ISL6594DCBZ Intersil, ISL6594DCBZ Datasheet - Page 8

ISL6594DCBZ
Manufacturer Part Number
ISL6594DCBZ
Description
IC MOSFET DRVR SYNC BUCK 8-SOIC
Manufacturer
Intersil
Datasheet
1.ISL6594DCBZ.pdf
(11 pages)
Specifications of ISL6594DCBZ
Configuration
High and Low Side, Synchronous
Input Type
PWM
Delay Time
10.0ns
Current - Peak
1.25A
Number Of Configurations
1
Number Of Outputs
2
High Side Voltage - Max (bootstrap)
36V
Voltage - Supply
6.8 V ~ 13.2 V
Operating Temperature
0°C ~ 85°C
Mounting Type
Surface Mount
Package / Case
8-SOIC (3.9mm Width)
Lead Free Status / RoHS Status
Lead free / RoHS Compliant
improvement suggestions. When designing the driver into an
application, it is recommended that the following calculations
are used to ensure safe operation at the desired frequency for
the selected MOSFETs. The total gate drive power losses due
to the gate charge of MOSFETs and the driver’s internal
circuitry and their corresponding average driver current can
be estimated with Equations 2 and 3, respectively:
where the gate charge (Q
particular gate to source voltage (V
corresponding MOSFET datasheet; I
quiescent current with no load at both drive outputs; N
and N
respectively; PVCC is the drive voltage for both upper and
lower FETs. The I
the driver without capacitive load and is typically 116mW at
300kHz and VCC = PVCC = 12V.
The total gate drive power losses are dissipated among the
resistive components along the transition path. The drive
resistance dissipates a portion of the total gate drive power
losses, the rest will be dissipated by the external gate
resistors (R
(R
typical upper and lower gate drives turn-on transition path.
The power dissipation on the driver can be roughly
estimated as:
P
P
P
P
R
I
DR
Qg_TOT
DR
DR_UP
DR_LOW
EXT1
GI1
P
P
=
=
Q2
Qg_Q2
and R
Qg_Q1
⎛
⎜
⎝
P
=
Q
-----------------------------------------------------
DR_UP
=
are number of upper and lower MOSFETs,
=
R
G1
=
⎛
⎜
⎝
G1
G1
P
GI2
--------------------------------------
R
⎛
⎜
⎝
=
•
=
Qg_Q1
HI1
--------------------------------------
R
PVCC N
+
and R
V
Q
-------------------------------------- - f
HI2
Q
-------------------------------------- - f
) of MOSFETs. Figures 3 and 4 show the
+
R
-------------
GS1
R
N
G2
G1
+
Q*
P
GI1
HI1
Q1
R
R
+
DR_LOW
V
V
HI2
+
•
VCC product is the quiescent power of
•
EXT1
R
GS2
GS1
G2
•
PVCC
P
PVCC
EXT2
Qg_Q2
) and the internal gate resistors
Q1
G1
+
+
+
+
2
--------------------------------------- -
R
2
Q
-----------------------------------------------------
and Q
I
•
LO1
--------------------------------------- -
R
•
+
Q
R
8
G2
LO2
EXT2
I
SW
SW
•
Q
R
VCC
+
LO1
R
•
•
•
+
•
PVCC N
R
LO2
VCC
GS1
G2
V
N
N
EXT1
R
GS2
Q
=
Q2
Q1
) is defined at a
EXT2
R
and V
is the driver’s total
G2
⎞
⎟
⎠
•
•
⎞
⎟
⎠
+
P
---------------------
•
Q2
GS2
R
-------------
Qg_Q1
N
P
---------------------
GI2
⎞
⎟
⎠
Q2
Qg_Q2
2
•
2
) in the
f
SW
(EQ. 2)
(EQ. 3)
(EQ. 4)
+
Q1
I
Q
ISL6594D
Application Information
Layout Considerations
The parasitic inductances of the PCB and of the power
devices’ packaging (both upper and lower MOSFETs) can
cause serious ringing, exceeding absolute maximum rating
of the devices. Careful layout can help minimize such
unwanted stress. The following advice is meant to lead to an
optimized layout:
• Keep decoupling loops (PVCC-GND and BOOT-PHASE)
• Minimize trace inductance, especially on low-impedance
• Minimize the inductance of the PHASE node. Ideally, the
• Minimize the current loop of the output and input power
In addition, for heat spreading, place copper underneath the
IC whether it has an exposed pad or not. The copper area
can be extended beyond the bottom area of the IC and/or
connected to buried power ground plane(s) with thermal
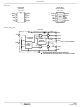
FIGURE 4. TYPICAL LOWER-GATE DRIVE TURN-ON PATH
as short as possible.
lines. All power traces (UGATE, PHASE, LGATE, GND,
PVCC) should be short and wide, as much as possible.
source of the upper and the drain of the lower MOSFET
should be as close as thermally allowable.
trains. Short the source connection of the lower MOSFET
to ground as close to the transistor pin as feasible. Input
capacitors (especially ceramic decoupling) should be
placed as close to the drain of upper and source of lower
MOSFETs as possible.
FIGURE 3. TYPICAL UPPER-GATE DRIVE TURN-ON PATH
PVCC
PVCC
PHASE
R
R
BOOT
LO2
R
HI2
R
LO1
HI1
R
G2
R
G
G1
G
R
C
GI2
R
GD
C
C
GI1
GD
GS
C
GS
S
S
D
December 3, 2007
D
Q2
C
Q1
DS
C
FN9282.1
DS