A80386DX33 Intel, A80386DX33 Datasheet - Page 41

A80386DX33
Manufacturer Part Number
A80386DX33
Description
IC MPU 32-BIT 5V 33MHZ 132-PGA
Manufacturer
Intel
Datasheet
1.A80386DX33.pdf
(139 pages)
Specifications of A80386DX33
Processor Type
386DX
Features
32-bit
Speed
33MHz
Voltage
5V
Mounting Type
Surface Mount
Package / Case
132-PGA
Family Name
Intel386 DX
Device Core Size
32b
Frequency (max)
33MHz
Supply Voltage 1 (typ)
5V
Operating Supply Voltage (max)
5.25V
Operating Supply Voltage (min)
4.75V
Operating Temp Range
0C to 85C
Operating Temperature Classification
Commercial
Mounting
Through Hole
Pin Count
132
Package Type
PGA
Lead Free Status / RoHS Status
Contains lead / RoHS non-compliant
Other names
807129
Available stocks
Company
Part Number
Manufacturer
Quantity
Price
Task gates are used to switch tasks Task gates
may only refer to a task state segment (see section
4 4 6 Task Switching) therefore only the destination
selector portion of a task gate descriptor is used
and the destination offset is ignored
Exception 13 is generated when a destination selec-
tor does not refer to a correct descriptor type i e a
code segment for an interrupt trap or call gate a
TSS for a task gate
The access byte format is the same for all gate de-
scriptors P
valid P
causes exception 11 if referenced DPL is the de-
scriptor privilege level and specifies when this de-
scriptor may be used by a task (see section 4 4 Pro-
tection) The S field bit 4 of the access rights byte
must be 0 to indicate a system control descriptor
The type field specifies the descriptor type as indi-
cated in Figure 4-8
4 3 4 7 DIFFERENCES BETWEEN Intel386
In order to provide operating system compatibility
between the 80286 and Intel386 DX the Intel386
DX supports all of the 80286 segment descriptors
Figure 4-9 shows the general format of an 80286
system segment descriptor The only differences be-
tween 80286 and Intel386 DX descriptor formats are
that the values of the type fields and the limit and
base address fields have been expanded for the In-
tel386 DX The 80286 system segment descriptors
contained a 24-bit base address and 16-bit limit
while the Intel386 DX system segment descriptors
have a 32-bit base address a 20-bit limit field and a
granularity bit
By supporting 80286 system segments the Intel386
DX is able to execute 80286 application programs
on an Intel386 DX operating system This is possible
because the processor automatically understands
which descriptors are 80286-style descriptors and
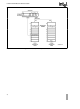
31
BASE
LIMIT
P
SEGMENT BASE 15
Intel Reserved
Set to 0
e
AND 80286 DESCRIPTORS
0 indicates the contents are not valid and
e
Base Address of the segment
The length of the segment
Present Bit
1 indicates that the gate contents are
1
e
Figure 4-9 80286 Code and Data Segment Descriptors
Present
0
0
e
Not Present
TM
DX
SEGMENT LIMIT 15
P
which descriptors are Intel386 DX-style descriptors
In particular if the upper word of a descriptor is zero
then that descriptor is a 80286-style descriptor
The only other differences between 80286-style de-
scriptors and Intel386 DX descriptors is the interpre-
tation of the word count field of call gates and the B
bit The word count field specifies the number of
16-bit quantities to copy for 80286 call gates and
32-bit quantities for Intel386 DX call gates The B bit
controls the size of PUSHes when using a call gate
if B
bits
4 3 4 8 SELECTOR FIELDS
A selector in Protected Mode has three fields Local
or Global Descriptor Table Indicator (TI) Descriptor
Entry Index (Index) and Requestor (the selector’s)
Privilege Level (RPL) as shown in Figure 4-10 The
TI bits select one of two memory-based tables of
descriptors (the Global Descriptor Table or the Local
Descriptor Table) The Index selects one of 8K de-
scriptors in the appropriate descriptor table The
RPL bits allow high speed testing of the selector’s
privilege attributes
4 3 4 9 SEGMENT DESCRIPTOR CACHE
In addition to the selector value every segment reg-
ister has a segment descriptor cache register asso-
ciated with it Whenever a segment register’s con-
tents are changed the 8-byte descriptor associated
with that selector is automatically loaded (cached)
on the chip Once loaded all references to that seg-
ment use the cached descriptor information instead
of reaccessing the descriptor The contents of the
descriptor cache are not visible to the programmer
Since descriptor caches only change when a seg-
ment register is changed programs which modify
the descriptor tables must reload the appropriate
segment registers after changing a descriptor’s
value
DPL
S
TYPE
DPL
e
0 PUSHes are 16 bits if B
Intel386
S
Descriptor Privilege Level 0 –3
System Descriptor
Type of Segment
0
TM
TYPE
DX MICROPROCESSOR
0
e
System
e
1 PUSHes are 32
23
BASE
1
e
User
16
0
a
0
4
41