M66291GP#201 Renesas Electronics America, M66291GP#201 Datasheet

M66291GP#201
Specifications of M66291GP#201
Available stocks
Related parts for M66291GP#201
M66291GP#201 Summary of contents
Page 1
M66291GP/HP ASSP (USB2.0 Device Controller) Overview 1 The M66291 is a general purpose USB (Universal Serial Bus) device controller compliant with the USB Specification Revision 2.0 and supports full speed transfer. The USB transceiver circuit is included, and the M66291 ...
Page 2
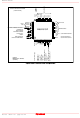
PIN CONFIGURATION (TOP VIEW) DATA BUS HIGH-WRITE STROBE/BUS WIDTH SELECT INTERRUPT 0 READ STROBE LOW-WRITE STROBE CHIP SELECT RESET DMA REQUEST 0 DMA ACKNOWLEDGE 0 Outline M66291GP: 48P6Q- A(LQFP) ...
Page 3
PIN CONFIGURATION (TOP VIEW) D12/P4 D13/P5 D14/P6 D15/A0 HWR/BYTE INT0 LWR Dreq0 Dack0 Outline M66291HP:52PJV(VQFN ...
Page 4
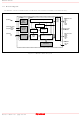
1.2 Block Diagram The M66291 contains an USB-IP block, an I/O block, a bus interface unit (BIU), and a FIFO memory. I/O Block (Oscillator) •Xin Oscillation •Xout Buffer /48MHzPLL ...
Page 5
1.2.1 USB-IP The USB-IP block contains a serial interface engine, a transfer controller, an endpoint controller, a FIFO memory controller, an interrupt controller, and a CPU interface register. (1) ...
Page 6
(1) USB Transceiver The USB transceiver, conforming to the USB Specification Revision 2.0, is composed of a pair of 2 pieces of drivers D+/D- complying with full speed transfer ...
Page 7
1.3 Pin Functions Item Pin name Input/ Output Bus D7~D0 Input/ interface Output D14/P6~ Input/ D8/P0 Output D15/A0 Input/ Output A6~A1 Input *CS Input *LWR Input *HWR/*BYTE Input *RD ...
Page 8
Item Pin Name Input/ Output DMA *Dack1 Input interface ( ) Note1 *TC1 Input USB D+ Input/ interface Output D- Input/ Output Vbus Input TrON Output Others *RST Input ...
Page 9
Registers 2 Bit Numbers : Each register is connected with an internal bus of 16-bit wide, so the bit numbers of the registers located at odd addresses are b15-b8, ...
Page 10
The M66291 register mapping is shown in Figure 2.1 and Figure 2.2, and each register is described below. Address b15 H’00 H’02 H’04 H’06 H’08 H’0A H’0C H’0E H’10 ...
Page 11
Address b15 H’38 H’3A H’3C H’3E H’40 H’42 H’44 H’46 H’48 H’4A H’4C H’4E H’50 H’52 H’54 H’56 H’58 H’5A H’5C H’5E H’60 H’62 H’64 H’66 H’68 H’6A H’6C ...
Page 12
2.1 USB Operation Enable Register USB Operation Enable Register (USB_ENABLE) b15 XCKE PLLC Xtal ...
Page 13
(3) Xtal (Clock Select) Bits (b13~b12) These bits set the multiplication factor of the external clock into PLL. Since it is necessary to supply 48 MHz to the core ...
Page 14
2.2 Remote Wakeup Register Remote Wakeup Register (REMOTE_WAKEUP) b15 Bit name 15~1 Reserved. ...
Page 15
2.3 Sequence Bit Clear Register Sequence Bit Clear Register (SEQUENCE_BIT) b15 Bit name ...
Page 16
2.4 USB_Address Register USB_Address Register (USB_ADDRESS) b15 Bit name 15~7 Reserved. Set it ...
Page 17
2.5 Isochronous Status Register Isochronous Status Register (ISOCHRONOUS_STATUS) b15 FMOD Bit name 15~12 ...
Page 18
2.6 SOF Control Register SOF Control Register (SOF_CNT) b15 SOFOE SOFA Bit name ...
Page 19
2.7 Polarity Set Register Polarity Set Register (POLARITY_CNT) b15 VB01 RM01 SF01 DS01 ...
Page 20
(6) BE01 (Buffer Empty/Size Over Error Interrupt Assign) Bit (b10) This bit selects the pin to output the buffer empty/size over error interrupt signal. (7) NR01 (Buffer Not Ready ...
