SAF1562HL/N2-T NXP Semiconductors, SAF1562HL/N2-T Datasheet
SAF1562HL/N2-T
Specifications of SAF1562HL/N2-T
Related parts for SAF1562HL/N2-T
SAF1562HL/N2-T Summary of contents
Page 1
SAF1562 Hi-Speed Universal Serial Bus PCI Host Controller Rev. 2 — 24 November 2010 1. General description The SAF1562HL is a Peripheral Component Interconnect (PCI)-based, single-chip Universal Serial Bus (USB) Host Controller. It integrates two Original USB Open Host Controller ...
Page 2
... NXP Semiconductors Compliant with PCI Bus Power Management Interface Specification Rev. 1.1 for all hosts (EHCI and OHCI), and supports all power states: D0, D1, D2, D3 CLKRUN support for mobile applications, such as internal notebook design Configurable subsystem ID and subsystem vendor ID through external EEPROM ...
Page 3
PME# 99 PCICLK 22, 32 AD[31: 31, 33, 34 54, 56, 57, PCI CORE 59, 62, 63 C/BE#[3:0] 23, 35, 48, 60 REQ# 9 PCI MASTER ...
Page 4
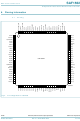
... NXP Semiconductors 6. Pinning information 6.1 Pinning GNDA 1 2 AUX1V8 V 3 I(VAUX3V3) INTA# 4 RST# 5 GNDD 6 7 PCICLK GNT# 8 REQ# 9 AD[31 CC(I/O) 12 AD[30] AD[29] 13 AD[28] 14 AD[27 I(VREG3V3) 17 GNDA 18 REG1V8 GNDD 19 AD[26] 20 AD[25 AD[24] 23 C/BE#[3] IDSEL CC(I/O) Fig 2. Pin configuration for LQFP100 SAF1562 Product data sheet ...
Page 5
... NXP Semiconductors 6.2 Pin description Table 2. Symbol GNDA AUX1V8 V I(VAUX3V3) INTA# RST# GNDD PCICLK GNT# REQ# AD[31] V CC(I/O) AD[30] AD[29] AD[28] AD[27] V I(VREG3V3) GNDA REG1V8 GNDD AD[26] AD[25] AD[24] SAF1562 Product data sheet Hi-Speed Universal Serial Bus PCI Host Controller Pin description ...
Page 6
... NXP Semiconductors Table 2. Symbol C/BE#[3] IDSEL V CC(I/O) AD[23] AD[22] AD[21] AD[20] AD[19] AD[18] GNDD AD[17] AD[16] C/BE#[2] FRAME# IRDY# TRDY# DEVSEL# V CC(I/O) STOP# CLKRUN# SAF1562 Product data sheet Hi-Speed Universal Serial Bus PCI Host Controller Pin description …continued [1] Pin Type Description ...
Page 7
... NXP Semiconductors Table 2. Symbol REG1V8 PERR# SERR# GNDA PAR C/BE#[1] GNDD AD[15] AD[14] AD[13] AD[12] AD[11] V CC(I/O) AD[10] AD[9] REG1V8 AD[8] C/BE#[0] GNDA AD[7] AD[6] SAF1562 Product data sheet Hi-Speed Universal Serial Bus PCI Host Controller Pin description …continued [1] Pin Type ...
Page 8
... NXP Semiconductors Table 2. Symbol GNDD AD[5] AD[4] AD[3] AD[2] AD[1] AD[0] V CC(I/O) GNDA AUX1V8 XTAL1 XTAL2 GNDD V CC(I/O)_AUX OC1_N PWE1_N GNDA RREF GNDA DM1 GNDA DP1 V DDA_AUX OC2_N PWE2_N GNDA SAF1562 Product data sheet Hi-Speed Universal Serial Bus PCI Host Controller Pin description … ...
Page 9
... NXP Semiconductors Table 2. Symbol DM2 GNDA DP2 V DDA_AUX GNDD GNDD SCL SDA V CC(I/O)_AUX PME# V CC(I/O)_AUX [1] Symbol names ending with # represent active LOW signals for PCI pins, for example: NAME#. Symbol names ending with underscore N represent active LOW signals for USB pins, for example: NAME_N. ...
Page 10
... NXP Semiconductors The EHCI is responsible for the port-routing switching mechanism. Two register bits are used for ownership switching. During power-on and system reset, the default ownership of all downstream ports is the OHCI. The Enhanced Host Controller Driver (EHCD) controls the ownership during normal functionality. ...
Page 11
... NXP Semiconductors 7.8 Power supply The SAF1562 supports both single power supply and dual power supply. Figure 4 Figure 5 SAF1562 Product data sheet Hi-Speed Universal Serial Bus PCI Host Controller shows the SAF1562HL voltage pins connection with dual power supply. shows the SAF1562HL voltage pins connection with single power supply. ...
Page 12
... NXP Semiconductors SAF1562HL V I(VAUX3V3 CC(I/O)_AUX 77 V CC(I/O)_AUX 98 V CC(I/O)_AUX 100 V DDA_AUX 86 V DDA_AUX 93 V I(VREG3V3 CC(I/ CC(I/ CC(I/ CC(I/ CC(I/O) 71 AUX1V8 2 AUX1V8 73 REG1V8 18 REG1V8 43 REG1V8 58 Remark: Connect the decoupling capacitor very close to the supply pins. (1) The PCI V during power on should ramp up linearly from 3.3 V with the rise time between 5 ms and 11 ms. ...
