LTC4225CGN-1#TRPBF Linear Technology, LTC4225CGN-1#TRPBF Datasheet - Page 11

LTC4225CGN-1#TRPBF
Manufacturer Part Number
LTC4225CGN-1#TRPBF
Description
Manufacturer
Linear Technology
Datasheet
1.LTC4225CGN-1TRPBF.pdf
(24 pages)
Specifications of LTC4225CGN-1#TRPBF
Lead Free Status / RoHS Status
Compliant
applicaTions inForMaTion
During a normal power-up, the ideal diode MOSFET turns
on first. As soon as the internally generated supply, INTV
rises above its 2.2V undervoltage lockout threshold, the
internal charge pump is allowed to charge up the CPO
pins. Because the Hot Swap MOSFET is turned off at
power-up, OUT remains low. As a result, the ideal diode
gate drive amplifier senses a large forward drop between
the IN and OUT pins, causing it to pull up DGATE to the
CPO pin voltage.
Before the Hot Swap MOSFET can be turned on, EN must
remain low and ON must remain high for a 100ms debounce
cycle to ensure that any contact bounces during the inser-
tion have ceased. At the end of the debounce cycle, the
internal fault latches are cleared. The Hot Swap MOSFET
is then allowed to turn on by charging up HGATE with a
10µA current source from the charge pump. The voltage
at the HGATE pin rises with a slope equal to 10µA/C
the supply inrush current flowing into the load capacitor,
C
The OUT voltage follows the HGATE voltage when the
Hot Swap MOSFET turns on. If the voltage across the
current sense resistor, R
current will be limited by the internal current limiting
circuitry. Once the MOSFET gate overdrive exceeds 4.2V,
the corresponding PWRGD pin pulls low to indicate that
the power is good. Once OUT reaches the input supply
voltage, HGATE continues to ramp up. An internal 12V
clamp limits the HGATE voltage above OUT.
When both of the MOSFETs are turned on, the gate drive
amplifier controls the gate of the ideal diode MOSFET, to
servo its forward voltage drop across R
25mV. If the load current causes more than 25mV of drop,
the MOSFET gate is driven fully on and the voltage drop
across the MOSFET is equal to I
Turn-Off Sequence
The external MOSFETs can be turned off by a variety of
conditions. A normal turn-off for the Hot Swap MOSFET is
initiated by pulling the ON pin below its 1.155V threshold
L
, is limited to:
I
INRUSH
=
C
C
HG
L
• 10µA
S
, becomes too high, the inrush
LOAD
• R
S
DS(ON)
, M
D
and M
.
HG
H
and
CC
to
,
(80mV ON pin hysteresis), or pulling the EN pin above
its 1.235V threshold. Additionally, an overcurrent fault
of sufficient duration to trip the circuit breaker also turns
off the Hot Swap MOSFET. Normally, the LTC4225 turns
off the MOSFET by pulling the HGATE pin to ground with
a 300µA current sink.
All of the MOSFETs turn off when INTV
undervoltage lockout threshold (2.2V). The DGATE pin is
pulled down with a 100µA current to one diode voltage
below the IN pin, while the HGATE pin is pulled down to
the OUT pin by a 200mA current.
The gate drive amplifier controls the ideal diode MOSFET
to prevent reverse current when the input supply falls
below OUT. If the input supply collapses quickly, the gate
drive amplifier turns off the ideal diode MOSFET with a
fast pull-down circuit as soon as it detects that IN is 20mV
below OUT. If the input supply falls at a more modest rate,
the gate drive amplifier controls the MOSFET to maintain
OUT at 25mV below IN.
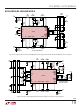
10V/DIV
10V/DIV
10V/DIV
10V/DIV
10V/DIV
10V/DIV
10V/DIV
PWRGD
5V/DIV
HGATE
DGATE
CPO
OUT
OUT
Figure 2. Ideal Diode Controller Start-Up Waveforms
ON
IN
Figure 3. Hot Swap Controller Power-Up Sequence
LTC4225-1/LTC4225-2
50ms/DIV
20ms/DIV
CC
falls below its
422512 F02
422512 F03
11
422512f