Page 21
<Edge sense> Interrupt factor 1 ("H" active) Interrupt factor 2 ("H" active) Interrupt pin ("L" active) <Leve sense> Interrupt factor 1 ("H" active) Interrupt factor 2 ("H" active) Interrupt ...
Page 22
2.8 Interrupt Enable Register 0 Interrupt Enable Register 0 (INT_ENABLE0) b15 VBSE RSME SOFE DVSE ...
Page 23
(1) VBSE (Vbus Interrupt Enable) Bit (b15) This bit sets enable/disable of Vbus interrupt. When this bit is set to “1”, the interrupt occurs if VBUS bit is set ...
Page 24
(11) SCFG (SET_CONFIGURATION Execute) Bit (b5) This bit selects whether to set the DVST bit to “1” or not at the SET_ CONFIGURATION execution. For details, refer to “DVST ...
Page 25
2.9 Interrupt Enable Register 1 Interrupt Enable Register 1 (INT_ENABLE1) b15 Bit name ...
Page 26
2.10 Interrupt Enable Register 2 Interrupt Enable Register 2 (INT_ENABLE2) b15 Bit name ...
Page 27
2.11 Interrupt Enable Register 3 Interrupt Enable Register 3 (INT_ENABLE3) b15 Bit name ...
Page 28
2.12 Interrupt Status Register 0 Interrupt Status Register 0 (INT_STATUS0) b15 VBUS RESM SOFR DVST ...
Page 29
Bit name 7 Vbus Vbus Level 6~4 DVSQ Device State 3 VALID Setup Packet Detect 2~0 CTSQ Control Transfer Stage Note : optional value. The ...
Page 30
(2) RESM (Resume Interrupt) Bit (b14) This bit indicates the change of USB bus state. This bit is set to “1” when the USB bus state is changed from ...
Page 31
(5) CTRT (Control Transfer Stage Transition Interrupt) Bit (b11) This bit indicates the transition of stage in control transfers. This bit is set to “1” when the stage transition ...
Page 32
USB bus reset detection (W hen URST bit="1", DVST bit is set to "1") USB bus reset detection (W hen URST bit="1", DVST bit is set to "1") SET ...
Page 33
(12) CTSQ (Control Transfer Stage) Bits (b2~b0) These bits indicate the present stage in the control transfer. Refer to Figure 2.7. 000 : Idle or Setup Stage 001 : ...
Page 34
2.13 Interrupt Status Register 1 Interrupt Status Register 1 (INT_STATUS1) b15 Bit name ...
Page 35
Endpoint 1~6 When set to OUT buffer (EPi_DIR bit = “0”) The condition for this bit to be set to “1” follows: <The endpoint not specified by ...
Page 36
2.14 Interrupt Status Register 2 Interrupt Status Register 2 (INT_STATUS2) b15 Bit name ...
Page 37
2.15 Interrupt Status Register 3 Interrupt Status Register 3 (INT_STATUS3) b15 Bit name ...
Page 38
2.16 Request Register Request Register (REQUEST_TYPE) b15 bRequest Bit name 15~8 bRequest Request ...
Page 39
2.17 Value Register Value Register (REQUEST_VALUE) b15 Bit name 15~0 wValue Value (1) ...
Page 40
2.18 Index Register Index Register (REQUEST_INDEX) b15 Bit name 15~0 wIndex Index (1) ...
Page 41
2.19 Length Register Length Register (REQUEST_LENGTH) b15 Bit name 15~0 wlength Length (1) ...
Page 42
2.20 Control Transfer Control Register Control Transfer Control Register (CONTROL_TRANSFER) b15 CTRR Ctr_Rd_Buf_Nmb ...
Page 43
(3) CTRW (Control Write Transfer Continuous Receive Mode) Bit (b7) This bit sets the receive mode at data stage of the control write transfer. In case of unit receive ...
Page 44
2.21 EP0 Packet Size Register EP0 Packet Size Register (EP0_PACKET_SIZE) b15 Bit name ...
Page 45
2.22 Automatic Response Control Register Automatic Response Control Register (AUTO_RESPONSE_CONTROL) b15 Bit name ...
Page 46
2.23 EP0_FIFO Select Register EP0_FIFO Select Register (EP0_FIFO_SELECT) b15 RCNT Bit name 15 ...
Page 47
(3) BSWP (Byte Swap Mode) Bit (b7) This bit sets the endian of the EP0_FIFO Data Register. When this bit is set to “0”, the EP0_FIFO Data Register gets ...