Page 13
... NXP Semiconductors SAF1562HL V I(VAUX3V3 CC(I/O)_AUX 77 V CC(I/O)_AUX 98 V CC(I/O)_AUX 100 V DDA_AUX 86 V DDA_AUX 93 V I(VREG3V3 CC(I/ CC(I/ CC(I/ CC(I/ CC(I/O) 71 AUX1V8 2 AUX1V8 73 REG1V8 18 REG1V8 43 REG1V8 58 Remark: Connect the decoupling capacitor very close to the supply pins. (1) The USB 3.3 V power supply during power on should ramp up linearly from 3.3 V with the rise time between 5 ms and 11 ms. (2) This electrolytic or tantalum capacitor must be a low ESR type (0.2 Ω ...
Page 14
... NXP Semiconductors 8. PCI 8.1 PCI interface The PCI interface has three functions. The first function (#0) and the second function (#1) are for the OHCI Host Controllers, and the third function (#2) is for the EHCI Host Controller. All functions support both master and target accesses, and share the same PCI interrupt signal INTA# ...
Page 15
... NXP Semiconductors Remark: In addition to the normal PCI header, from offset index 00h to 3Fh, implementation-specific registers are defined to support power management and function-specific features. Table 3. PCI configuration space registers of OHCI1, OHCI2 and EHCI Address Bits Bits PCI configuration header registers 00h Device ID[15:0] ...
Page 16
... R R/W R All information provided in this document is subject to legal disclaimers. Rev. 2 — 24 November 2010 SAF1562 Table 4. Description Vendor ID: This read-only register value is assigned to NXP Semiconductors by PCI-SIG as 1131h. Description Device ID: This register value is defined by NXP Semiconductors to identify the USB Host Controller IC product [ ...
Page 17
... NXP Semiconductors Table 7. Bit SAF1562 Product data sheet Hi-Speed Universal Serial Bus PCI Host Controller Command register (address 04h) bit description Symbol Description reserved - FBBE Fast Back-to-Back Enable: This bit controls whether a master can do fast back-to-back transactions to various devices. The initialization software must set this bit if all targets are fast back-to-back capable. 0 — ...
Page 18
... NXP Semiconductors Table 7. Bit 8.2.1.4 Status register The Status register read-only register used to record status information on PCI bus-related events. For bit allocation, see Table 8. Bit Symbol Reset Access Bit Symbol Reset Access Table 9. Bit SAF1562 Product data sheet Hi-Speed Universal Serial Bus PCI Host Controller ...
Page 19
... NXP Semiconductors Table 9. Bit 10 and 9 DEVSELT 8.2.1.5 Revision ID register This 1 B read-only register indicates a device-specific revision identifier. The value is chosen by the vendor. This field is a vendor-defined extension of the Device ID. The Revision ID register bit description is given in Table 10. Legend: * reset value Bit 8.2.1.6 Class Code register Class Code is a 24-bit read-only register used to identify the generic function of the device, and in some cases, a specific register-level programming interface ...
Page 20
... NXP Semiconductors The Class Code register is divided into three byte-size fields. The upper byte is a base class code that broadly classifies the type of function the device performs. The middle byte is a sub-class code that identifies more specifically the function of the device. The lower byte identifies a specific register-level programming interface, if any, so that device-independent software can interact with the device ...
Page 21
... NXP Semiconductors Table 13. Legend: * reset value Bit 8.2.1.8 Latency Timer register This register specifies—in units of PCI bus clocks—the value of the Latency Timer for the PCI bus master. Table 14. Legend: * reset value Bit Remark recommended to set the value of the Latency Timer register to 20h. ...
Page 22
... BAR 0[31:12] is assigned to the two OHCI ports, and BAR 0[31:8] is assigned to the EHCI port. Table 18. Description Subsystem Vendor ID: 1131h is the subsystem Vendor ID assigned to NXP Semiconductors. Description [1] Subsystem ID: For the SAF1562HL, NXP Semiconductors has defined OHCI functions as 1561h, and the EHCI function as 1562h. ...
Page 23
... NXP Semiconductors 8.2.1.14 Interrupt Line register This register used to communicate interrupt line routing information. This register must be implemented by any device or device function that uses an interrupt pin. The interrupt allocation is done by the BIOS. The POST software needs to write the routing information to this register because it initializes and configures the system. ...
Page 24
... NXP Semiconductors Table 24. Legend: * reset value Bit [ 2Ah for OHCI1 and OHCI2 10h for EHCI. 8.2.1.17 TRDY time-out register This is a read and write register at address 40h. The default and recommended value is 00h—TRDY time-out disabled. This value can, however, be modified implementation-specific register, and not a standard PCI configuration register. The TRDY timer is 13 bits— ...
Page 25
... NXP Semiconductors Table 26. Legend: * reset value Bit 8.2.2.2 FLADJ register This feature is used to adjust any offset from the clock source that generates the clock that drives the SOF counter. When a new value is written to these six bits, the length of the frame is adjusted. The bit allocation of the Frame Length Adjustment (FLADJ) register is given in Table 27 ...
Page 26
... NXP Semiconductors 8.2.2.3 PORTWAKECAP register Port Wake Capability (PORTWAKECAP register used to establish a policy about which ports are for wake events; see correspond to a physical port implemented on the current EHCI controller. Logic bit position indicates that a device connected below the port can be enabled as a wake-up device and the port may be enabled for disconnect or connect, or overcurrent events as wake-up events ...
Page 27
... NXP Semiconductors Table 32. Address: Value read from address 34h + 1h Legend: * reset value Bit NEXT_ITEM_ 8.2.3.3 PMC register The Power Management Capabilities (PMC) register register, and the bit allocation is given in function related to power management. Table 33. Address: Value read from address 34h + 2h Bit ...
Page 28
... NXP Semiconductors Table 34. Address: Value read from address 34h + 2h Bit 8.2.3.4 PMCSR register The Power Management Control/Status Register (PMCSR register used to manage the power management state of the PCI function, as well as to allow and monitor Power Management Events (PMEs). The bit allocation of the register is given in ...
