FAN6749 Fairchild Semiconductor, FAN6749 Datasheet - Page 11
FAN6749
Manufacturer Part Number
FAN6749
Description
The FAN6749 highly integrated PWM controller enhances the performance of flyback converters
Manufacturer
Fairchild Semiconductor
Datasheet
1.FAN6749.pdf
(16 pages)
Available stocks
Company
Part Number
Manufacturer
Quantity
Price
Part Number:
FAN6749MLM
Manufacturer:
FAIRCHILD/仙童
Quantity:
20 000
© 2012 Fairchild Semiconductor Corporation
FAN6749 • Rev. 1.0.0
Functional Description
Current Mode Control
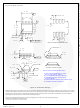
FAN6749 employs peak current mode control, as shown
in Figure 25. An opto-coupler (such as the H11A817A)
and a shunt regulator (such as the KA431) are typically
used to implement the feedback network. Comparing the
feedback voltage with the voltage across the R
resistor makes it possible to control the switching duty
cycle. A synchronized positive slope is added to the
sensed current signal to guarantee stable current mode
control over wide range of input voltage. The built-in
slope compensation stabilizes the current loop and
prevents sub-harmonic oscillation.
Green-Mode Operation
FAN6749 modulates the PWM frequency as a function
of the FB voltage to improve the medium- and light-load
efficiency, as shown in Figure 26. Since the output
power is proportional to the FB voltage in current mode
control, the switching frequency decreases as load
decreases. In heavy-load conditions, the switching
frequency is fixed at 65kHz. Once V
V
decreasing from 65kHz to 24kHz to reduce switching
losses. As V
frequency is decreased to 24kHz, the switching frequency
is fixed to avoid acoustic noise.
When V
further, FAN6749 enters Burst Mode, where PWM
switching is disabled. Then the output voltage starts to
drop, causing the feedback voltage to rise. Once V
rises above V
Mode alternately enables and disables switching,
thereby reducing switching loss for lower power
consumption, as shown in Figure 27
FB-N
Figure 25. Current Mode Control Circuit Diagram
(2.7V), the PWM frequency starts linearly
FB
falls below V
FB
FB-ZDCR
drops to V
(2.1V), switching resumes. Burst
FB-ZDC
FB-G
(2.0V) as load decreases
(2.25V), where switching
FB
decreases below
sense
FB
11
Operating Current
In normal condition, operating current is around 1.8mA
(I
reduced to 1mA (I
FAN6749. The low operating current improves light-load
efficiency and reduces the requirement of V
capacitance.
High-Voltage Startup and Line Sensing
The HV pin is typically connected to the AC line input
through an external diode and a resistor (R
in Figure 28. When AC line voltage is applied, the V
hold-up capacitor is charged by the line voltage through
the diodes and resistor. After V
turn-on threshold voltage (V
charging V
supplied by the auxiliary winding of the transformer.
Once FAN6749 starts up, it continues operation until
V
given AC line input voltage is given as:
t
STARTUP
DD-OP1
DD
f
OSC-G
f
OSC
drops below 6.5V (V
Figure 27. Burst Switching in Green Mode
f
S
); when V
V
FB-ZDC
Figure 26. V
DD
R
HV
V
capacitor is switched off and V
FB-ZDCR
C
FB
DD-OP2
DD
<1.4V, operating current is further
V
FB
ln
FB-G
) by disabling several blocks of
UVLO
V
vs. PWM Frequency
AC IN
). The IC startup time with a
V
DD-ON
AC IN
DD
V
), the startup circuit
2
FB-N
voltage reaches the
V
2
DD ON
HV
www.fairchildsemi.com
), as shown
DD
hold-up
V
DD
FB
(1)
DD
is