LM26001QMXAX/NOPB National Semiconductor, LM26001QMXAX/NOPB Datasheet - Page 15

LM26001QMXAX/NOPB
Manufacturer Part Number
LM26001QMXAX/NOPB
Description
IC REG SW 1.5A W/SLEEP 16-TSSOP
Manufacturer
National Semiconductor
Series
PowerWise®r
Type
Step-Down (Buck)r
Datasheet
1.LM26001QMXANOPB.pdf
(18 pages)
Specifications of LM26001QMXAX/NOPB
Internal Switch(s)
Yes
Synchronous Rectifier
No
Number Of Outputs
1
Voltage - Output
1.25 ~ 35 V
Current - Output
1.5A
Frequency - Switching
150kHz ~ 500kHz
Voltage - Input
4 ~ 38 V
Operating Temperature
-40°C ~ 125°C
Mounting Type
Surface Mount
Package / Case
16-TSSOP Exposed Pad, 16-eTSSOP, 16-HTSSOP
Power - Output
2.6W
Lead Free Status / RoHS Status
Lead free / RoHS Compliant
Other names
LM26001QMXAX
Available stocks
Company
Part Number
Manufacturer
Quantity
Price
Company:
Part Number:
LM26001QMXAX/NOPB
Manufacturer:
MOLEX
Quantity:
10 000
Where B is the desired feedback gain in v/v between fp and
fz, and gm is the transconductance of the error amplifier. A
gain value around 10dB (3.3v/v) is generally a good starting
point. Bandwidth increases with increasing values of R5.
3. Next, place a zero (fzc) near fp using C8. C8 can be de-
termined with the following equation:
The selected value of C8 should place fzc within a decade
above or below fpmax, and not less than fpmin. A higher C8
value (closer to fpmin) generally provides a more stable loop,
but too high a value will slow the transient response time.
Conversely, a smaller C8 value will result in a faster transient
response, but lower phase margin.
4. A second pole (fpc1) can also be placed at fz. This pole can
be created with a single capacitor, C9. The minimum value
for this capacitor can be calculated by:
C9 may not be necessary in all applications. However if the
operating frequency is being synchronized below the nominal
frequency, C9 is recommended. Although it is not required for
stability, C9 is very helpful in suppressing noise.
A phase lead capacitor can also be added to increase the
phase and gain margins. The phase lead capacitor is most
helpful for high input voltage applications or when synchro-
nizing to a frequency greater than nominal. This capacitor,
shown as C10 in Figure 10, should be placed in parallel with
the top feedback resistor, R1. C10 introduces an additional
zero and pole to the compensation network. These frequen-
cies can be calculated as shown below:
A phase lead capacitor will boost loop phase around the re-
gion of the zero frequency, fzff. fzff should be placed some-
what below the fpz1 frequency set by C9. However, if C10 is
too large, it will have no effect.
PCB Layout
Good board layout is critical for switching regulators such as
the LM26001. First, the ground plane area must be sufficient
for thermal dissipation purposes, and second, appropriate
guidelines must be followed to reduce the effects of switching
noise.
Switch mode converters are very fast switching devices. In
such devices, the rapid increase of input current combined
with parasitic trace inductance generates unwanted Ldi/dt
noise spikes at the SW node and also at the VIN node. The
15
magnitude of this noise tends to increase as the output current
increases. This parasitic spike noise may turn into electro-
magnetic interference (EMI), and can also cause problems in
device performance. Therefore, care must be taken in layout
to minimize the effect of this switching noise.
The current sensing circuit in current mode devices can be
easily affected by switching noise. This noise can cause duty
cycle jitter which leads to increased spectral noise. Although
the LM26001 has 100ns blanking time at the beginning of ev-
ery cycle to ignore this noise, some noise may remain after
the blanking time. Following the important guidelines below
will help minimize switching noise and its effect on current
sensing.
The switch node area should be as small as possible. The
catch diode, input capacitors, and output capacitors should
be grounded to a large ground plane, with the bulk input ca-
pacitor grounded as close as possible to the catch diode
anode. Additionally, the ground area between the catch diode
and bulk input capacitor is very noisy and should be some-
what isolated from the rest of the ground plane.
A ceramic input capacitor must be connected as close as
possible to the VIN pin and grounded close to the GND pin.
Often this capacitor is most easily located on the bottom side
of the pcb. If placement close to the GND pin is not practical,
the ceramic input capacitor can also be grounded close to the
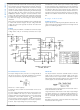
catch diode ground. The above layout recommendations are
illustrated below in
It is a good practice to connect the EP, GND pin, and small
signal components (COMP, FB, FREQ) to a separate ground
plane, shown in
as a signal ground symbol. Both the exposed pad and the
GND pin must be connected to ground. This quieter plane
should be connected to the high current ground plane at a
quiet location, preferably near the Vout ground as shown by
the dashed line in
The EP GND plane should be made as large as possible,
since it is also used for thermal dissipation. Several vias can
be placed directly below the EP to increase heat flow to other
layers when they are available. The recommended via hole
diameter is 0.3mm.
The trace from the FB pin to the resistor divider should be
short and the entire feedback trace must be kept away from
the inductor and switch node. See Application Note AN-1229
for more information regarding PCB layout for switching reg-
ulators.
FIGURE 11. Example PCB Layout
Figure 11
Figure
Figure
11.
as EP GND, and in the schematics
11.
20179449
www.national.com