AT89C51RD2 Atmel Corporation, AT89C51RD2 Datasheet - Page 14

AT89C51RD2
Manufacturer Part Number
AT89C51RD2
Description
Manufacturer
Atmel Corporation
Specifications of AT89C51RD2
Flash (kbytes)
64 Kbytes
Max. Operating Frequency
60 MHz
Cpu
8051-12C
Max I/o Pins
32
Spi
1
Uart
1
Sram (kbytes)
2
Self Program Memory
API
Operating Voltage (vcc)
2.7 to 5.5
Timers
4
Isp
UART
Watchdog
Yes
Available stocks
Company
Part Number
Manufacturer
Quantity
Price
Company:
Part Number:
AT89C51RD2-3CSIM
Manufacturer:
ATMEL
Quantity:
1 080
Company:
Part Number:
AT89C51RD2-CM
Manufacturer:
IR
Quantity:
11
Part Number:
AT89C51RD2-CM
Manufacturer:
ATMEL/爱特梅尔
Quantity:
20 000
Company:
Part Number:
AT89C51RD2-IM
Manufacturer:
AT
Quantity:
5
Part Number:
AT89C51RD2-IM
Manufacturer:
ATMEL/爱特梅尔
Quantity:
20 000
Company:
Part Number:
AT89C51RD2-RDTUM
Manufacturer:
MICRON
Quantity:
1 000
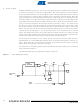
5. Port Types
Figure 5-1.
14
AT89C51RD2/ED2
Port Latch
Data
Quasi-Bidirectional Output
AT89C51RD2/ED2 I/O ports (P1, P2, P3, P4, P5) implement the quasi-bidirectional output that
is common on the 80C51 and most of its derivatives. This output type can be used as both an
input and output without the need to reconfigure the port. This is possible because when the port
outputs a logic high, it is weakly driven, allowing an external device to pull the pin low. When the
pin is pulled low, it is driven strongly and able to sink a fairly large current. These features are
somewhat similar to an open drain output except that there are three pull-up transistors in the
quasi-bidirectional output that serve different purposes. One of these pull-ups, called the "weak"
pull-up, is turned on whenever the port latch for the pin contains a logic 1. The weak pull-up
sources a very small current that will pull the pin high if it is left floating. A second pull-up, called
the "medium" pull-up, is turned on when the port latch for the pin contains a logic 1 and the pin
itself is also at a logic 1 level. This pull-up provides the primary source current for a quasi-bidi-
rectional pin that is outputting a 1. If a pin that has a logic 1 on it is pulled low by an external
device, the medium pull-up turns off, and only the weak pull-up remains on. In order to pull the
pin low under these conditions, the external device has to sink enough current to overpower the
medium pull-up and take the voltage on the port pin below its input threshold.
The third pull-up is referred to as the "strong" pull-up. This pull-up is used to speed up low-to-
high transitions on a quasi-bidirectional port pin when the port latch changes from a logic 0 to a
logic 1. When this occurs, the strong pull-up turns on for a brief time, two CPU clocks, in order to
pull the port pin high quickly. Then it turns off again.
The DPU bit (bit 7 in AUXR register) allows to disable the permanent weak pull up of all ports
when latch data is logical 0.
The quasi-bidirectional port configuration is shown in Figure 5-1.
2 CPU
Clock Delay
Input
Data
P
N
Strong
AUXR.7
DPU
P
Weak
P
Medium
Pin
4235K–8051–05/08