Page 29
... NXP Semiconductors Table 35. Address: Value read from address 34h + 4h Bit Symbol Reset Access Bit Symbol Reset Access [1] Sticky bit, if the function supports PME# from D3 system boot the function does not support PME# from D3 [2] The reserved bits should always be written with the reset value. ...
Page 30
... NXP Semiconductors Table 36. Address: Value read from address 34h + 4h Bit and 0 8.2.3.5 PMCSR_BSE register The PMCSR PCI-to-PCI Bridge Support Extensions (PMCSR_BSE) register supports PCI bridge-specific functionality and is required for all PCI-to-PCI bridges. The bit allocation of this register is given in Table 37. Address: Value read from address 34h + 6h ...
Page 31
... NXP Semiconductors Table 38. Address: Value read from address 34h + 6h Bit Table 39. Originating device’s bridge PM state hot D3 cold 8.2.3.6 Data register The Data register is an optional register that provides a mechanism for the function to report state dependent operating data, such as power consumed or heat dissipated. ...
Page 32
... NXP Semiconductors C-bus interface A simple I product ID and some other configuration bits from an external EEPROM. 2 The I C-bus interface is for bidirectional communication between ICs using two serial bus wires: SDA (data) and SCL (clock). Both lines are driven by open-drain circuits and must be connected to the positive supply voltage through pull-up resistors when in use; ...
Page 33
... Therefore, pins A0, A1 and A2 of the EEPROM must be connected to ground (logic 0). 9.3 Information loading from EEPROM Figure 7 default values of Device ID, Vendor ID, subsystem VID and subsystem DID assigned to NXP Semiconductors by PCI-SIG will be loaded. For default values, see address Fig 7. 10. Power management 10.1 PCI bus power states The PCI bus can be characterized by one of the four power management states: B0, B1, B2 and B3 ...
Page 34
... NXP Semiconductors 10.2 USB bus states Reset state — When the USB bus is in the reset state, the USB system is stopped. Operational state — When the USB bus is in the active state, the USB system is operating normally. Suspend state — When the USB bus is in the suspend state, the USB system is stopped. Resume state — ...
Page 35
... NXP Semiconductors Table 41. USB Host Controller registers Address OHCI register 4Ch HcRhDescriptorB 50h HcRhStatus 54h HcRhPortStatus[1] 58h HcRhPortStatus[2] 5Ch reserved 60h reserved 64h reserved 68h reserved 6Ch reserved 70h reserved [1] Reset values that are highlighted—for example, 0—are the SAF1562HL implementation-specific reset values; and reset values that are not highlighted— ...
Page 36
... NXP Semiconductors Bit 15 Symbol Reset 0 Access R Bit 7 Symbol Reset 0 Access R Table 43. HcRevision - Host Controller Revision register bit description Address: Content of the base address register + 00h Bit Symbol Description reserved - REV[7:0] Revision: This read-only field contains the BCD representation of the version of the HCI specification that is implemented by this Host Controller ...
Page 37
... NXP Semiconductors Table 45. Address: Content of the base address register + 04h Bit and 6 5 SAF1562 Product data sheet Hi-Speed Universal Serial Bus PCI Host Controller HcControl - Host Controller Control register bit description Symbol Description reserved - RWE Remote Wakeup Enable: This bit is used by the HCD to enable or disable the remote wake-up feature on detecting upstream resume signaling ...
Page 38
... NXP Semiconductors Table 45. Address: Content of the base address register + 04h Bit and 0 11.1.3 HcCommandStatus register The HcCommandStatus register is used by the Host Controller to receive commands issued by the HCD. It also reflects the current status of the Host Controller. To the HCD, it appears as a ‘write to set’ register. The Host Controller must ensure that bits written as logic 1 become set in the register while bits written as logic 0 remain unchanged in the register ...
Page 39
... NXP Semiconductors Table 46. Address: Content of the base address register + 08h Bit Symbol Reset Access Bit Symbol Reset Access Bit Symbol Reset Access Bit Symbol Reset Access [1] The reserved bits should always be written with the reset value. Table 47. Address: Content of the base address register + 08h ...
Page 40
... NXP Semiconductors Table 47. Bit 11.1.4 HcInterruptStatus register This register that provides the status of the events that cause hardware interrupts. The bit allocation of the register is given in Controller sets the corresponding bit in this register. When a bit becomes set, a hardware interrupt is generated, if the interrupt is enabled in the HcInterruptEnable register (see Table 50) and the MIE (MasterInterruptEnable) bit is set ...
Page 41
... NXP Semiconductors Bit Symbol Reset Access Bit Symbol Reset Access Bit Symbol Reset Access [1] The reserved bits should always be written with the reset value. Table 49. Address: Content of the base address register + 0Ch Bit SAF1562 Product data sheet Hi-Speed Universal Serial Bus PCI Host Controller ...
Page 42
... NXP Semiconductors 11.1.5 HcInterruptEnable register Each enable bit in the HcInterruptEnable register corresponds to an associated interrupt bit in the HcInterruptStatus register. The HcInterruptEnable register is used to control which events generate a hardware interrupt. A hardware interrupt is requested on the host bus if the following conditions occur: • A bit is set in the HcInterruptStatus register • ...
Page 43
... NXP Semiconductors Table 51. Bit 11.1.6 HcInterruptDisable register Each disable bit in the HcInterruptDisable register corresponds to an associated interrupt bit in the HcInterruptStatus register. The HcInterruptDisable register is coupled with the HcInterruptEnable register. Therefore, writing logic bit in this register clears the corresponding bit in the HcInterruptEnable register, whereas writing logic bit in this register leaves the corresponding bit in the HcInterruptEnable register unchanged ...
