atmega103 ATMEL Corporation, atmega103 Datasheet - Page 21

atmega103
Manufacturer Part Number
atmega103
Description
Atmega103 8-bit With 128k Bytes Of In-system Programmable Flash
Manufacturer
ATMEL Corporation
Datasheet
1.ATMEGA103.pdf
(141 pages)
Available stocks
Company
Part Number
Manufacturer
Quantity
Price
Company:
Part Number:
atmega103-6AC
Manufacturer:
ATMEL
Quantity:
1
Company:
Part Number:
atmega103-6AI
Manufacturer:
ATMEL
Quantity:
586
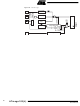
Stack Pointer – SP
0945I–AVR–02/07
ied into T by the BST instruction and a bit in T can be copied into a bit in a register in the
register file by the BLD instruction.
• Bit 5 – H: Half-carry Flag
The Half-carry Flag H indicates a Half-carry in some arithmetic operations. See the
instruction set description on page 135 for detailed information.
• Bit 4 – S: Sign Bit, S = N ⊕ V
The S-bit is always an exclusive or between the Negative Flag N and the Two’s Comple-
ment Overflow Flag V. See the instruction set description on page 135 for detailed
information.
• Bit 3 – V: Two’s Complement Overflow Flag
The Two’s Complement Overflow Flag V supports two’s complement arithmetics. See
the instruction set description on page 135 for detailed information.
• Bit 2 – N: Negative Flag
The Negative Flag N indicates a negative result from an arithmetical or logical operation.
See the Instruction set description on page 135 for detailed information.
• Bit 1 – Z: Zero Flag
The Zero Flag Z indicates a zero result from an arithmetical or logical operation. See the
instruction set description on page 135 for detailed information.
• Bit 0 – C: Carry Flag
The Carry Flag C indicates a carry in an arithmetical or logical operation. See the
instruction set description on page 135 for detailed information.
Note that the Status Register is not automatically stored when entering an interrupt rou-
tine or restored when returning from an interrupt routine. This must be handled by
software.
The general AVR 16-bit Stack Pointer is effectively built up of two 8-bit registers in the
I/O space locations $3E ($5E) and $3D ($5D). As the ATmega103(L) supports up to
64K bytes memory, all 16 bits are used.
The Stack Pointer points to the Data SRAM Stack area where the Subroutine and Inter-
rupt Stacks are located. This Stack space in the Data SRAM must be defined by the
program before any subroutine calls are executed or interrupts are enabled. The Stack
Pointer must be set to point above $60. The Stack Pointer is decremented by one when
data is pushed onto the Stack with the PUSH instruction and it is decremented by 2
when an address is pushed onto the Stack with subroutine calls and interrupts. The
Stack Pointer is incremented by 1 when data is popped from the Stack with the POP
Bit
$3E ($5E)
$3D ($5D)
Read/Write
Initial Value
SP15
R/W
R/W
SP7
15
7
0
0
SP14
SP6
R/W
R/W
14
6
0
0
SP13
SP5
R/W
R/W
13
5
0
0
SP12
SP4
R/W
R/W
12
4
0
0
SP11
SP3
R/W
R/W
11
3
0
0
SP10
R/W
R/W
SP2
10
2
0
0
ATmega103(L)
R/W
SP9
SP1
R/W
9
1
0
0
SP8
SP0
R/W
R/W
8
0
0
0
SPH
SPL
21