL[CEPMF] RCWL[CEPDF] 01011 01101 01111 10001 10011 10101 10111 11001 11011 11101 Note: 1. Reserved modes are not listed. The RCWL[CEVCOD] denotes the QUICC Engine Block PLL VCO internal frequency as ...
Page 82
Clocking 22.4 Suggested PLL Configurations To simplify the PLL configurations, the device might be separated into two clock domains. The first domain contains the CSB PLL and the core PLL. The core PLL is connected serially to the CSB PLL, ...
Page 83
Table 74. Suggested PLL Configurations (continued) Conf CORE SPMF CEPMF 1 No. PLL c5 æ æ 10000 c6 æ æ 10001 s1h 0011 0000110 æ s2h 0011 0000101 æ s3h 0011 0000110 æ s4h 0100 0000011 æ s5h 0100 0000100 ...
Page 84
Thermal • To configure the device with CSB clock rate of 266 MHz, core rate of 400 MHz, and QUICC Engine clock rate 300 MHz while the input clock rate is 33 MHz. Conf No. ‘s10’ and ‘c1’ are selected ...
Page 85
Estimation of Junction Temperature with Junction-to-Ambient Thermal Resistance An estimation of the chip junction temperature, T × θ where junction temperature (° ambient temperature for ...
Page 86
Thermal 23.2.3 Experimental Determination of Junction Temperature To determine the junction temperature of the device in the application after prototypes are available, the Thermal Characterization Parameter (Ψ measurement of the temperature at the top center of the package case using ...
Page 87
Table 76 shows heat sinks and junction-to-ambient thermal resistance for PBGA package. Table 76. Heat Sinks and Junction-to-Ambient Thermal Resistance of PBGA Package Heat Sink Assuming Thermal Grease × × AAVID 30 30 9.4 mm Pin Fin × × AAVID ...
Page 88
Thermal Millennium Electronics (MEI) Loroco Sites 671 East Brokaw Road San Jose, CA 95112 Internet: www.mei-millennium.com Tyco Electronics Chip Coolers™ P.O. Box 3668 Harrisburg, PA 17105-3668 Internet: www.chipcoolers.com Wakefield Engineering 33 Bridge St. Pelham, NH 03076 Internet: www.wakefield.com Interface material ...
Page 89
Experimental Determination of the Junction Temperature with a Heat Sink When heat sink is used, the junction temperature is determined from a thermocouple inserted at the interface between the case of the package and the interface material. A clearance ...
Page 90
System Design Information This circuit is intended to filter noise in the PLLs resonant frequency range from a 500 kHz to 10 MHz range. It should be built with surface mount capacitors with minimum Effective Series Inductance (ESL). Consistent with ...
Page 91
Output Buffer DC Impedance The device drivers are characterized over process, voltage, and temperature. For all buses, the driver is a push-pull single-ended driver type (open drain for I To measure Z for the single-ended drivers, an external resistor ...
Page 92
Ordering Information Table 77. Impedance Characteristics (continued) Local Bus, Ethernet, DUART, Impedance Control, Configuration, Power Management Differential Note: Nominal supply voltages. See Table 24.6 Configuration Pin Muxing The device provides the user with power-on configuration options that can be set ...
Page 93
Each part number also contains a revision code that refers to the die mask revision number. MPC nnnn e Product Part Encryption Code Identifier Acceleration MPC 8358 Blank = Not ...
Page 94
Document Revision History 26 Document Revision History Table 80 provides a revision history for this hardware specification. Rev. Date Number 3 01/2011 • Updated references to the LCRR register throughout • Removed references to DDR DLL mode in Specifications.” • ...
Page 95
How to Reach Us: Home Page: www.freescale.com Web Support: http://www.freescale.com/support USA/Europe or Locations Not Listed: Freescale Semiconductor, Inc. Technical Information Center, EL516 2100 East Elliot Road Tempe, Arizona 85284 1-800-521-6274 or +1-480-768-2130 www.freescale.com/support Europe, Middle East, and Africa: Freescale Halbleiter ...