Page 44
... NXP Semiconductors Bit Symbol Reset Access Bit Symbol Reset Access [1] The reserved bits should always be written with the reset value. Table 53. Address: Content of the base address register + 14h Bit SAF1562 Product data sheet Hi-Speed Universal Serial Bus PCI Host Controller 15 14 ...
Page 45
... NXP Semiconductors 11.1.7 HcHCCA register The HcHCCA register contains the physical address of the Host Controller Communication Area (HCCA). The bit allocation is given in determines the alignment restrictions by writing all ones to HcHCCA and reading the content of HcHCCA. The alignment is evaluated by examining the number of zeroes in the lower order bits. The minimum alignment is 256 B ...
Page 46
... NXP Semiconductors Table 56. Address: Content of the base address register + 1Ch Bit Symbol Reset Access Bit Symbol Reset Access Bit Symbol Reset Access Bit Symbol Reset Access Table 57. Address: Content of the base address register + 1Ch Bit 11.1.9 HcControlHeadED register The HcControlHeadED register contains the physical address of the first ED of the control list ...
Page 47
... NXP Semiconductors Bit Symbol Reset Access Bit Symbol Reset Access Table 59. Address: Content of the base address register + 20h Bit 11.1.10 HcControlCurrentED register The HcControlCurrentED register contains the physical address of the current ED of the control list. The bit allocation is given in Table 60. ...
Page 48
... NXP Semiconductors Table 61. Address: Content of the base address register + 24h Bit 11.1.11 HcBulkHeadED register This register (see Table 62. Address: Content of the base address register + 28h Bit Symbol Reset Access Bit Symbol Reset Access Bit Symbol Reset Access Bit Symbol Reset Access [1] The reserved bits should always be written with the reset value ...
Page 49
... NXP Semiconductors 11.1.12 HcBulkCurrentED register This register contains the physical address of the current endpoint of the bulk list. The endpoints are ordered according to their insertion to the list because the bulk list must be served in a round-robin fashion. The bit allocation is given in Table 64. ...
Page 50
... NXP Semiconductors Table 66. Address: Content of the base address register + 30h Bit Symbol Reset Access Bit Symbol Reset Access Bit Symbol Reset Access Bit Symbol Reset Access [1] The reserved bits should always be written with the reset value. Table 67. Address: Content of the base address register + 30h ...
Page 51
... NXP Semiconductors Bit Symbol Reset Access Bit Symbol Reset Access Bit Symbol Reset Access [1] The reserved bits should always be written with the reset value. Table 69. Address: Content of the base address register + 34h Bit and 14 reserved 11.1.15 HcFmRemaining register This register is a 14-bit down counter showing the bit time remaining in the current frame. ...
Page 52
... NXP Semiconductors Bit Symbol Reset Access Bit Symbol Reset Access [1] The reserved bits should always be written with the reset value. Table 71. Address: Content of the base address register + 38h Bit 11.1.16 HcFmNumber register This register is a 16-bit counter, and the bit allocation is given in timing reference among events happening in the Host Controller and the HCD ...
Page 53
... NXP Semiconductors Bit Symbol Reset Access [1] The reserved bits should always be written with the reset value. Table 73. Address: Content of the base address register + 3Ch Bit 11.1.17 HcPeriodicStart register This register has a 14-bit programmable value that determines when is the earliest time for the Host Controller to start processing the periodic list. For bit allocation, see Table 74 ...
Page 54
... NXP Semiconductors Table 75. Address: Content of the base address register + 40h Bit 11.1.18 HcLSThreshold register This register contains an 11-bit value used by the Host Controller to determine whether to commit to the transfer of a maximum low-speed packet before EOF. Neither the Host Controller nor the HCD can change this value. For bit allocation, see Table 76 ...
Page 55
... NXP Semiconductors 11.1.19 HcRhDescriptorA register This register is the first of two registers describing the characteristics of the Root Hub. Reset values are implementation-specific. Table 78 Table 78. Address: Content of the base address register + 48h Bit Symbol Reset Access Bit Symbol Reset Access Bit Symbol Reset ...
Page 56
... NXP Semiconductors Table 79. Address: Content of the base address register + 48h Bit 11.1.20 HcRhDescriptorB register The HcRhDescriptorB register is the second of two registers describing the characteristics of the Root Hub. The bit allocation is given in initialization to correspond to the system implementation. Reset values are implementation-specific. Table 80. ...
Page 57
... NXP Semiconductors Bit Symbol Reset Access Table 81. Address: Content of the base address register + 4Ch Bit PPCM 11.1.21 HcRhStatus register This register is divided into two parts. The lower word of a double word represents the Hub Status field, and the upper word represents the Hub Status Change field. Reserved bits should always be written as logic 0 ...
Page 58
... NXP Semiconductors Bit Symbol Reset Access [1] The reserved bits should always be written with the reset value. Table 83. Address: Content of the base address register + 50h Bit reserved SAF1562 Product data sheet Hi-Speed Universal Serial Bus PCI Host Controller reserved R/W R/W R/W ...
Page 59
... NXP Semiconductors 11.1.22 HcRhPortStatus[4:1] register The HcRhPortStatus[4:1] register is used to control and report port events on a per-port basis. Number Downstream Ports represents the number of HcRhPortStatus registers that are implemented in hardware. The lower word reflects the port status. The upper word reflects the status change bits. Some status bits are implemented with special write behavior transaction— ...
Page 60
... NXP Semiconductors Table 85. Address: Content of the base address register + 54h Bit reserved 9 SAF1562 Product data sheet Hi-Speed Universal Serial Bus PCI Host Controller HcRhPortStatus[4:1] - Host Controller Root Hub Port Status[4:1] register bit description …continued Symbol Description PSSC Port Suspend Status Change: This bit is set when the resume sequence is completed ...
