mc68hc912bc32 Freescale Semiconductor, Inc, mc68hc912bc32 Datasheet - Page 217
mc68hc912bc32
Manufacturer Part Number
mc68hc912bc32
Description
M68hc12 Microcontrollers
Manufacturer
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet
1.MC68HC912BC32.pdf
(334 pages)
- Current page: 217 of 334
- Download datasheet (2Mb)
15.5.3 BDLC Stop and CPU Stop Mode
This power-conserving mode is entered automatically from run mode when the WCM bit in the BCR1
register is set followed by a CPU STOP instruction. This is the lowest-power mode that the BDLC can
enter.
In this mode:
The first passive-to-active transition on the J1850 network generates a non-maskable ($20) CPU interrupt
request by the BDLC, allowing the CPU clocks to restart and the BDLC internal clocks to restart.
Therefore, the new message which wakes up the BDLC from the BDLC stop mode and the CPU from the
CPU wait mode are not received correctly. This is due primarily to the time required for the MCU’s
oscillator to stabilize before the clocks can be applied internally to the other MCU modules, including the
BDLC.
15.6 Loopback Modes
Two loopback modes are used to determine the source of bus faults.
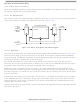
15.6.0.1 Digital Loopback Mode
When a bus fault has been detected, the digital loopback mode is used to determine if the fault condition
is caused by failure in the node’s internal circuits or elsewhere in the network, including the node’s analog
physical interface. In this mode, the transmit digital output pin (BDTxD) and the receive digital input pin
(BDRxD) of the digital interface are disconnected from the analog physical interface and tied together to
allow the digital portion of the BDLC to transmit and receive its own messages without driving the J1850
bus.
15.6.0.2 Analog Loopback Mode
Analog loopback mode is used to determine if a bus fault has been caused by a failure in the node’s
off-chip analog transceiver or elsewhere in the network. The BDLC analog loopback mode does not
modify the digital transmit or receive functions of the BDLC. It does, however, ensure that once analog
loopback mode is exited, the BDLC waits for an idle bus condition before participation in network
communication resumes. If the off-chip analog transceiver has a loopback mode, it usually causes the
input to the output drive stage to be looped back into the receiver, allowing the node to receive messages
it has transmitted without driving the J1850 bus. In this mode, the output to the J1850 bus typically is high
impedance. This allows the communication path through the analog transceiver to be tested without
interfering with network activity. Using the BDLC analog loopback mode in conjunction with the analog
transceiver’s loopback mode ensures that, once the off-chip analog transceiver has exited loopback
mode, the BDLC does not begin communicating before a known condition exists on the J1850 bus.
Freescale Semiconductor
•
•
•
The BDLC internal clocks are stopped.
The CPU internal clocks are stopped.
The BDLC awaits J1850 network activity.
Ensure that all transmissions are complete or aborted prior to putting the
BDLC into stop mode (WCM = 1 in BCR1).
M68HC12B Family Data Sheet, Rev. 9.1
NOTE
Loopback Modes
217
Related parts for mc68hc912bc32
Image
Part Number
Description
Manufacturer
Datasheet
Request
R
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet: