AD9851/FSPCB Analog Devices Inc, AD9851/FSPCB Datasheet - Page 17

AD9851/FSPCB
Manufacturer Part Number
AD9851/FSPCB
Description
BOARD EVAL FOR AD9851/FS
Manufacturer
Analog Devices Inc
Series
AgileRF™r
Datasheet
1.AD9851BRSZ.pdf
(24 pages)
Specifications of AD9851/FSPCB
Rohs Status
RoHS non-compliant
Main Purpose
Timing, Direct Digital Synthesis (DDS)
Utilized Ic / Part
AD9851/FS
Secondary Attributes
-
Embedded
-
Primary Attributes
-
PCB LAYOUT INFORMATION
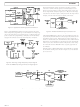
The AD9851/CGPCB and AD9851/FSPCB evaluation boards
(Figures 22 through 25 and TPCs 1 and 2) represent typical
implementations of the AD9851 and exemplify the use of high
frequency/high resolution design and layout practices. The print-
ed circuit board that contains the AD9851 should be a multilayer
board that allows dedicated power and ground planes. The power
and ground planes should (as much as possible) be free of etched
traces that cause discontinuities in the planes. It is recommended
that the top layer of the board also contain an interspatial ground
plane that makes ground available without vias for the surface-
mount devices. If separate analog and digital system ground
planes exist, they should be connected together at the AD9851
evaluation board for optimum performance.
Avoid running digital lines under the device as these will couple
unnecessary noise onto the die. The power supply lines to the
AD9851 should use as large a trace as possible to provide a low-
impedance path and reduce the effects of switching currents on
the power supply line. Fast switching signals like clocks should
use microstrip, controlled impedance techniques where pos-
sible. Avoid crossover of digital and analog signal paths. Traces
on opposite sides of the board should run at right angles to each
other. This will reduce crosstalk between the lines.
Good power supply decoupling is also an important consid-
eration. The analog (AVDD) and digital (DVDD) supplies
to the AD9851 are independent and separately pinned out to
minimize coupling between analog and digital sections of the
device. All analog and digital supply pins should be decoupled
to AGND and DGND, respectively, with high quality ceramic
chip capacitors. To achieve best performance from the decou-
pling capacitors, they should be placed as close as possible to
the device. In systems where a common supply is used to drive
both the AVDD and DVDD supplies of the AD9851, it is rec-
ommended that the system’s AVDD supply be used.
Analog Devices applications engineering support is available to
answer additional questions on grounding and PCB layout. Call
1-800-ANALOGD.
EVALUATION BOARDS
Two versions of the AD9851 evaluation board are available. The
evaluation boards facilitate easy implementation of the device for
bench-top analysis and serve as a reference for PCB layout.
The AD9851/FSPCB is intended for applications where the
device will primarily be used as a frequency synthesizer. This
version is optimized for connection of the AD9851 internal D/A
converter output to a 50 spectrum analyzer input. The internal
comparator of the AD9851 is made available for use via wire hole
access. The comparator inputs are externally pulled to opposing
voltages to prevent comparator chatter due to floating inputs. The
DDS DAC output is unfiltered and no reference oscillator is pro-
vided. This is done in recognition of the fact that many users may
find an oscillator to be a liability rather than an asset. See Figure 22
for an electrical schematic.
The AD9851/CGPCB is intended for applications using the
device as a CMOS output clock generator. It connects the
AD9851 DAC output to the internal comparator input via a
single-ended, 70 MHz low pass, 7th order, elliptic filter. To
minimize output jitter of the comparator, special attention has
REV. D
–17–
been given to the low-pass filter design. Primary considerations
were input and output impedances (200 ) and a very steep roll-
off characteristic to attenuate unwanted, nearby alias signals. The
high impedance of the filter allows the DAC to develop 1 V p-p
(with 10 mA) across the two 200 resistors at the input and
output of the filter. This voltage is entirely sufficient to opti-
mally drive the AD9851 comparator. This filter was designed
with the assumption that the AD9851 DDS is at full clock
speed (180 MHz). If this is not the case, filter specifications
may need to change to achieve proper attenuation of anticipated
alias signals. BNC connectors allow convenient observation
of the comparator CMOS output and input, as well as that of
the DAC. No reference oscillator is provided for reasons stated
above. This model allows easy evaluation of the AD9851 as
a frequency and phase-agile CMOS output clock source (see
Figure 24 for electrical schematic).
Jitter Reduction Note
The AD9851/CGPCB has a wideband DDS fundamental output,
dc to 70 MHz, and the on-chip comparator has even more band-
width. To optimize low jitter performance users should consider
bandpass filtering of the DAC output if only a narrow bandwidth
is required. This will reduce jitter caused by spurious, nonhar-
monic signals above and below the desired signal. Lowering
the applied V
by reducing V/T of the comparator outputs. For optimum
jitter performance, users should avoid the very busy digital envi-
ronment of the on-chip comparator and opt for an external, high
speed comparator.
Both versions of the AD9851 evaluation boards are designed
to interface to the parallel printer port of a PC. The operating
software (C++) runs under Microsoft
3.1 and Windows 95); Windows NT
vides a user-friendly and intuitive format for controlling the
functionality and observing the performance of the device.
The 3.5-in disk provided with the evaluation board contains
an executable file that displays the AD9851 function-selection
screen. The evaluation board may be operated with 3.0 V or
5 V supplies. Evaluation boards are configured at the factory
for an external clock input. If the optional on-board crystal
clock source is installed, resistor R2 (50 ) must be removed.
EVALUATION BOARD INSTRUCTIONS
Required Hardware/Software
Personal computer operating in Windows 3.1 or 95 environment
(does not support Windows NT)
Printer port, 3.5-in floppy drive, mouse, and Centronics com-
patible printer cable, 3 V to 5 V voltage supply
Crystal clock oscillator or high frequency signal generator (sine
wave output) with dc offset capability
AD9851 Evaluation Board Software disk and AD9851/FSPCB or
AD9851/CGPCB Evaluation Board
Setup
Copy the contents of the AD9851 disk onto the host PCs hard
drive. (There are two files, WIN9851.EXE version 1.x and
Bwcc.dll.) Connect the printer cable from the computer to the
evaluation board. Use a good quality cable as some cables do not
connect every wire that the printer port supports.
DD
helps in reducing comparator switching noise
®
®
not supported and pro-
Windows
AD9851
®
(Windows