ADP5589 Analog Devices, ADP5589 Datasheet - Page 19

ADP5589
Manufacturer Part Number
ADP5589
Description
Keypad Decoder and I/O Expansion
Manufacturer
Analog Devices
Datasheet
1.ADP5589.pdf
(48 pages)
Specifications of ADP5589
Vin Range
1.8 to 3.0V
Number Of I/os
19
Application
Mobil I-0 Exp-Keybd Cont,Mobil I-O Expander
Qwerty Keypad
Yes
Other Functions
I2C I/O & register
Function Flag
Mobil I-O
Package
24-Lead LFCSP,25-Ball WLCSP
Available stocks
Company
Part Number
Manufacturer
Quantity
Price
Part Number:
ADP5589ACPZ-00-R7
Manufacturer:
ADI/亚德诺
Quantity:
20 000
REGISTER INTERFACE
Register access of the
serial interface. The interface can support clock frequencies of
up to 1 MHz. If the user is accessing the FIFO or key event
counter (KEC), FIFO/KEC updates are paused. If the clock
frequency is very low, events may not be recorded in a timely
manner. FIFO or KEC updates can happen up to 23 μs after an
interrupt is asserted because of the number of I
to perform an I
an issue to the user.
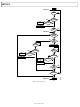
Figure 27 shows a typical write sequence for programming an
internal register. The cycle begins with a start condition, followed
by the hard coded 7-bit device address, which for the ADP5589
is 0x34, followed by the R/ W bit set to 0 for a write cycle. The
ADP5589
low. The address of the register to which data is to be written is
sent next. The
by pulling the data line low. The data byte to be written is sent
next. The
data line low. A stop condition completes the sequence.
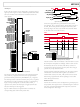
Figure 28 shows a typical multibyte write sequence for program-
ming internal registers. The cycle begins with a start condition
followed by the 7-bit device address (0x34), followed by the
START
START
acknowledges the address byte by pulling the data line
ADP5589
7-BIT DEVICE ADDRESS
7-BIT DEVICE ADDRESS
ADP5589
2
C read or write. This delay should not present
acknowledges the data byte by pulling the
ADP5589
START
acknowledges the register pointer byte
0 = WRITE
7-BIT DEVICE ADDRESS
ADP5589 ACK
is acquired via its I
0
0 = WRITE
ADP5589 ACK
0
0
8-BIT REGISTER POINTER
0
8-BIT REGISTER POINTER
2
C cycles required
0 = WRITE
ADP5589 ACK
2
C-compatible
0
Figure 27. I
Figure 29. I
0
Figure 28. I
ADP5589 ACK
8-BIT REGISTER POINTER
ADP5589 ACK
Rev. A | Page 19 of 48
0
2
2
REPEAT START
C Single-Byte Write Sequence
2
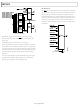
C Single-Byte Read Sequence
C Multibyte Write Sequence
WRITE BYTE 1
0
7-BIT DEVICE ADDRESS
ADP5589 ACK
R/ W bit set to 0 for a write cycle. The
the address byte by pulling the data line low. The address of the
register to which data is to be written is sent next. The
acknowledges the register pointer byte by pulling the data line
low. The data byte to be written is sent next. The
acknowledges the data byte by pulling the data line low. The
pointer address is then incremented to write the next data byte,
until it finishes writing the n data byte. The
data line low after every byte, and a stop condition completes
the sequence.
Figure 29 shows a typical byte read sequence for reading internal
registers. The cycle begins with a start condition followed by the
7-bit device address (0x34), followed by the R/ W bit set to 0 for
a write cycle. The
pulling the data line low. The address of the register from which
data is to be read is sent next. The
register pointer byte by pulling the data line low. A start condi-
tion is repeated, followed by the 7-bit device address (0x34),
followed by the R/
acknowledges the address byte by pulling the data line low. The
8-bit data is then read. The host pulls the data line high (no
acknowledge), and a stop condition completes the sequence.
ADP5589 ACK
0
0
WRITE BYTE 2
8-BIT WRITE DATA
1 = READ
ADP5589 ACK
ADP5589 ACK
1
ADP5589
W bit set to 1 for a read cycle. The
0
0
ADP5589 ACK
8-BIT READ DATA
acknowledges the address byte by
ADP5589 ACK
0
0
STOP
ADP5589
WRITE BYTE n
ADP5589
ADP5589
acknowledges the
NO ACK
ADP5589 ACK
1
acknowledges
STOP
ADP5589
ADP5589
0
ADP5589
STOP
ADP5589
pulls the