MC68030RC25C Freescale Semiconductor, MC68030RC25C Datasheet - Page 539
MC68030RC25C
Manufacturer Part Number
MC68030RC25C
Description
IC MPU 32BIT ENHANCED 128-PGA
Manufacturer
Freescale Semiconductor
Datasheet
1.MC68030FE20C.pdf
(599 pages)
Specifications of MC68030RC25C
Processor Type
M680x0 32-Bit
Speed
25MHz
Voltage
5V
Mounting Type
Surface Mount
Package / Case
128-PGA
Lead Free Status / RoHS Status
Lead free / RoHS Compliant
Features
-
Available stocks
Company
Part Number
Manufacturer
Quantity
Price
Company:
Part Number:
MC68030RC25C
Manufacturer:
MOT
Quantity:
100
Company:
Part Number:
MC68030RC25C
Manufacturer:
MOTOROLA
Quantity:
60
Company:
Part Number:
MC68030RC25C
Manufacturer:
MOT
Quantity:
1 368
Part Number:
MC68030RC25C
Manufacturer:
FREESCALE
Quantity:
20 000
Company:
Part Number:
MC68030RC25C01F91C
Manufacturer:
SYNERGY
Quantity:
114
- Current page: 539 of 599
- Download datasheet (23Mb)
1 2
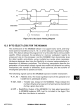
12.4.1 Access Time Calculations
12-14
the negating strobes and to avoid any bus contention with the following bus
ways accessed in fewer than "no wait states", regardless of the external
The timing paths that are typically critical in any memory interface are illus-
trated and defined in Figure 12-8. For burst transfers, the first long word
transferred also uses these parameters, but the subsequent transfers are
The type of device that is interfaced to the MC68030 determines exactly which
for dynamic devices since the cycle must be validated before an access can
Write operations also use this data bus timing to allow data hold times from
cycle. This usually allows the system to be designed with a minimum of bus
buffers and latches.
One of the benefits of the MC68030's on-chip caches is that the effect of
external wait states on performance is lessened because the caches are al-
unique among other general-purpose microprocessors.
different and are discussed in 12.4.2 Burst Mode Cycles.
of the paths is most critical. The address-to-data paths are typically the critical
paths for static devices since there is no penalty for initiating a cycle to these
devices and later validating that access with the appropriate bus control
signal. Conversely, the address-strobe-to-data-valid path is often most critical
be initiated. For devices that signal termination of a bus cycle before data is
validated (e.g., error detection and correction hardware and some external
caches) to improve performance, the critical path may be from the address
or strobes to the assertion of BERR (or BERR and HALT). Finally, the address-
valid-to-DSACKx-or-STERM-asserted path is most critical for very fast devices
and external caches, since the time available between when the address is
valid and when DSACKx or STERM must be asserted to terminate the bus
cycle is minimal. Table 12-2 provides the equations required to calculate the
various memory access times assuming a 50-percent duty cycle clock.
During read operations, M68000 processors latch data on the last falling clock
edge of the bus cycle, one-half clock before the bus cycle ends (burst mode
is a special case). Latching data here, instead of the next rising clock edge,
helps to avoid data bus contention with the next bus cycle and allows the
MC68030 to receive the data into its execution unit sooner for a net perform-
ance increase.
memory configuration. This feature makes the MC68030 (and MC68020)
MC68030 USER'S MANUAL
MOTOROLA
Related parts for MC68030RC25C
Image
Part Number
Description
Manufacturer
Datasheet
Request
R

Part Number:
Description:
(MC600 Series) INTEGRATED CIRCUITS
Manufacturer:
ETC
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet: