isl6307b Intersil Corporation, isl6307b Datasheet - Page 13

isl6307b
Manufacturer Part Number
isl6307b
Description
6-phase Vr11 Pwm Controller With 8-bit Vid Code Capable Of Precision Rds On Or Dcr Differential Current Sensing For Applications In Which Supply Voltage Is Higher Than 5v
Manufacturer
Intersil Corporation
Datasheet
1.ISL6307B.pdf
(33 pages)
Available stocks
Company
Part Number
Manufacturer
Quantity
Price
Part Number:
isl6307bCRZ
Manufacturer:
INTERSIL
Quantity:
20 000
Part Number:
isl6307bCRZ-T
Manufacturer:
INTERSIL
Quantity:
20 000
PWM Operation
The timing of each converter leg is set by the number of
active channels. The default channel setting for the
ISL6307B is four. One switching cycle is defined as the time
between PWM1 pulse termination signals. The pulse
termination signal is an internally generated clock signal
which triggers the falling edge of PWM1. The cycle time of
the pulse termination signal is the inverse of the switching
frequency set by the resistor between the FS pin and
ground. Each cycle begins when the clock signal commands
the channel-1 PWM output to go low. The PWM1 transition
signals the channel-1 MOSFET driver to turn off the
channel-1 upper MOSFET and turn on the channel-1
synchronous MOSFET. In the default channel configuration,
the PWM2 pulse terminates 1/4 of a cycle after PWM1. The
PWM3 output follows another 1/4 of a cycle after PWM2.
PWM4 terminates another 1/4 of a cycle after PWM3.
If PWM3 is connected to VCC, two channel operation is
selected and the PWM2 pulse terminates 1/2 of a cycle later.
Connecting PWM4 to VCC selects three channel operation
and the pulse-termination times are spaced in 1/3 cycle
increments. Connecting both PWM3 and PWM4 to VCC
selects single-channel operation.
Once a PWM signal transitions low, it is held low for a
minimum of 1/3 cycle. This forced off time is required to
ensure an accurate current sample. Current sensing is
described in the next section. After the forced off time
expires, the PWM output is enabled. The PWM output state
is driven by the position of the error amplifier output signal,
V
sawtooth ramp as illustrated in Figure 7. When the modified
V
transitions high. The MOSFET driver detects the change in
state of the PWM signal and turns off the synchronous
(lower) MOSFET and turns on the upper MOSFET. The
PWM signal will remain high until the pulse termination
signal marks the beginning of the next cycle by triggering the
PWM signal low.
Current Sampling
During the forced off-time following a PWM transition low,
the associated channel current sense amplifier uses the
ISEN inputs to reproduce a signal proportional to the
inductor current, I
period after each PWM goes low and continuously gets
sampled for 1/3 period, or until the PWM goes high,
whichever comes first. No matter the current sense method,
the sense current, I
inductor current. Coincident with the falling edge of the PWM
signal, the sample and hold circuitry samples the sensed
current signal I
Therefore, the sample current, I
output current and held for one switching cycle. The sample
current is used for current balance, load-line regulation, and
overcurrent protection.
COMP
COMP
, minus the current correction signal relative to the
voltage crosses the sawtooth ramp, the PWM output
SEN
L
. This current gets sampled starting 1/6
, as illustrated in Figure 3.
SEN
, is simply a scaled version of the
13
n
, is proportional to the
ISL6307B
Current Sensing
The ISL6307B supports inductor DCR sensing, MOSFET
R
internal circuitry, shown in Figures 4, 5, and 6, represents
one channel of an N-channel converter. This circuitry is
repeated for each channel in the converter, but may not be
active depending on the status of the PWM3 and PWM4
pins, as described in the PWM Operation section.
INDUCTOR DCR SENSING
An inductor’s winding is characteristic of a distributed
resistance as measured by the DCR (Direct Current
Resistance) parameter. Consider the inductor DCR as a
separate lumped quantity, as shown in Figure 4. The
channel current I
pass through the DCR. Equation 3 shows the s-domain
equivalent voltage across the inductor V
A simple R-C network across the inductor extracts the DCR
voltage, as shown in Figure 4.
The voltage on the capacitor V
proportional to the channel current I
If the R-C network components are selected such that the
RC time constant (= R*C) matches the inductor time
constant (= L/DCR), the voltage across the capacitor V
equal to the voltage drop across the DCR, i.e. proportional to
the channel current.
V
V
DS(ON)
C
L
=
=
-------------------------------------------------------------------- -
I
L
s
⋅
⋅
sensing, or resistive sensing techniques. The
(
-------------
DCR
s L
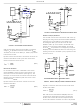
FIGURE 3. SAMPLE AND HOLD TIMING
L
⋅
(
s RC
+
+
⋅
DCR
1
L
, flowing through the inductor, will also
⋅
+
PWM
(
DCR I
)
1
)
0.5Tsw
SWITCHING PERIOD
⋅
L
)
I
L
TIME
C
SAMPLE CURRENT, I
, can be shown to be
L
, see Equation 4.
I
SEN
L
.
n
March 9, 2006
(EQ. 3)
(EQ. 4)
FN9225.0
C
is