Page 48
2.24 EP0_FIFO Control Register EP0_FIFO Control Register (EP0_FIFO_CONTROL) b15 EP0_PID IVAL BCLR Bit ...
Page 49
(1) EP0_PID (Response PID) Bits (b15~b14) These bits set the PID for response to the host at data/status stage of the control transfer. At setup stage, the ACK response ...
Page 50
(2) IVAL (IN Buffer Set/OUT Buffer Status) Bit (b13) This bit indicates valid value when the E0req bit of this register is set to “0”. When set to control ...
Page 51
Note: Refer to “3.2 FIFO Buffer” for CPU/SIE side. Note: In case the transmit data exists in the buffer for EP0_FIFO, the buffer empty interrupt occurs in the concerned ...
Page 52
2.25 EP0_FIFO Data Register EP0_FIFO Data Register (EP0_FIFO_DATA) b15 Bit name 15~0 EP0_FIFO ...
Page 53
2.26 EP0 Continuous Transmit Data Length Register EP0 Continuous Transmit Data Length Register (EP0_SEND_LEN) b15 ...
Page 54
2.27 CPU_FIFO Select Register CPU_FIFO Select Register (CPU_FIFO_SELECT) b15 RCNT RWND Bit name ...
Page 55
(2) RWND (Buffer Rewind) Bit (b12) This bit rewinds (initializes) the buffer pointer. When set to OUT buffer (EPi_DIR bit = “0”) When the IVAL bit of the CPU_FIFO ...
Page 56
2.28 CPU_FIFO Control Register CPU_FIFO Control Register (CPU_FIFO_CONTROL) b15 IDLY IVAL BCLR Bit ...
Page 57
(1) IDLY (Isochronous Transmit Delay Set) Bit (b14) In isochronous transfer, transmission can be started by writing “1” to this bit or to the IVAL bit after writing the ...
Page 58
When set to IN buffer (EPi_DIR bit = “1”) When this bit is set to “0”, the CPU side buffer is ready to write the transmit data. This bit ...
Page 59
(5) CPU_DTLN (CPU_FIFO Receive Data Length Register) Bits (b10~b0) These bits are valid against the endpoint set to the OUT buffer (EPi_DIR bit = “0”) and indicates the receive ...
Page 60
2.29 CPU_FIFO Data Register CPU_FIFO Data Register (CPU_FIFO_DATA) b15 Bit name 15~0 CPU_FIFO ...
Page 61
2.30 SIE_FIFO Status Register SIE_FIFO Status Register (SIE_FIFO_STATUS) b15 TGL SCLR Bit name ...
Page 62
(2) SCLR (Buffer Clear) Bit (b12) This bit is valid against the endpoint set to the IN buffer (EPi_DIR bit = “1”). Do not write “1” when set to ...
Page 63
2.31 Dn_FIFO Select Registers (n=0~1) D0_FIFO Select Register (D0_FIFO_SELECT) D1_FIFO Select Register (D1_FIFO_SELECT) b15 BUST DFORM RWND ACKA ...
Page 64
(1) BUST (Burst Mode) Bit (b15) When set to cycle steal transfer, the assertion and negation of the DREQ signal are repeated every time the signal is subjected to ...
Page 65
(6) INTM (DMA Interrupt Mode) Bit (b9) This bit sets the timing of setting “1” to the EPB_RDY bit. <When set to OUT buffer (EPi_DIR bit = “0”)> When ...
Page 66
(9) Octl (Register 8-Bit Mode) Bit (b6) This bit sets the access mode of the Dn_FIFO Data Register. When this bit is set to “0”, the Dn_FIFO Data Register ...
Page 67
2.32 Dn_FIFO Control Registers (n=0~1) D0_FIFO Control Register (D0_FIFO_CONTROL) D1_FIFO Control Register (D1_FIFO_CONTROL) b15 TRCLR TREN IVAL BCLR ...
Page 68
(3) IVAL (IN Buffer Set/OUT Buffer Status) Bit (b13) This bit indicates valid value when the Dreq bit of this register is equal to “0”. The operation of this ...
Page 69
2.33 Dn_FIFO Data Registers (n=0~1) D0_FIFO Data Register (D0_FIFO_DATA) D1_FIFO Data Register (D1_FIFO_DATA) b15 ...
Page 70
2.34 DMAn_Transaction Count Registers (n=0~1) DMA0_Transaction Count Register (DMA0_TRN_COUNT) DMA1_Transaction Count Register (DMA1_TRN_COUNT) b15 ...
Page 71
2.35 FIFO Status Register FIFO Status Register (FIFO_STATUS) b15 Bit name 15~7 Reserved. ...
Page 72
2.36 Port Control Register Port Control Register (PORT_CNTL) b15 Bit name 15 Reserved. ...
Page 73
(1) PIEN (Port Input Enable) Bits (b14~b8) These bits set the enable/disable of port input. When “0” is written to this bit, the related port pin does not work ...
Page 74
2.37 Port Data Register Port Data Register (PORT_DATA) b15 Bit name 15~7 Reserved. ...
Page 75
2.38 Drive Current Adjust Register Drive Current Adjust Register (I_ADJ) b15 Bit name ...
Page 76
2.39 EPi Configuration Registers 0 (i=1~6) EP1 Configuration Register 0 (EP1_0CONFIG) EP2 Configuration Register 0 (EP2_0CONFIG) EP3 Configuration Register 0 (EP3_0CONFIG) EP4 Configuration Register 0 (EP4_0CONFIG) EP5 Configuration Register ...
Page 77
(4) EPi_Buf_siz (Buffer Size) Bits (b11~b8) These bits set the buffer size in 64-byte unit (Note). When set to double buffer mode (EPi_DBLB bit = “1”), the buffer double ...
Page 78
(6) EPi_RWMD (Continuous Transmit/Receive Mode) Bit (b6) This bit sets the transmit/receive mode at bulk transfer. This bit can be set to “1” only when the transfer type is ...
Page 79
2.40 Epi Configuration Registers 1 (i=1~6) EP1 Configuration Register 1 (EP1_1CONFIG) EP2 Configuration Register 1 (EP2_1CONFIG) EP3 Configuration Register 1 (EP3_1CONFIG) EP4 Configuration Register 1 (EP4_1CONFIG) EP5 Configuration Register ...
Page 80
This bit is valid at continuous transmit/receive mode (EPi_RWMD bit = “1”) when set to IN buffer (EPi_DIR bit = “1”). Set to “0” for the other modes. In ...
Page 81
M66291 OPERATIONS 3 3.1 Interrupt Function There are 8 factors of interrupts in the M66291. For details, refer to the “Interrupt Status Registers 0 to 3”. The enable/disable of ...
Page 82
Edge/level generator INT0 circuit INT0/INT1 INT1 assign circuit Bit name <<<Interrupt Enable Register 0>>> Bit name <<<Interrupt Status Register 0>>> ...
Page 83
3.2 FIFO Buffer The M66291 has 6 endpoints available for bulk/interrupt/isochronous transfers in addition to endpoint 0 for control transfer. The M66291 is equipped with a total of 3 ...
Page 84
3.2.3 Buffer State and IVAL Bit (1) Buffer state and IVAL bit of the OUT buffer The relation between buffer state and IVAL bit is shown in Figure 3.2 ...
Page 85
(2) Buffer state and IVAL bit of the IN buffer The relation between buffer state and IVAL bit is shown in Figure 3.3 when the buffer is set to ...
Page 86
3.2.4 IVAL Bit and EPB_RDY Bit The IVAL bit is available per endpoint. These IVAL bits can be specified by the CPU_EP bits and the DMA_EP bits, and the ...
Page 87
3.3 USB Data Transfer Function Overview The M66291 is capable of executing the USB transfer by processing the operations as follows: (1) Response against the control transfer request (2) ...
Page 88
3.3.4 DMA Transfer Overview The M66291 is capable of DMA transfer in 16-bit/8-bit width (specified by the Octl bit) against the endpoint The DREQ pin is ...
Page 89
(A-1) DFO RM=00 W rite DMA_REQ DMA_ACK W rite Data • read pin is ignored. (A-2) DFO RM=01 W rite DMA_REQ DMA_ACK Data • read/write ...