Page 61
... NXP Semiconductors Table 85. Address: Content of the base address register + 54h Bit SAF1562 Product data sheet Hi-Speed Universal Serial Bus PCI Host Controller HcRhPortStatus[4:1] - Host Controller Root Hub Port Status[4:1] register bit description …continued Symbol Description PPS On read—Port Power Status: This bit reflects the port power status, regardless of the type of power switching implemented ...
Page 62
... NXP Semiconductors Table 85. Address: Content of the base address register + 54h Bit 11.2 EHCI controller capability registers Other than the OHCI Host Controller, there are some registers in EHCI that define the capability of EHCI. The address range of these registers is located before the operational registers ...
Page 63
... NXP Semiconductors Table 86. Address: Content of the base address register + 00h Bit Symbol Reset Access Bit Symbol Reset Access Bit Symbol Reset Access Bit Symbol Reset Access Table 87. Address: Content of the base address register + 00h Bit HCIVERSION 11.2.2 HCSPARAMS register The Host Controller Structural Parameters (HCSPARAMS) register is a set of fields that are structural parameters ...
Page 64
... NXP Semiconductors Bit Symbol Reset Access Bit Symbol Reset Access Table 89. Address: Content of the base address register + 04h Bit and SAF1562 Product data sheet Hi-Speed Universal Serial Bus PCI Host Controller N_CC[3: PRR reserved HCSPARAMS - Host Controller Structural Parameters register bit description ...
Page 65
... NXP Semiconductors 11.2.3 HCCPARAMS register The Host Controller Capability Parameters (HCCPARAMS) register register, and the bit allocation is given in Table 90. Address: Content of the base address register + 08h Bit Symbol Reset Access Bit Symbol Reset Access Bit Symbol Reset Access Bit Symbol Reset Access Table 91 ...
Page 66
... NXP Semiconductors 11.2.4 HCSP-PORTROUTE register The HCSP-PORTROUTE (Companion Port Route Description) register is an optional read-only field that is valid only if PRR (bit 7 in the HCSPARAMS register) is logic 1. Its address is the value read from content of the base address register + 0Ch. This field is a 15-element nibble array—each 4 bits is one array element. Each array location corresponds one-to-one with a physical port provided by the Host Controller ...
Page 67
... NXP Semiconductors Table 93. Address: Content of the base address register + 20h Bit SAF1562 Product data sheet Hi-Speed Universal Serial Bus PCI Host Controller USBCMD - USB Command register bit description Symbol Description reserved - ITC[7:0] Interrupt Threshold Control: Default = 08h. This field is used by the system software to select the maximum rate at which the Host Controller will issue interrupts ...
Page 68
... NXP Semiconductors Table 93. Address: Content of the base address register + 20h Bit and 11.3.2 USBSTS register The USB Status (USBSTS) register indicates pending interrupts and various states of the Host Controller. The status resulting from a transaction on the serial bus is not indicated in this register. Software clears the register bits by writing ones to them. The bit allocation is ...
Page 69
... NXP Semiconductors Table 94. Address: Content of the base address register + 24h Bit Symbol Reset Access Bit Symbol Reset Access Bit Symbol Reset Access Bit Symbol Reset Access [1] The reserved bits should always be written with the reset value. Table 95. Address: Content of the base address register + 24h ...
Page 70
... NXP Semiconductors Table 95. Address: Content of the base address register + 24h Bit 11.3.3 USBINTR register The USB Interrupt Enable (USBINTR) register enables and disables reporting of the corresponding interrupt to the software. When a bit is set and the corresponding interrupt is active, an interrupt is generated to the host. Interrupt sources that are disabled in this register still appear in USBSTS to allow the software to poll for events ...
Page 71
... NXP Semiconductors Table 96. Address: Content of the base address register + 28h Bit Symbol Reset Access Bit Symbol Reset Access Bit Symbol Reset Access Bit Symbol Reset Access [1] The reserved bits should always be written with the reset value. Table 97. Address: Content of the base address register + 28h ...
Page 72
... NXP Semiconductors 11.3.4 FRINDEX register The Frame Index (FRINDEX) register is used by the Host Controller to index into the periodic frame list. The register updates every 125 μs—once each micro frame. Bits are used to select a particular entry in the periodic frame list during periodic schedule execution ...
Page 73
... NXP Semiconductors Table 99. Address: Content of the base address register + 2Ch Bit 11.3.5 PERIODICLISTBASE register The Periodic Frame List Base Address (PERIODLISTBASE) register contains the beginning address of the periodic frame list in the system memory. If the Host Controller is in 64-bit mode—as indicated by logic 1 in 64AC (bit 0 of the HCCSPARAMS register)— ...
Page 74
... NXP Semiconductors Bit Symbol Reset Access [1] The reserved bits should always be written with the reset value. Table 101. PERIODICLISTBASE - Periodic Frame List Base Address register bit description Address: Content of the base address register + 34h Bit 11.3.6 ASYNCLISTADDR register This 32-bit register contains the address of the next asynchronous queue head to be executed. If the Host Controller is in 64-bit mode— ...
Page 75
... NXP Semiconductors Table 103. ASYNCLISTADDR - Current Asynchronous List Address register bit description Address: Content of the base address register + 38h Bit 11.3.7 CONFIGFLAG register The bit allocation of the Configure Flag (CONFIGFLAG) register is given in Table 104. CONFIGFLAG - Configure Flag register bit allocation Address: Value read from func2 of address 10h + 60h ...
Page 76
... NXP Semiconductors 11.3.8 PORTSC registers 1, 2 The Port Status and Control (PORTSC) register is in the auxiliary power well only reset by hardware when the auxiliary power is initially applied or in response to a Host Controller reset. The initial conditions of a port are: • No device connected • ...
