ST72C334J2B6 STMicroelectronics, ST72C334J2B6 Datasheet - Page 25

ST72C334J2B6
Manufacturer Part Number
ST72C334J2B6
Description
8-bit Microcontrollers - MCU Flash 8K SPI/SCI
Manufacturer
STMicroelectronics
Datasheet
1.ST72C334J2B6.pdf
(153 pages)
Specifications of ST72C334J2B6
Product Category
8-bit Microcontrollers - MCU
Core
ST7
Data Bus Width
8 bit
Maximum Clock Frequency
8 MHz
Program Memory Size
8 KB
Data Ram Size
384 B
On-chip Adc
Yes
Operating Supply Voltage
3.2 V to 5.5 V
Package / Case
SDIP-42
Mounting Style
Through Hole
A/d Bit Size
8 bit
A/d Channels Available
8
Data Rom Size
256 B
Interface Type
SCI, SPI
Maximum Operating Temperature
+ 85 C
Minimum Operating Temperature
- 40 C
Number Of Programmable I/os
32
Number Of Timers
4 bit
Program Memory Type
Flash
Factory Pack Quantity
13
Supply Voltage - Max
5 V
Supply Voltage - Min
3.2 V
Available stocks
Company
Part Number
Manufacturer
Quantity
Price
Company:
Part Number:
ST72C334J2B6
Manufacturer:
ST
Quantity:
507
- Current page: 25 of 153
- Download datasheet (2Mb)
CENTRAL PROCESSING UNIT (Cont’d)
Stack Pointer (SP)
Read/Write
Reset Value: 01 FFh
The Stack Pointer is a 16-bit register which is al-
ways pointing to the next free location in the stack.
It is then decremented after data has been pushed
onto the stack and incremented before data is
popped from the stack (see
Since the stack is 256 bytes deep, the 8th most
significant bits are forced by hardware. Following
an MCU Reset, or after a Reset Stack Pointer in-
struction (RSP), the Stack Pointer contains its re-
set value (the SP7 to SP0 bits are set) which is the
stack higher address.
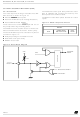
Figure 11. Stack Manipulation Example
@ 0100h
@ 01FFh
SP7
15
0
7
SP
SP6
0
Subroutine
Stack Higher Address = 01FFh
Stack Lower Address = 0100h
CALL
PCH
PCL
SP5
0
SP
SP4
0
SP3
Interrupt
0
Event
Figure
PCH
PCH
PCL
PCL
CC
A
X
SP2
0
11).
SP
SP1
0
PUSH Y
SP0
PCH
PCH
PCL
PCL
8
1
0
CC
Y
A
X
SP
The least significant byte of the Stack Pointer
(called S) can be directly accessed by a LD in-
struction.
Note: When the lower limit is exceeded, the Stack
Pointer wraps around to the stack upper limit, with-
out indicating the stack overflow. The previously
stored information is then overwritten and there-
fore lost. The stack also wraps in case of an under-
flow.
The stack is used to save the return address dur-
ing a subroutine call and the CPU context during
an interrupt. The user may also directly manipulate
the stack by means of the PUSH and POP instruc-
tions. In the case of an interrupt, the PCL is stored
at the first location pointed to by the SP. Then the
other registers are stored in the next locations as
shown in
– When an interrupt is received, the SP is decre-
– On return from interrupt, the SP is incremented
A subroutine call occupies two locations and an in-
terrupt five locations in the stack area.
mented and the context is pushed on the stack.
and the context is popped from the stack.
ST72334J/N, ST72314J/N, ST72124J
POP Y
PCH
PCL
PCH
PCL
CC
Figure
A
X
11.
SP
IRET
PCH
PCL
SP
or RSP
RET
25/153
Related parts for ST72C334J2B6
Image
Part Number
Description
Manufacturer
Datasheet
Request
R

Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
STMicroelectronics
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
STMicroelectronics [RIPPLE-CARRY BINARY COUNTER/DIVIDERS]
Manufacturer:
STMicroelectronics
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
STMicroelectronics [LIQUID-CRYSTAL DISPLAY DRIVERS]
Manufacturer:
STMicroelectronics
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
BOARD EVAL FOR MEMS SENSORS
Manufacturer:
STMicroelectronics
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
NPN TRANSISTOR POWER MODULE
Manufacturer:
STMicroelectronics
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
TURBOSWITCH ULTRA-FAST HIGH VOLTAGE DIODE
Manufacturer:
STMicroelectronics
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
STMicroelectronics
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
DIODE / SCR MODULE
Manufacturer:
STMicroelectronics
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
DIODE / SCR MODULE
Manufacturer:
STMicroelectronics
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Search -----> STE16N100
Manufacturer:
STMicroelectronics
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Search ---> STE53NA50
Manufacturer:
STMicroelectronics
Datasheet: