LM49200TLX/NOPB National Semiconductor, LM49200TLX/NOPB Datasheet - Page 19
LM49200TLX/NOPB
Manufacturer Part Number
LM49200TLX/NOPB
Description
IC AUDIO SUB 1.25W AB 20USMD
Manufacturer
National Semiconductor
Series
Boomer®r
Type
Class ABr
Datasheet
1.LM49200TLNOPB.pdf
(26 pages)
Specifications of LM49200TLX/NOPB
Output Type
2-Channel (Stereo) with Stereo Headphones
Max Output Power X Channels @ Load
1.25W x 2 @ 8 Ohm; 38mW x 2 @ 32 Ohm
Voltage - Supply
2.7 V ~ 5.5 V
Features
Depop, Differential Inputs, I²C, Shutdown, Thermal Protection, Volume Control
Mounting Type
Surface Mount
Package / Case
20-MicroSMD
Lead Free Status / RoHS Status
Lead free / RoHS Compliant
Other names
LM49200TLX
TURN_ON_TIME BIT
The Turn_On_Time bit determines the delay time from the
Power_On bit set to '1' and the internal circuits ready. For
input capacitor values up to 0.47μF the Turn_On_Time bit can
be set to fast mode by setting the bit to a '1'. When the input
capacitor values are larger than 0.47μF then the
Turn_On_Time bit should be set to '0' for normal turn-on time
and higher delay. This allows sufficient time to charge the in-
put capacitors to the ½ V
POWER_ON BIT
The Power_On bit is the master control bit to activate or de-
activate the LM49200. All registers can be loaded indepen-
dent of the Power_On bit setting as long as the IC is powered
correctly. Cycling the Power_On bit does not change the val-
ues of any registers nor return all bits to the default power on
value of zero. The Power_On bit only determines whether the
IC is on or off.
HPR_SD BIT
The HPR_SD bit will deactivate the right headphone output
amplifier. This bit is provided to reduce power consumption
when only one headphone output is needed.
MODE_CONTROL BITS
In the LM49200 OUTPUT MODE CONTROL register (Table
4), Bit B5 (EP Bypass) controls the operation of the Earpiece
Bypass path. If EP Bypass = 0, it would act under normal out-
put mode operation set by bits B3, B2, B1, and B0. If EP
Bypass = 1, it overrides the B3, B2, B1, and B0 Bits and en-
ables the Receiver Bypass path, a class AB amplifier, to the
speaker output.
Bit B4 (HPR_SD) of the OUPUT MODE CONTROL register
controls the right headphone shutdown. If HPR_SD = 1, the
right headphone output is disabled.
The LM49200 includes a comprehensive mixer multiplexer
controlled through the I
lows any input combination to appear on any output of
LM49200. Multiple input paths can be selected simultane-
ously. Under these conditions, the selected inputs are mixed
together and output on the selected channel. Table 5 shows
how the input signals are mixed together for each possible
input selection.
HP_GAIN BITS
The headphone outputs have an additional, single volume
control set by the three HP_Gain bits in the Output Gain Con-
trol register. The HP_Gain volume setting controls the output
level for both the left and the right headphone outputs.
LS (EP_MODE) BIT
The LS (EP_Mode) bit selects the amount of bias current in
the loudspeaker amplifier. Setting the LS (EP_Mode) bit to a
'1' will reduce the amount of current from the V
by approximately 0.5mA. The THD performance of the loud-
speaker amplifier will be reduced as a result of lower bias
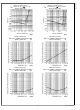
current. See the performance graphs in the Typical Perfor-
mance Characteristics section above.
VOLUME CONTROL BITS
The LM49200 has three independent 32-step volume con-
trols, one for each of the inputs. The five bits of the Volume
Control registers sets the volume for the specified input chan-
nel.
SHUTDOWN FUNCTION
The LM49200 features the following shutdown controls.
2
C interface. The mixer/multiplexer al-
DD
LS bias voltage.
DD
LS supply
19
Bit B4 (GAMP_SD) of the SHUTDOWN CONTROL register
controls the gain amplifiers. When GAMP_SD = 1, it disables
the gain amplifiers that are not in use. For example, in Modes
1, 4 and 5, the Mono inputs are in use, so the Left and Right
input gain amplifiers are disabled, causing the I
imized.
Bit B0 (PWR_On) of the SHUTDOWN CONTROL register is
the global shutdown control for the entire device. Set
PWR_On = 0 for normal operation. PWR_On = 1 overrides
any other shutdown control bit.
DIFFERENTIAL AMPLIFIER EXPLANATION
The LM49200 features a differential input stage, which offers
improved noise rejection compared to a single-ended input
amplifier. Because a differential input amplifier amplifies the
difference between the two input signals, any component
common to both signals is cancelled. An additional benefit of
the differential input structure is the possible elimination of the
DC input blocking capacitors. Since the DC component is
common to both inputs, and thus cancelled by the amplifier,
the LM49200 can be used without input coupling capacitors
when configured with a differential input signal.
BRIDGE CONFIGURATION EXPLAINED
By driving the load differentially through the MONO outputs,
an amplifier configuration commonly referred to as “bridged
mode” is established. Bridged mode operation is different
from the classical single-ended amplifier configuration where
one side of the load is connected to ground.
A bridge amplifier design has a few distinct advantages over
the single-ended configuration, as it provides differential drive
to the load, thus doubling output swing for a specified supply
voltage. Four times the output power is possible as compared
to a single-ended amplifier under the same conditions. This
increase in attainable output power assumes that the ampli-
fier is not current limited or clipped.
A bridge configuration, such as the one used in LM49200,
also creates a second advantage over single-ended ampli-
fiers. Since the differential outputs are biased at half-supply,
no net DC voltage exists across the load. This eliminates the
need for an output coupling capacitor which is required in a
single supply, single-ended amplifier configuration. Without
an output coupling capacitor, the half-supply bias across the
load would result in both increased internal IC power dissipa-
tion and also possible loudspeaker damage.
POWER DISSIPATION
Power dissipation is a major concern when designing a suc-
cessful amplifier, whether the amplifier is bridged or single-
ended. A direct consequence of the increased power
delivered to the load by a bridge amplifier is an increase in
internal power dissipation. The power dissipation of the
LM49200 varies with the mode selected. The maximum pow-
er dissipation occurs in modes where all inputs and outputs
are active (Modes 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 13, 14, 15). The power
dissipation is dominated by the Class AB amplifier. The max-
imum power dissipation for a given application can be derived
from the power dissipation graphs or from Equation 1.
It is critical that the maximum junction temperature (T
150°C is not exceeded. T
power derating curves by using P
area. By adding additional copper foil, the thermal resistance
P
DMAX
= 4*(V
JMAX
DD
)
2
/ (2
can be determined from the
DMAX
π
2
R
and the PC board foil
L
)
DD
www.national.com
to be min-
JMAX
) of
(1)