Page 77
... NXP Semiconductors Table 107. PORTSC Port Status and Control 1, 2 register bit description Address: Content of the base address register + 64h + ( Bit and 14 reserved and 10 LS[1:0] 9 SAF1562 Product data sheet Hi-Speed Universal Serial Bus PCI Host Controller Symbol Description PTC[3:0] Port Test Control: Default = 0000b. When this field is logic 0, the port is not operating in test mode ...
Page 78
... NXP Semiconductors Table 107. PORTSC Port Status and Control 1, 2 register bit description Address: Content of the base address register + 64h + ( Bit 8 7 SAF1562 Product data sheet Hi-Speed Universal Serial Bus PCI Host Controller Symbol Description PR Port Reset: Logic 1 means the port is in reset. Logic 0 means the port is not in reset ...
Page 79
... NXP Semiconductors Table 107. PORTSC Port Status and Control 1, 2 register bit description Address: Content of the base address register + 64h + ( Bit SAF1562 Product data sheet Hi-Speed Universal Serial Bus PCI Host Controller Symbol Description FPR Force Port Resume: Logic 1 means resume detected or driven on the port ...
Page 80
... NXP Semiconductors [1] These fields read logic 0, if the PP bit is logic 0. 12. Power consumption Table 108 Table 108. Power consumption Power pins group Total power V CC(I/O)_AUX + V DDA_AUX + V I(VREG3V3) Auxiliary power V CC(I/O)_AUX + V DDA_AUX V CC(I/O) [1] When one or two full-speed or low-speed power devices are connected, the power consumption is comparable to the power consumption when no high-speed devices are connected ...
Page 81
... NXP Semiconductors 13. Limiting values Table 110. Limiting values In accordance with the Absolute Maximum Rating System (IEC 60134). Symbol Parameter V supply voltage to I/O pins CC(I/O) V supply voltage to internal regulator I(VREG3V3) V auxiliary supply voltage to I/O pins CC(I/O)_AUX V auxiliary input voltage to internal regulator I(VAUX3V3) ...
Page 82
... NXP Semiconductors Table 114. Static characteristics: digital pins − 3 3 CC(I/O) amb Symbol Parameter V HIGH-level input voltage IH V LOW-level input voltage IL I input leakage current LI V LOW-level output voltage OL V HIGH-level output voltage OH Table 115. Static characteristics: PCI interface block − ...
Page 83
... NXP Semiconductors Table 116. Static characteristics: USB interface block (pins DM1 to DM2 and DP1 to DP2 3 3 DDA_AUX amb Symbol Parameter V differential common mode range CM Output levels for full-speed and low-speed V HIGH-level output voltage OH V LOW-level output voltage OL V SE1 OSE1 V output signal crossover point ...
Page 84
... NXP Semiconductors Table 120. Dynamic characteristics: high-speed source electrical characteristics DDA_AUX amb Symbol Parameter Driver characteristics t high-speed differential rise time HSR t high-speed differential fall time HSF Z drive output resistance; also serves as a HSDRV high-speed termination Clock timing t data rate HSDRAT ...
Page 85
... NXP Semiconductors 16.1 Timing Table 123. PCI clock and IO timing Abstract of the USB specification rev. 2.0. Symbol Parameter PCI clock timing; see Figure 8 T PCICLK cycle time cyc(PCICLK) t PCICLK HIGH time HIGH(PCICLK) t PCICLK LOW time LOW(PCICLK) SR PCICLK slew rate PCICLK SR RST# slew rate RST# PCI input timing ...
Page 86
... NXP Semiconductors CLK INPUT DELAY Fig 9. PCI input timing CLK OUTPUT DELAY OUTPUT Fig 10. PCI output timing t USBbit +3.3 V differential data lines the bit duration (USB data). USBbit [ the source jitter for differential transition to SEO transition. DEOP (1) Full-speed and low-speed timing symbols have a subscript prefix ‘F’ and ‘L’, respectively. ...
Page 87
... NXP Semiconductors 17. Package outline LQFP100: plastic low profile quad flat package; 100 leads; body 1 pin 1 index 100 DIMENSIONS (mm are the original dimensions) A UNIT max. 0.15 1.45 mm 1.6 0.25 0.05 1.35 Note 1. Plastic or metal protrusions of 0.25 mm maximum per side are not included. ...
Page 88
... NXP Semiconductors 18. Soldering of SMD packages This text provides a very brief insight into a complex technology. A more in-depth account of soldering ICs can be found in Application Note AN10365 “Surface mount reflow soldering description”. 18.1 Introduction to soldering Soldering is one of the most common methods through which packages are attached to Printed Circuit Boards (PCBs), to form electrical circuits ...
Page 89
... NXP Semiconductors 18.4 Reflow soldering Key characteristics in reflow soldering are: • Lead-free versus SnPb soldering; note that a lead-free reflow process usually leads to higher minimum peak temperatures (see reducing the process window • Solder paste printing issues including smearing, release, and adjusting the process window for a mix of large and small components on one board • ...
Page 90
... NXP Semiconductors Fig 13. Temperature profiles for large and small components For further information on temperature profiles, refer to Application Note AN10365 “Surface mount reflow soldering description”. 19. Appendix 19.1 Erratum 1 A higher than expected suspend current is measured in D3 19.1.1 Problem description The D3 The higher suspend current is due to internal leakage supplied ...
Page 91
... NXP Semiconductors 19.2.1 Problem description After the USB device resume signaling is completed, incorrect resume signaling is observed on the SAF1562 port which triggers the remote wake-up result, the hub will be disconnected. This requires new enumeration of the hub and all USB peripherals connected to its downstream ports. ...
