AD9851/FSPCB Analog Devices Inc, AD9851/FSPCB Datasheet - Page 12

AD9851/FSPCB
Manufacturer Part Number
AD9851/FSPCB
Description
BOARD EVAL FOR AD9851/FS
Manufacturer
Analog Devices Inc
Series
AgileRF™r
Datasheet
1.AD9851BRSZ.pdf
(24 pages)
Specifications of AD9851/FSPCB
Rohs Status
RoHS non-compliant
Main Purpose
Timing, Direct Digital Synthesis (DDS)
Utilized Ic / Part
AD9851/FS
Secondary Attributes
-
Embedded
-
Primary Attributes
-
THEORY OF OPERATION AND APPLICATION
The AD9851 uses direct digital synthesis (DDS) technology,
in the form of a numerically controlled oscillator (NCO), to
generate a frequency/phase-agile sine wave. The digital sine
wave is converted to analog form via an internal 10-bit high
speed D/A converter. An on-board high speed comparator
is provided to translate the analog sine wave into a low-jitter
TTL/CMOS-compatible output square wave. DDS technol-
ogy is an innovative circuit architecture that allows fast and
precise manipulation of its output word, under full digital con-
trol. DDS also enables very high resolution in the incremental
selection of output frequency. The AD9851 allows an output
frequency resolution of approximately 0.04 Hz at an 180 MSPS
clock rate with the option of directly using the reference clock or
by engaging the 6 REFCLK multiplier. The AD9851’s out-
put waveform is phase-continuous from one output frequency
change to another.
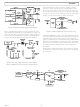
The basic functional block diagram and signal flow of the
AD9851 configured as a clock generator is shown in Figure 11.
The DDS circuitry is basically a digital frequency divider function
whose incremental resolution is determined by the frequency of
the system clock, and N (number of bits in the tuning word). The
phase accumulator is a variable-modulus counter that increments
the number stored in it each time it receives a clock pulse. When
the counter reaches full-scale it wraps around, making the phase
accumulator’s output phase-continuous. The frequency tuning
word sets the modulus of the counter, which effectively determines
the size of the increment ( Phase) that will be added to the value
in the phase accumulator on the next clock pulse. The larger
the added increment, the faster the accumulator wraps around,
which results in a higher output frequency.
The AD9851 uses an innovative and proprietary angle rotation
algorithm that mathematically converts the 14-bit truncated
AD9851
TUNING WORD SPECIFIES
OUTPUT FREQUENCY AS A
FRACTION OF REF CLOCK
FREQUENCY
N
(DC)
0Hz
ACCUMULATOR
Figure 11. Basic DDS Block Diagram and Signal Flow of AD9851
REFERENCE
20MHz
F
OUT
CLOCK
PHASE
Figure 12. Output Spectrum of a Sampled Sin(x)/x Signal
SYSTEM CLOCK FREQUENCY
1ST IMAGE
DDS CIRCUITRY
80MHz
SIN (X)/ ENVELOPE
= ()F/F
F
C
–F
CONV ALGORITHM
AMPLITUDE/SINE
O
100MHz
F
C
IN DIGITAL
C
DOMAIN
2ND IMAGE
F
120MHz
C
+F
O
–12–
3RD IMAGE
180MHz
CONVERTER
2F
value of the 32-bit phase accumulator to the 10-bit quantized
amplitude that is passed to the DAC. This unique algorithm uses a
much-reduced ROM look-up table and DSP to perform this func-
tion.This contributes to the small size and low power dissipation of
the AD9851.
The relationship between the output frequency, system clock, and
tuning word of the AD9851 is determined by the expression:
where
Phase = decimal value of 32-bit frequency tuning word.
System Clock = direct input reference clock (in MHz) or 6 the
input clock (in MHz) if the 6 REFCLK multiplier is engaged.
f
f
f
The digital sine wave output of the DDS core drives the internal
high speed 10-bit D/A converter that will construct the sine wave
in analog form. This DAC has been optimized for dynamic per-
formance and low glitch energy, which results in the low spurious
and jitter performance of the AD9851. The DAC can be operated
in either the single-ended (Figures 2 and 8) or differential output
configuration (Figures 9 and 10). DAC output current and R
values are determined using the following expressions:
Since the output of the AD9851 is a sampled signal, its output
spectrum follows the Nyquist sampling theorem. Specifically,
its output spectrum contains the fundamental plus aliased sig-
nals (images) that occur at integer multiples of the system clock
frequency ± the selected output frequency. A graphical repre-
sentation of the sampled spectrum, with aliased images, is shown
in Figure 12. Normal usable bandwidth is considered to extend
from dc to 1/2 the system clock.
OUT
OUT
OUT
OUT
C
–F
D/A
O
= frequency of the output signal in MHz.
= frequency of the output signal in MHz.
4TH IMAGE
2F
220MHz
C
+F
f
f
f
LP
OUT
OUT
OUT
OUT
O
= (
= (
= (
= ( Phase System Clock)/2
COMPARATOR
5TH IMAGE
3F
280MHz
I
I
I
R
C
OUT
OUT
OUT
OUT
SET
SET
SET
–F
O
= 39.93/
= 39.93/
= 39.93/
= 39.93/
CLOCK
OUT
R
I
I
I
OUT
OUT
SET
32
REV. D
SET