LTC4225CGN-1#TRPBF Linear Technology, LTC4225CGN-1#TRPBF Datasheet - Page 9

LTC4225CGN-1#TRPBF
Manufacturer Part Number
LTC4225CGN-1#TRPBF
Description
Manufacturer
Linear Technology
Datasheet
1.LTC4225CGN-1TRPBF.pdf
(24 pages)
Specifications of LTC4225CGN-1#TRPBF
Lead Free Status / RoHS Status
Compliant
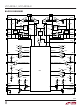
operaTion
The LTC4225 functions as an ideal diode with inrush cur-
rent limiting and overcurrent protection by controlling
two external back-to-back N-channel MOSFETs (M
M
inserted and removed in systems with a backplane pow-
ered by redundant supplies, such as µTCA applications.
The LTC4225 has two separate ideal diode and Hot Swap
controllers, each providing independent control for the
two input supplies.
When the LTC4225 is first powered up, the gates of the
back-to-back MOSFETs are held low, keeping them off.
The gate drive amplifier (GA1, GA2) monitors the voltage
between the IN and OUT pins and drives the DGATE pin.
The amplifier quickly pulls up the DGATE pin, turning
on the MOSFET for ideal diode control, when it senses
a large forward voltage drop. The stored charge in an
external capacitor connected between the CPO and IN
pins provides the charge needed to quickly turn on the
ideal diode MOSFET. An internal charge pump charges up
this capacitor at device power-up. The DGATE pin sources
current from the CPO pin and sinks current into the IN
and GND pins.
Pulling the ON pin high and the EN pin low initiates a
100ms debounce timing cycle. After this timing cycle, a
10µA current source from the charge pump ramps up the
HGATE pin. When the Hot Swap MOSFET turns on, the
inrush current is limited at a level set by an external sense
resistor (R
An active current limit amplifier (A1, A2) servos the gate
of the MOSFET to 65mV across the current sense resistor.
Inrush current can be further reduced, if desired, by add-
ing a capacitor from HGATE to GND. When the MOSFET ’s
gate overdrive (HGATE to OUT voltage) exceeds 4.2V, the
PWRGD pin pulls low.
H
) on a supply path. This allows boards to be safely
S
) connected between the IN and SENSE pins.
D
and
When both of the MOSFETs are turned on, the gate drive
amplifier controls DGATE to servo the forward voltage drop
(V
MOSFETs to 25mV. If the load current causes more than
25mV of voltage drop, the gate voltage rises to enhance
the MOSFET used for ideal diode control. For large output
currents, the MOSFET ’s gate is driven fully on and the
voltage drop across the MOSFETs is equal to the sum of
the I
In the case of an input supply short circuit when the
MOSFETs are conducting, a large reverse current starts
flowing from the load towards the input. The gate drive
amplifier detects this failure condition as soon as it ap-
pears and turns off the ideal diode MOSFET by pulling
down the DGATE pin.
In the case where an overcurrent fault occurs on the sup-
ply output, the current is limited to 65mV/R
filter delay set by 100µA charging the TMR pin capacitor,
the circuit breaker trips and pulls the HGATE pin low, turn-
ing off the Hot Swap MOSFET. Only the supply at fault is
affected, with the corresponding FAULT pin latched low.
At this point, the DGATE pin continues to pull high and
keeps the ideal diode MOSFET on.
Internal clamps limit both the DGATE to IN and CPO to IN
voltages to 12V. The same clamp also limits the CPO and
DGATE pins to a diode voltage below the IN pin. Another
internal clamp limits the HGATE to OUT voltage to 12V
and also clamps the HGATE pin to a diode voltage below
the OUT pin.
Power to the LTC4225 is supplied from either the IN or
OUT pins, through an internal diode-OR circuit to a low
dropout regulator (LDO). That LDO generates a 5V supply
at the INTV
voltage circuitry.
IN
– V
LOAD
OUT
• R
) across the sense resistor and the back-to-back
CC
LTC4225-1/LTC4225-2
DS(ON)
pin and powers the LTC4225’s internal low
of the two MOSFETs in series.
S
. After a fault
422512f
9