LTC2494CUHF-PBF LINER [Linear Technology], LTC2494CUHF-PBF Datasheet - Page 28

LTC2494CUHF-PBF
Manufacturer Part Number
LTC2494CUHF-PBF
Description
16-Bit 8-/16-Channel ?? ADC with PGA and Easy Drive Input Current Cancellation
Manufacturer
LINER [Linear Technology]
Datasheet
1.LTC2494CUHF-PBF.pdf
(36 pages)
APPLICATIONS INFORMATION
LTC2494
For many applications, the sensor output impedance
combined with external input bypass capacitors produces
RC time constants much greater than the 580ns requied
for 1ppm accuracy. For example, a 10k bridge driving a
0.1μF capacitor has a time constant an order of magnitude
greater than the required maximum.
The LTC2494 uses a propriatary switching algorithm
that forces the average differential input current to zero
independent of external settling errors. This allows direct
digitization of high impedance sensors without the need
of buffers.
The switching algorithm forces the average input current
on the positive input (I
current in the negative input (I
conversion cycle, the average input current (I
is zero. While the differential input current is zero, the
common mode input current (I
to the difference between the common mode input volt-
age (V
(V
In applications where the input common mode voltage is
equal to the reference common mode voltage, as in the
case of a balanced bridge, both the differential and com-
28
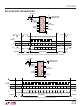
SWITCHING FREQUENCY
f
f
SW
SW
REF
REF
I
I
IN +
IN
I
I
REF
REF
REF(CM)
IN
IN
= 123kHz INTERNAL OSCILLATOR
= 0.4 • f
–
+
–
+
–
+
–
IN(CM)
EOSC
MULTIPLEXER
).
INPUT
100Ω
100Ω
EXTERNAL OSCILLATOR
) and the common mode reference voltage
MUXOUTN
MUXOUTP
IN
+
) to be equal to the average input
CONNECTION
CONNECTION
EXTERNAL
EXTERNAL
IN
+
IN
+ I
–
ADCINP
ADCINN
). Over the complete
IN
Figure 12. LTC2494 Equivalent Analog Input Circuit
–
)/2 is proportional
10k
10k
10k
10k
INTERNAL
NETWORK
SWITCH
IN
+
– I
IN
–
)
2494 F12
mon mode input current are zero. The accuracy of the
converter is not compromised by settling errors.
In applications where the input common mode voltage is
constant but different from the reference common mode
voltage, the differential input current remains zero while
the common mode input current is proportional to the
difference between V
common mode voltage of 2.5V and an input common mode
of 1.5V, the common mode input current is approximately
0.74μA (in simultaneous 50Hz/60Hz rejection mode). This
common mode input current does not degrade the accuracy
if the source impedances tied to IN
Mismatches in source impedance lead to a fi xed offset
error but do not effect the linearity or full scale reading.
A 1% mismatch in a 1k source resistance leads to a 74μV
shift in offset voltage.
In applications where the common mode input voltage
varies as a function of the input signal level (single ended
type sensors), the common mode input current varies
proportionally with input voltage. For the case of balanced
input impedances, the common mode input current effects
are rejected by the large CMRR of the LTC2494, leading
to little degradation in accuracy. Mismatches in source
C
12pF
EQ
I IN
I I REF
where
R
R
R
V
V
V
V
( )
( )
IN
IN CM
REF
REF CM
EQ
EQ
EQ
(
=
+
(
=
=
=
=
IN
+
:
)
AVG
2 71
2.98M INTERNAL OSCILLATOR 50Hz/60
(
REF
0.833 10
=
) )
+
.
AVG
=
⎛
⎜
⎜
⎝
−
=
M INTERNAL OSCILLATOR
⎛
⎜
⎜
⎝
IN
+
IN WHERE IN AN
≈
REF
I IN
Ω
Ω
−
+
•
( )
−
1 5
REF
,
– –
2
.
+
–
IN
12
V
–
2
IN(CM)
−
REF
−
AVG
)
REF
⎞
⎟
⎟
⎠
/f
EOSC
+
=
−
(
0 5
V
V
+
. •
⎞
⎟
⎟
⎠
IN CM
REF CM
EXTERNAL OSCIL
(
and V
R
. 0 5
(
D D IN ARE THE SELECTED INPUT CHANNELS
E E Q
)
−
)
•
–
R
−
V
REF CM
EQ
V
IN CM
REF(CM)
(
(
6
+
0 0 Hz MODE
)
)
and IN
)
L L ATOR
–
V
H H z MODE
REF
. For a reference
V
IN
•
–
2
R
EQ
are matched.
2494fb