Page 92
... NXP Semiconductors 19.4.1 Problem description To enhance data throughput performance for large data packets, the SAF1562 implements a watermark level. This is the level at which data transfer on the USB is triggered when the CPU fills up data on the PCI bus. The watermark level is 191 bytes, 255 bytes, 383 bytes, 511 bytes, 639 bytes, 767 bytes and so on. ...
Page 93
... NXP Semiconductors [Page 3] 4 096 bytes [Page 4] 4 096 bytes If a short packet data is located on this boundary, a single transaction can occur on the PCI bus, causing the CRC error. The software must be modified so that a short packet does not exist at a page boundary. ...
Page 94
... NXP Semiconductors 19.6.1 Problem description The PME# voltage level will drop to an intermediate level when the SAF1562 PCI board is inserted into the PCI slot because of internal leakage from PME the normal voltage level of the PME# signal because V pulled resistor on the system board. ...
Page 95
... NXP Semiconductors 19.8.2 Implication The implication is moderate. Device drivers will disable normal OHCI or EHCI functionality when an interrupt is generated because of the setting of the UE or HSE bit. The MIE bit will be disabled. 19.8.3 Workaround The retry time-out is an SAF1562-specific feature and not a standard PCI feature. ...
Page 96
... NXP Semiconductors 19.11 Erratum 11 Interrupt devices cannot work under the SAF1562 in a Microsoft Windows CE system with default OHCI drivers. This is applicable for Windows CE 4.2 as well as Windows CE 5.0. 19.11.1 Problem description When an interrupt device, such as keyboard or mouse, is connected to the SAF1562 in a Windows CE system using the native Microsoft driver, this device does not function. ...
Page 97
... NXP Semiconductors Table 126. Field definitions for a general TD Symbol CBP NextTD BE 19.12.2 Implication The implication depends on the application and the device because the problem appears only in certain applications with a series of NAKs from the device with a certain signal quality (e.g. a mass storage device connected to a full-speed hub with cable in both downstream and upstream port) ...
Page 98
... NXP Semiconductors The root cause issue is described as follows. The SAF1562 has internal mechanism which will clear any buffer that is locked for 2 successive SOFs. If the SAF1562 cannot finish writing the buffer to the system memory during this time, the buffer will be cleared. This condition will lock the SAF1562 state machine out of the idle state result, the EHCI stops accessing the PCI bus ...
Page 99
... NXP Semiconductors 19.16 Erratum 16 The OHCI returns the same TD to the HCD in 2 consecutive USB frames result, memory pointer faulty could occur. 19.16.1 Problem description The TD and ED are updated consecutively upon completing each USB transfer. Meanwhile, the HccaFrameNumber and HccaDoneHead are updated in the next SOF if the ongoing transfers are completed ...
Page 100
... NXP Semiconductors boolean TDInEDTransferList (TDStruct TD Remark: Windows XP has implemented the improvement in the OHCI driver to handle this limitation. 19.17 Erratum 17 A data toggle error occurs when an IN transfer sent by a full-speed device is completed with either a short packet or a zero-length packet result, the OHCI driver could not get the complete data ...
Page 101
... NXP Semiconductors 19.17.3 Workaround Whenever receiving IN transfer completed with a halted bit in the ED and the bit CC is set to DATAUNDERRUN, the HCD must toggle the bit toggleCarry and clear the halted bit in the ED. 19.18 Erratum 18 There is a register access issue when IRDY# (pin 37) is asserted later than the third clock cycle ...
Page 102
... NXP Semiconductors Fig 15. IRDY# asserted at the fourth clock In Figure to which it is written. 19.18.2 Implication This limitation is very rarely seen because most of the processor platforms do not exhibit such behavior. 19.18.3 Workaround In the system implementation, ensure that IRDY# is asserted within three clock cycles. ...
Page 103
... NXP Semiconductors If noise or spike occurs on the key signals during PCI reset assertion, it could accidentally turn on the enable signal of test modes result, the EHCI does not get a proper reset. This improper reset will cause the high-speed intermittent issue (for example, high-speed device cannot get enumerated due to data corruption). ...
Page 104
... NXP Semiconductors cold start-up 3.3 V USB_3. 3.3 V PCI_reset 0 V signal on pins OC1_N, PWE1_N and PWE2_N 0 V Fig 16. SAF1562 signals during cold start-up and PCI reset assertion 19.19.3.1 Workaround for repeated PCI reset assertion Ensure that the signal on pins OC1_N, PWE1_N and PWE2_N is not HIGH or toggling ...
Page 105
... NXP Semiconductors USB_3. 100 μF 0.1 μF 10 kΩ GPIO-1 Fig 17. Workaround when all ports are needed in an implementation 19.19.3.2 Workaround for PCI reset assertion during cold start-up Ensure that the PCI reset is HIGH during cold start-up (refer to diagram). 19.19.3.3 Workaround for the unexpected power supply behavior during cold start-up Ensure that the power supply during cold start-up ramps up linearly from ...
Page 106
... NXP Semiconductors The problem occurs whenever the new EHCI base address is a subregion of the previous OHCI base address. When this happens, the EHCI will return an incorrect value while it is being read during the EHCI enable process. The EHCI driver typically uses the value of Capability Length (CAPLENGTH) register to determine the offset where EHCI registers begin ...
Page 107
... NXP Semiconductors 19.21.3 Workaround Ensure that whenever allocated, its entire data structure is initialized to zero. This will set the TailP of the used ED to the HeadP of the unused ED. 19.22 Erratum 22 Cumulative USB errors cause the TD to retire prematurely. 19.22.1 Problem description The SAF1562 implements the ErrorCount of OHCI cumulative error counter rather than as a consecutive error counter ...
