FAN6756 Fairchild Semiconductor, FAN6756 Datasheet - Page 10
FAN6756
Manufacturer Part Number
FAN6756
Description
Manufacturer
Fairchild Semiconductor
Datasheet
1.FAN6756.pdf
(18 pages)
Available stocks
Company
Part Number
Manufacturer
Quantity
Price
Part Number:
FAN6756AHLMX
Manufacturer:
FAIRCHILD/仙童
Quantity:
20 000
Part Number:
FAN6756HL
Manufacturer:
FAIRCHILD/仙童
Quantity:
20 000
Part Number:
FAN6756MLMY
Manufacturer:
FAIRCHILD/仙童
Quantity:
20 000
Part Number:
FAN6756MR
Manufacturer:
F
Quantity:
20 000
Part Number:
FAN6756MRMY
Manufacturer:
FSC/ON
Quantity:
20 000
© 2011 Fairchild Semiconductor Corporation
FAN6756 • Rev. 1.0.4
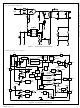
Functional Description
Current Mode Control
FAN6756 employs Peak-Current Mode control, as
shown in Figure 22. An opto-coupler (such as the
H11A817A) and a shunt regulator (such as the KA431)
are typically used to implement the feedback network.
Comparing the feedback voltage with the voltage across
the R
switching duty cycle. A synchronized positive slope is
added to the sensed current signal to guarantee stable
Current-Mode control over a wide range of input
voltages. The built-in slope compensation stabilizes the
current loop and prevents sub-harmonic oscillation.
Leading-Edge Blanking (LEB)
Each time the power MOSFET is switched on, a turn-on
spike occurs on the sense resistor. To avoid premature
termination of the switching pulse, a leading-edge
blanking time, t
period, the current-limit comparator is disabled and
cannot switch off the gate driver.
mWSaver™ Technology
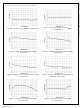
Green-Mode
FAN6756 modulates the PWM frequency as a function
of the FB voltage to improve the medium and light load
efficiency, as shown in Figure 23. Since the output
power is proportional to the FB voltage in Current-Mode
control, the switching frequency decreases as load
decreases. In heavy-load conditions, the switching
frequency is fixed at 65kHz. Once V
V
decreasing from 65kHz to 23kHz to reduce switching
losses. As V
frequency is decreased to 23kHz, the switching frequency
is fixed to avoid acoustic noise.
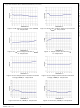
When V
further, FAN6756 enters Burst Mode where PWM
switching is disabled. Then the output voltage starts to
drop, causing the feedback voltage to rise. Once V
rises above V
Mode alternately enables and disables switching,
thereby reducing switching loss for lower power
consumption, as shown in Figure 24.
FB-N
Figure 22. Current Mode Control Circuit Diagram
sense
(2.8V), the PWM frequency starts linearly
FB
falls below V
resistor makes it possible to control the
FB
FB-ZDCR1
LEB
drops to V
, is introduced. During this blanking
(2.1V), switching resumes. Burst
FB-ZDC1
FB-G
(2.0 V) as load decreases
(2.3V), where switching
FB
decreases below
FB
10
Standby Mode & Feedback Impedance Switching
Standby Mode is defined as a special operational mode
to minimize power consumption at extremely light-load
or no-load condition where, not only the switching loss,
but also power consumption of FAN6756 itself, are
reduced further than in Green Mode. Standby Mode is
initiated when the non-switching state of burst switching
in Green Mode persists longer than 10ms for three
consecutive burst switchings (as shown in Figure 25).
To prevent entering Standby Mode during dynamic load
change, there is 900ms delay. If there are more than
104 consecutive switching pulses during the 900ms
delay, FAN6756 does not go into Standby Mode.
Once FAN6756 enters Standby Mode, the feedback
impedance, Z
modulator, as shown in Figure 26. When V
threshold level, the impedance modulator clamps V
and disables switching. When V
higher than V
Z
operation. As shown in Figure 27, by clamping V
disable switching, while modulating Z
switching, the system is forced into deep Burst Mode to
reduce switching loss.
Deep Burst Mode maintains V
power consumption can be minimized. When FAN6756
enters Standby Mode, several blocks are disabled and
the operation current is reduced from 1.8mA (I
The feedback voltage thresholds where FAN6756
enters and exits Burst Mode change from V
FB
f
OSC-G
f
OSC
, allowing V
Figure 24. Burst Switching in Green Mode
f
S
V
FB-ZDC1
Figure 23. V
DD-OFF
V
FB
FB-ZDCR1
, is modulated by the impedance
FB
), the impedance modulator controls
to rise and resume switching
V
FB
FB-G
vs. PWM Frequency
DD
DD
as low as possible so
V
FB-N
drops to 7V (0.5V
FB
www.fairchildsemi.com
FB
to enable
DD-OP1
is under a
FB-ZDC1
V
FB
FB
).
FB
to