Page 90
3.4 Control Transfer Overview The control transfer is composed of three stages as follows: (1) Setup stage (2) Data stage (some control transfers don't include) (3) Status stage The ...
Page 91
USB bus SETUP ADDR EP CRC5 DATA0 8 bytes data (CW) ACK OUT ADDR EP CRC5 DATA1 MAX packet size data NAK CRC5 OUT ADDR EP DATA1 MAX packet ...
Page 92
USB bus SETUP ADDR EP CRC5 DATA0 8 bytes data (CR) ACK IN ADDR EP CRC5 NAK IN ADDR EP CRC5 NAK CRC5 IN ADDR EP DATA1 MAX packet ...
Page 93
USB bus SETUP ADDR EP CRC5 DATA0 8 bytes data (ND) ACK CRC5 IN ADDR EP NAK IN ADDR EP CRC5 NAK CRC5 IN ADDR EP NAK IN ADDR ...
Page 94
USB bus SETUP ADDR EP CRC5 DATA0 8 bytes data (CR) ACK CRC5 IN ADDR EP NAK IN ADDR EP CRC5 NAK OUT ADDR EP CRC5 DATA1 CRC16 STALL ...
Page 95
USB bus SETUP ADDR EP CRC5 DATA0 8 bytes data (CR) ACK IN ADDR EP CRC5 NAK CRC5 SETUP ADDR EP DATA0 8 bytes data (CR) ACK CRC5 IN ...
Page 96
USB bus SETUP ADDR EP CRC5 DATA0 8 bytes data (CR) ACK IN ADDR EP CRC5 NAK CRC5 IN ADDR EP NAK IN ADDR EP CRC5 DATA1 MAX packet ...
Page 97
3.5 Enumeration Figure 3.13 shows the overview of enumeration operations. Host side procedure USBbus connect (PC power O N etc.) FullSpeed device recognition USB bus reset G ET_DESCRIPT O ...
Page 98
3.5.1 FIFO Buffer Management The M66291 is equipped with the registers below in order to execute high-level management of the FIFO buffer set to continuous transmit/receive mode. (1) SIE_FIFO ...
Page 99
3.5.3 CPU Interface Bus Width Selection The bus width is selected by the *HWR/*BYTE pin level at the rising of the *RST pin. The 8-bit width is selected when ...
Page 100
3.5.5 Register Data Access (1) Writing when CPU interface 16-bit width is selected When 16-bit width is selected becomes valid. Further, *HWR pin becomes valid as ...
Page 101
3.5.6 Clock 48 MHz clock is needed for the internal operation of the M66291. A built-in PLL enables an external clock of 6, 12, 24 MHz to ...
Page 102
ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS 4 4.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings Symbol Parameter CoreVcc USB Core supply voltage IOVcc System interface supply voltage Vbus Vbus input voltage VI(IO) System interface input voltage VO(IO) ...
Page 103
4.3 Electrical Characteristics (IOVcc=2.7~3.6V,CoreVcc=3.0~3.6V) Symbol Parameter VIH "H" input voltage VIL "L" input voltage VIH "H" input voltage VIL "L" input voltage Threshold voltage in positive VT+ direction Threshold ...
Page 104
Note 1: A6-1, TEST input pins and D15-0 input/output pins Note 2: *CS, *RD, *LWR, *HWR/*BYTE, *Dack0, *Dack1, *TC1, *RST input pins Note 3: *INT0, *Dreq0, *Dreq1 output pins ...
Page 105
4.4 Electrical Characteristics (IOVcc=4.5~5.5V,CoreVcc=3.0~3.6V) Symbol Parameter VIH "H" input voltage VIL "L" input voltage VIH "H" input voltage VIL "L" input voltage Threshold voltage in positive VT+ direction Threshold ...
Page 106
Note 1: A6-1, TEST input pins and D15-0 input/output pins Note 2: *CS, *RD, *LWR, *HWR/*BYTE, *Dack0, *Dack1, *TC1, *RST input pins Note 3: *INT0, *Dreq0, *Dreq1 output pins ...
Page 107
4.5 Electrical Characteristics (D+/D-) 4.5.1 DC Characteristics Symbol Parameter VDI Differential input sensitivity VCM Differential common mode range Single ended receiver threshold VSE VOL "L" output voltage VOH "H" ...
