LM9801CCV NSC [National Semiconductor], LM9801CCV Datasheet - Page 22

LM9801CCV
Manufacturer Part Number
LM9801CCV
Description
Greyscale/24-Bit Color Linear CCD Sensor Processor
Manufacturer
NSC [National Semiconductor]
Datasheet
1.LM9801CCV.pdf
(34 pages)
Available stocks
Company
Part Number
Manufacturer
Quantity
Price
Company:
Part Number:
LM9801CCV
Manufacturer:
VISHAY
Quantity:
5 510
Part Number:
LM9801CCV
Manufacturer:
NS/国半
Quantity:
20 000
http
Applications Information
of the CCD is AC coupled to the LM9801 through a DC
blocking capacitor C
used) The value of this capacitor is determined by the leak-
age current of the LM9801’s OS input and the output imped-
ance of the CCD The leakage through the OS input deter-
mines how quickly the capacitor value will drift from the
clamp value of REF OUT
many pixels can be processed before the droop causes er-
rors in the conversion (
The output impedance of the CCD determines how quickly
the capacitor can be charged to the clamp value during the
black reference period at the beginning of every line
The minimum clamp capacitor value is determined by the
maximum droop the LM9801 can tolerate while converting
one CCD line The following equation takes the maximum
leakage current into the OS input the maximum allowable
droop (100 mV) the number of pixels on the CCD and the
pixel conversion rate (f
clamp capacitor value
For example if the OS input leakage current is 20 nA worst-
case the CCD has 2700 active pixels the conversion rate is
2 5 MHz (f
0 1V the minimum clamp capacitor value is
The maximum size of the clamp capacitor is determined by
the amount of time available to charge it to the desired val-
ue during the optical black portion of the CCD output The
internal clamp is on for each pixel from the rising edge of
the S H ref pulse to the falling edge of the S H signal pulse
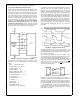
(see Diagrams 7 and 8) This time can be calculated using
the values stored in the Sample Signal and Sample Refer-
ence configuration registers and the MCLK frequency For
normal CCDs
And for even odd CCDs
Where SS is the value in the Sample Signal Position register
(0 –15) SR is the value in the Sample Reference Position
register (0 –14) f
the amount of time (per pixel) that the clamp is on
The following equation takes the number of optical black
pixels the amount of time (per pixel) that the clamp is
closed the CCD’s output impedance and the desired accu-
racy of the final clamp voltage and provides the maximum
clamp capacitor value that allows the clamp capacitor to
settle to the desired accuracy within a single line
www national com
C
CLAMP MIN
MCLK
C
C
e
e
CLAMP MAX
CLAMP MIN
t
e
MCLK
DARK
dV
t
leakage current (A)
DARK
i
20 MHz) and the max droop desired is
max droop (V)
dt
CLAMP
(s)
is the MCLK frequency and t
MCLK
(s)
g
e
MID
0 1V is the recommended limit)
e
e
e
e
e
(the CCD’s DOS output is not
18
8) and provides the minimum
2
2f
2f
20 nA
R
216 pF
R
0 1V
t
which then determines how
a
MCLK
MCLK
OUT
a
In(accuracy)
n
SS –SR
SS– SR
( )
2 5 MHz
conversion rate (Hz)
(Hz)
(Hz)
2700
1
number of pixels
In(accuracy)
t
DARK
(Continued)
(s)
DARK
is
22
Where n
amount of time (per pixel) that the clamp is on R
output impedance of the CCD and accuracy is the ratio of
the worst-case initial capacitor voltage to the desired final
capacitor voltage For example if a CCD has 18 black refer-
ence pixels the output impedance of the CCD is 1500
LM9801 is configured to clamp for 300 ns the worst case
initial voltage across the capacitor is 10V and the desired
voltage after clamping is 0 1V (accuracy
then
The final value for C
C
470 pF will work in this example
In some cases depending primarily on the choice of CCD
C
C
to its final voltage during the black pixels at the beginning of
a line and hold its voltage without drooping for the duration
of that line This is usually not a problem because in most
applications the CCD is clocked continuously as soon as
power is applied In this case a larger capacitor can be
used (guaranteeing that the C
met) and the final clamp voltage is forced across the ca-
pacitor over multiple lines This equation calculates how
many lines are required before the capacitor settles to the
desired accuracy
Using the values shown before and a clamp capacitor value
of 0 01 F this works out to be
At a 2 5 MHz conversion rate this is about 14 ms
In this example a 0 01 F capacitor takes 14 ms after pow-
er-up to charge to its final value but its droop across all
subsequent lines is now less than 2 mV (using the previous
example’s values) This wide margin is the reason a C
value of 0 01 F will work in most applications
4 3 VGA
The LM9801 has a VGA (Variable Gain Amplifier) that can
be used to increase the amplitude of the CCD signal prior to
sampling correction and digitization The gain of the VGA is
0 dB to 9 dB and is determined by the codes in the 4-bit
VGA Gain register as given by the equation
This gain may be changed at the line rate (not the pixel rate)
by writing to the configuration register You can write to the
configuration register to change the gain at any time but if
you write during a line the remaining pixels of that line may
be corrupted It is best to change the gain after all active
pixels have been read out or while SYNC is low
CLAMP MAX
CLAMP
CLAMP MIN
lines
lines
e
e
MAX
the number of optical black pixels t
e
meaning that the capacitor cannot be charged
Gain
1500
C
but no less than C
CLAMP MAX
18
R
may
OUT
VGA
n
CLAMP
0 01 F
300 ns
C
(dB)
t
CLAMP
DARK
actually
e
e
should be less than or equal to
e
1500
514 pF
VGA code
In
CLAMP MIN
18
In
16
CLAMP MIN
0 1V
be
10V
Initial Voltage
Final Voltage
In(100)
300 ns
e
9 55
less
e
10 0 1
requirement is
12 8 lines
DARK
A value of
than
OUT
e
CLAMP
is the
is the
100)
the
the