A80386DX33 Intel, A80386DX33 Datasheet - Page 46

A80386DX33
Manufacturer Part Number
A80386DX33
Description
IC MPU 32-BIT 5V 33MHZ 132-PGA
Manufacturer
Intel
Datasheet
1.A80386DX33.pdf
(139 pages)
Specifications of A80386DX33
Processor Type
386DX
Features
32-bit
Speed
33MHz
Voltage
5V
Mounting Type
Surface Mount
Package / Case
132-PGA
Family Name
Intel386 DX
Device Core Size
32b
Frequency (max)
33MHz
Supply Voltage 1 (typ)
5V
Operating Supply Voltage (max)
5.25V
Operating Supply Voltage (min)
4.75V
Operating Temp Range
0C to 85C
Operating Temperature Classification
Commercial
Mounting
Through Hole
Pin Count
132
Package Type
PGA
Lead Free Status / RoHS Status
Contains lead / RoHS non-compliant
Other names
807129
Available stocks
Company
Part Number
Manufacturer
Quantity
Price
Intel386
4 4 PROTECTION
4 4 1 Protection Concepts
The Intel386 DX has four levels of protection which
are optimized to support the needs of a multi-tasking
operating system to isolate and protect user pro-
grams from each other and the operating system
The privilege levels control the use of privileged in-
structions I O instructions and access to segments
and segment descriptors Unlike traditional micro-
processor-based systems where this protection is
achieved only through the use of complex external
hardware and software the Intel386 DX provides the
protection as part of its integrated Memory Manage-
ment Unit The Intel386 DX offers an additional type
of protection on a page basis when paging is en-
abled (See section 4 5 3 Page Level Protection)
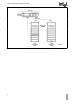
The four-level hierarchical privilege system is illus-
trated in Figure 4-14 It is an extension of the user
supervisor privilege mode commonly used by mini-
computers and in fact the user supervisor mode is
fully supported by the Intel386 DX paging mecha-
nism The privilege levels (PL) are numbered 0
through 3 Level 0 is the most privileged or trusted
level
4 4 2 Rules of Privilege
The Intel386 DX controls access to both data and
procedures between levels of a task according to
the following rules
46
Figure 4-14 Four-Level Hierachical Protection
Data stored in a segment with privilege level p can
be accessed only by code executing at a privilege
level at least as privileged as p
A code segment procedure with privilege level p
can only be called by a task executing at the same
or a lesser privilege level than p
TM
DX MICROPROCESSOR
231630– 63
4 4 3 Privilege Levels
4 4 3 1 TASK PRIVILEGE
At any point in time a task on the Intel386 DX al-
ways executes at one of the four privilege levels
The Current Privilege Level (CPL) specifies the
task’s privilege level A task’s CPL may only be
changed by control transfers through gate descrip-
tors to a code segment with a different privilege lev-
el (See section 4 4 4 Privilege Level Transfers)
Thus an application program running at PL
call an operating system routine at PL
gate) which would cause the task’s CPL to be set to
1 until the operating system routine was finished
4 4 3 2 SELECTOR PRIVILEGE (RPL)
The privilege level of a selector is specified by the
RPL field The RPL is the two least significant bits of
the selector The selector’s RPL is only used to es-
tablish a less trusted privilege level than the current
privilege level for the use of a segment This level is
called the task’s effective privilege level (EPL) The
EPL is defined as being the least privileged (i e nu-
merically larger) level of a task’s CPL and a selec-
tor’s RPL Thus if selector’s RPL
always specifies the privilege level for making an ac-
cess using the selector On the other hand if RPL
3 then a selector can only access segments at level
3 regardless of the task’s CPL The RPL is most
commonly used to verify that pointers passed to an
operating system procedure do not access data that
is of higher privilege than the procedure that origi-
nated the pointer Since the originator of a selector
can specify any RPL value the Adjust RPL (ARPL)
instruction is provided to force the RPL bits to the
originator’s CPL
4 4 3 3 I O PRIVILEGE AND I O PERMISSION
The I O privilege level (IOPL a 2-bit field in the
EFLAG register) defines the least privileged level at
which I O instructions can be unconditionally per-
formed I O instructions can be unconditionally per-
formed when CPL
IN OUT INS OUTS REP INS and REP OUTS )
When CPL
ed with a 286 TSS attempted I O instructions cause
an exception 13 fault When CPL
current task is associated with an Intel386 DX TSS
the I O Permission Bitmap (part of an Intel386 DX
TSS) is consulted on whether I O to the port is al-
lowed or an exception 13 fault is to be generated
BITMAP
l
IOPL and the current task is associat-
s
IOPL (The I O instructions are
e
l
0 then the CPL
IOPL and the
e
e
1 (via a
3 may
e