Page 108
4.6 Switching Characteristics (IOVcc=2.7~3.6V or 4.5~5.5V) Symbol Parameter ta(A) Address access time tv(A) Data valid time after address ta(CTRL) Control access time tv(CTRL) Data valid time after control ten(CTRL) ...
Page 109
4.7 Timing Requirements (IOVcc=2.7~3.6V or 4.5~5.5V) Symbol Parameter tsuw(A) Address write setup time tsur(A) Address read setup time thw(A) Address write hold time thr(A) Address read hold time tw(CTRL) ...
Page 110
4.8 Measurement circuit 4.8.1 Pins except for USB buffer block Input Vcc Elem ents to P. easured Ω 4.8.2 USB buffer block V c ...
Page 111
4.9 Timing Diagram 4.9.1 CPU interface timing (1-1) Write timing (*RD=”H”) A6-1 (A6- (HW R) Note 2 D15-0 (D7-0) Note 7 (1-2) Read timing (*LWR=”H”, *HWR=”H”) ...
Page 112
Note 1: tw(cycle), trec(CTRL) are necessary for making access to FIFO. Further trecr(CTRL) is valid at the time of register access. Note 2: Writing through the combination of *CS, ...
Page 113
4.9.2 DMA Transfer Timing 1 When set to Cycle Steal Transfer (DMA Transfer Mode Register: BUST = 0) (2-1) Write timing 1 (DMAEN=1, DFORM=00) Dreq Note 4 Dack LW ...
Page 114
Note 4: *Dack="L" level is the condition for inactive *Dreq, and the latter signal of twh(Dreq) or ten(CTRL-Dreq) becomes valid as the specification of active *Dreq at the time ...
Page 115
(2-3) Write timing 2 (DMAEN=1, DFORM=01) Dreq Note 4 Dack D15-0 (D7-0) Note 7 (2-4) Read timing 2 (DMAEN=1, DFORM=01) Dreq Note 4 Dack 9 ten(Dack) 10 D15-0 (D7-0) ...
Page 116
(2-5) Write timing 3 (DMAEN=1, DFORM=10) Dreq tsud(A) A6-1 (A6-0) CS Note (HW R) Note 2 D15-0 (D7-0) Note 7 Note 2: Writing through the combination ...
Page 117
(2-6) Read timing 3 (DMAEN=1, DFORM=10) (*LWR=”H”, *HWR=”H”) Dreq ta(A) 31 tsur(A) A6-1 (A6-0) CS Note Note 3 ten(CTRL) 5 D15-0 (D7-0) Note 7 Note 3: ...
Page 118
4.9.3 DMA Transfer Timing 2 When set to Burst Transfer (DMA Transfer Mode Register : BUST=1) (3-1) Write timing (DMAEN=1, DFORM=00) Dreq Dack (HW R) Note ...
Page 119
(3-3) Write timing (DMAEN=1, DFORM=10) 30 A6-1 (A6-0) CS Dreq RD tw(CTRL) trec(CTRL (HW R) Note 5 D15-0 (D7-0) Note 7 (3-4) Read timing (DMAEN=1, DFORM=10) ...
Page 120
Note 5: Writing through the combination of *Dack, *HWR and *LWR is carried out during the overlap of active (“L). The specification from the rising edge is valid from ...
Page 121
(3-5) TC timing 48 td1(Dack-TC) Dack TC 4.10 Interrupt Timing INT CS (HW R) Note 2 4.11 Reset Timing tw(RST) RST CS (HW R) Note ...
Page 122
4.12 Bus Interface Select Timing RST HW R/BYTE ...
Page 123
REVISION HISTORY Rev. Date Page 1.00 Apr 9, 2001 1,6 1.01 Nov 1, 2004 10,42,43,60, 69,77,78 102 125 Description - First edition issued Modified: USB Specification Revision 2.0 Added: 3 M66291HP Pin Configration Moved: 9 How to Read Register Tables ...
Page 124
MMP EIAJ Package Code JEDEC Code LQFP48-P-77-0.50 – Weight(g) Lead Material – Cu Alloy Detail F Plastic ...
Page 125
Plastic 52pin 7 X 7mm body VQFN ...
Page 126
Sales Strategic Planning Div. Keep safety first in your circuit designs! 1. Renesas Technology Corp. puts the maximum effort into making semiconductor products better and more reliable, but there is always the possibility that trouble may occur with them. Trouble ...