Page 108
... NXP Semiconductors 19.24.1 Problem description In Figure work properly. Normally in Windows environment, interoperability testing is done with a gold tree setup observed that the SAF1562 cannot properly perform an isochronous transfer through a web camera (e.g. Logitech QuickCam Ultravision) and simultaneously an interrupt transfer through a mouse (e.g. Microsoft basic optical mouse or Dell mouse) connected to the high-speed hub ...
Page 109
... NXP Semiconductors 19.25.1 Problem description In the SAF1562, if the OHCI bit BM is set to logic 0 and the EHCI bit BM is set to logic 1, the OHCI bus master still occurs. The same condition also applies to the SAF1562 EHCI. When the EHCI bit BM is set to logic 0 and the OHCI bit BM is set to logic 1, the EHCI bus mastering still occurs ...
Page 110
... NXP Semiconductors 19.28 Erratum 28 When using certain EEPROM ICs for programming, data downloading could fail if the data line (SDA) is stuck at LOW after PCI reset. 19.28.1 Problem description If system reset occurs during the scanning process of the I get stuck at LOW. When this happens, the SAF1562 cannot download data from the ...
Page 111
... NXP Semiconductors Table 127. Abbreviations Acronym CRC DID DMA ED EEPROM EHCI EMI ESD ESR GPIO HC HCCA HCD IN ISR LAN LSB MSB NAK OHCI OS OUT PCI PCI-SIG PID PLL PMC PME PMCSR POR QH RTOS SDA SOF STB TD TPL USB VID WLAN SAF1562 ...
Page 112
... NXP Semiconductors 21. References [1] Universal Serial Bus Specification Rev. 2.0 [2] Enhanced Host Controller Interface Specification for Universal Serial Bus Rev. 1.0 [3] Open Host Controller Interface Specification for USB Rev. 1.0a [4] PCI Local Bus Specification Rev. 2.2 [5] PCI Bus Power Management Interface Specification Rev. 1.1 ...
Page 113
... In no event shall NXP Semiconductors be liable for any indirect, incidental, punitive, special or consequential damages (including - without limitation - lost profits, lost savings, business interruption, costs related to the removal or ...
Page 114
... NXP Semiconductors Export control — This document as well as the item(s) described herein may be subject to export control regulations. Export might require a prior authorization from national authorities. 24. Contact information For more information, please visit: For sales office addresses, please send an email to: SAF1562 Product data sheet Hi-Speed Universal Serial Bus PCI Host Controller 23 ...
Page 115
... NXP Semiconductors 25. Tables Table 1. Ordering information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2 Table 2. Pin description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .5 Table 3. PCI configuration space registers of OHCI1, OHCI2 and EHCI . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .15 Table 4. VID - Vendor ID register (address 00h) bit description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .16 Table 5. DID - Device ID register (address 02h) bit description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .16 Table 6. Command register (address 04h) bit allocation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .16 Table 7 ...
Page 116
... NXP Semiconductors Disable register bit description . . . . . . . . . . . . .44 Table 54. HcHCCA - Host Controller Communication Area register bit allocation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .45 Table 55. HcHCCA - Host Controller Communication Area register bit description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .45 Table 56. HcPeriodCurrentED - Host Controller Period Current Endpoint Descriptor register bit allocation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .46 Table 57. HcPeriodCurrentED - Host Controller Period Current Endpoint Descriptor register bit description ...
Page 117
... NXP Semiconductors Table 103. ASYNCLISTADDR - Current Asynchronous List Address register bit description . . . . . . . . . . . .75 Table 104. CONFIGFLAG - Configure Flag register bit allocation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .75 Table 105. CONFIGFLAG - Configure Flag register bit description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .75 Table 106. PORTSC Port Status and Control 1, 2 register bit allocation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .76 Table 107. PORTSC Port Status and Control 1, 2 register bit description ...
Page 118
... NXP Semiconductors 26. Figures Fig 1. Block diagram of SAF1562HL . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .3 Fig 2. Pin configuration for LQFP100 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .4 Fig 3. Power-on reset . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .10 Fig 4. SAF1562HL voltage pins connection with dual power supply . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .12 Fig 5. SAF1562HL voltage pins connection with single power supply . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .13 Fig 6. EEPROM connection diagram . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .32 Fig 7. Information loading from EEPROM . . . . . . . . . . .33 Fig 8 ...
Page 119
... NXP Semiconductors 27. Contents 1 General description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1 2 Features and benefits . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1 3 Applications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2 4 Ordering information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2 5 Block diagram . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3 6 Pinning information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4 6.1 Pinning . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4 6.2 Pin description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5 7 Functional description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9 7.1 OHCI Host Controller . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9 7.2 EHCI Host Controller . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9 7.3 Dynamic port-routing logic . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9 7.4 Hi-Speed USB analog transceivers ...
Page 120
... NXP Semiconductors 11.3.2 USBSTS register . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 68 11.3.3 USBINTR register . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 70 11.3.4 FRINDEX register . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 72 11.3.5 PERIODICLISTBASE register . . . . . . . . . . . . 73 11.3.6 ASYNCLISTADDR register 11.3.7 CONFIGFLAG register . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 75 11.3.8 PORTSC registers Power consumption Limiting values Thermal characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 81 15 Static characteristics Dynamic characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 83 16.1 Timing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 85 17 Package outline . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 87 18 Soldering of SMD packages . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 88 18 ...
Page 121
... NXP Semiconductors 19.19.3.1 Workaround for repeated PCI reset assertion . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 104 19.19.3.2 Workaround for PCI reset assertion during cold start- 105 19.19.3.3 Workaround for the unexpected power supply behavior during cold start-up 105 19.20 Erratum 105 19.20.1 Problem description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 105 19.20.2 Implication . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 106 19 ...