ATmega1284RZAP Atmel Corporation, ATmega1284RZAP Datasheet - Page 244

ATmega1284RZAP
Manufacturer Part Number
ATmega1284RZAP
Description
Manufacturer
Atmel Corporation
Specifications of ATmega1284RZAP
Flash (kbytes)
128 Kbytes
Max. Operating Frequency
20 MHz
Max I/o Pins
32
Spi
3
Twi (i2c)
1
Uart
2
Adc Channels
8
Adc Resolution (bits)
10
Adc Speed (ksps)
15
Analog Comparators
1
Crypto Engine
No
Sram (kbytes)
16
Eeprom (bytes)
4096
Operating Voltage (vcc)
1.8 to 3.6
Timers
3
Frequency Band
2.4 GHz
Max Data Rate (mb/s)
0.25
Antenna Diversity
No
External Pa Control
No
Power Output (dbm)
3
Receiver Sensitivity (dbm)
-101
Receive Current Consumption (ma)
16.0
Transmit Current Consumption (ma)
17.0
Link Budget (dbm)
104
- Current page: 244 of 380
- Download datasheet (7Mb)
8059D–AVR–11/09
in ADCSRA. The prescaler keeps running for as long as the ADEN bit is set, and is continuously
reset when ADEN is low.
When initiating a single ended conversion by setting the ADSC bit in ADCSRA, the conversion
starts at the following rising edge of the ADC clock cycle. See
page 246
A normal conversion takes 13 ADC clock cycles. The first conversion after the ADC is switched
on (ADEN in ADCSRA is set) takes 25 ADC clock cycles in order to initialize the analog circuitry.
When the bandgap reference voltage is used as input to the ADC, it will take a certain time for
the voltage to stabilize. If not stabilized, the first value read after the first conversion may be
wrong.
The actual sample-and-hold takes place 1.5 ADC clock cycles after the start of a normal conver-
sion and 13.5 ADC clock cycles after the start of a first conversion. When a conversion is
complete, the result is written to the ADC Data Registers, and ADIF is set. In single conversion
mode, ADSC is cleared simultaneously. The software may then set ADSC again, and a new
conversion will be initiated on the first rising ADC clock edge.
When Auto Triggering is used, the prescaler is reset when the trigger event occurs. This assures
a fixed delay from the trigger event to the start of conversion. In this mode, the sample-and-hold
takes place 2 ADC clock cycles after the rising edge on the trigger source signal. Three addi-
tional CPU clock cycles are used for synchronization logic.
When using Differential mode, along with Auto Trigging from a source other than the ADC Con-
version Complete, each conversion will require 25 ADC clocks. This is because the ADC must
be disabled and re-enabled after every conversion.
In Free Running mode, a new conversion will be started immediately after the conversion com-
pletes, while ADSC remains high. For a summary of conversion times, see
246.
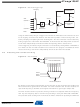
Figure 21-4. ADC Timing Diagram, First Conversion (Single Conversion Mode)
Cycle Number
ADC Clock
ADEN
ADSC
ADIF
ADCH
ADCL
for details on differential conversion timing.
1
2
MUX and REFS
Update
12
13
14
15
Sample & Hold
16
First Conversion
17
18
19
20
21
”Differential Gain Channels” on
22
Conversion
Complete
23
ATmega1284P
24
25
Table 21-1 on page
MSB of Result
LSB of Result
Next
Conversion
1
MUX and REFS
Update
2
3
244
Related parts for ATmega1284RZAP
Image
Part Number
Description
Manufacturer
Datasheet
Request
R

Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
ATMEL Corporation
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Microcontroller with 128K bytes In-system programmable flash, 8 MHz, power supply =2.7 - 5.5V
Manufacturer:
ATMEL Corporation
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
8-bit Microcontroller with 128K Bytes In-System Programmable Flash
Manufacturer:
ATMEL Corporation
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
IC AVR MCU 2.4GHZ XCEIVER 64QFN
Manufacturer:
Atmel
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Atmel
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
MCU ATMEGA644/AT86RF230 40-DIP
Manufacturer:
Atmel
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
BUNDLE ATMEGA644P/AT86RF230 QFN
Manufacturer:
Atmel
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
BUNDLE ATMEGA644P/AT86RF230 TQFP
Manufacturer:
Atmel
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
MCU ATMEGA1281/AT86RF230 64-TQFP
Manufacturer:
Atmel
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
MCU, 8BIT, AVR, 16K FLASH, 28PDIP
Manufacturer:
Atmel
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Microcontroller Modules MCU CARD BIGAVR6 100P W/ ATMEGA2560
Manufacturer:
mikroElektronika