L6385D STMicroelectronics, L6385D Datasheet - Page 5

L6385D
Manufacturer Part Number
L6385D
Description
IC DRIVER HIGH/LOW SIDE 8-SOIC
Manufacturer
STMicroelectronics
Type
Driverr
Datasheet
1.L6385.pdf
(9 pages)
Specifications of L6385D
Configuration
Half Bridge
Input Type
Non-Inverting
Delay Time
110ns
Current - Peak
400mA
Number Of Configurations
1
Number Of Outputs
2
High Side Voltage - Max (bootstrap)
600V
Voltage - Supply
17V
Operating Temperature
-40°C ~ 125°C
Mounting Type
Surface Mount
Package / Case
8-SOIC (3.9mm Width)
Rise Time
50 ns
Fall Time
30 ns
Supply Current
0.32 mA
Maximum Power Dissipation
750 mW
Maximum Operating Temperature
+ 125 C
Mounting Style
SMD/SMT
Minimum Operating Temperature
- 45 C
Number Of Drivers
2
For Use With
497-5492 - EVAL BOARD FOR L6384/L6385/L6386
Lead Free Status / RoHS Status
Lead free / RoHS Compliant
Other names
497-1435-5
497-1435-5
497-3650-5
497-1435-5
497-3650-5
Available stocks
Company
Part Number
Manufacturer
Quantity
Price
Part Number:
L6385D013TR
Manufacturer:
ST
Quantity:
20 000
leakage losses.
e.g.: HVG steady state consumption is lower than
200 A, so if HVG T
supply 1 C to C
pacitor means a voltage drop of 1V.
The internal bootstrap driver gives great advan-
tages: the external fast recovery diode can be
avoided (it usually has great leakage current).
This structure can work only if V
GND (or lower) and in the meanwhile the LVG is
on. The charging time (T
the time in which both conditions are fulfilled and
it has to be long enough to charge the capacitor.
The bootstrap driver introduces a voltage drop
due to
Ohm). At low frequency this drop can be ne-
glected. Anyway
must be taken in to account.
The following equation is useful to compute the
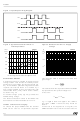
Figure 4. Bootstrap Driver.
Figure 5. Turn On Time vs. Temperature
250
200
150
100
50
V
S
0
-45
Typ.
the DMOS R
-25
D
BOOT
EXT
0
a
increasing the frequency
. This charge on a 1 F ca-
HVG
LVG
ON
DSON
25
Tj (°C)
is 5ms, C
charge
50
(typical value: 125
@ Vcc = 15V
) of the C
V
V
BOOT
OUT
OUT
75
H.V.
BOOT
is close to
100
BOOT
has to
C
TO LOAD
BOOT
125
is
it
drop on the bootstrap DMOS:
V
where Q
power MOS, R
bootstrap DMOS, and T
of the bootstrap capacitor.
For example: using a power MOS with a total
gate charge of 30nC the drop on the bootstrap
DMOS is about 1V, if the T
V
age drop on C
too high, or the circuit topology doesn’t allow a
sufficient charging time, an external diode can be
used.
Figure 6. Turn Off Time vs. Temperature
S
drop
250
200
150
100
50
V
0
has to be taken into account when the volt-
drop
-45
Typ.
gate
V
I
charge
-25
drop
is the gate charge of the external
b
BOOT
dson
HVG
LVG
R
30nC
0
dson
5 s
is the on resistance of the
is calculated: if this drop is
Tj (°C)
25
charge
125 ~
V
charge
drop
V
V
50
is the charging time
BOOT
OUT
@ Vcc = 15V
H.V.
T
is 5 s. In fact:
0.8V
Q
charge
75
gate
D99IN1056
R
C
TO LOAD
100
BOOT
dson
L6385
125
5/9