isl6312a Intersil Corporation, isl6312a Datasheet - Page 32

isl6312a
Manufacturer Part Number
isl6312a
Description
Four-phase Buck Pwm Controller With Integrated Mosfet Drivers For Intel Vr10, Vr11, And Amd Applications
Manufacturer
Intersil Corporation
Datasheet
1.ISL6312A.pdf
(35 pages)
Available stocks
Company
Part Number
Manufacturer
Quantity
Price
Company:
Part Number:
isl6312aCRZ
Manufacturer:
INTERSIL
Quantity:
120
Company:
Part Number:
isl6312aCRZ-T
Manufacturer:
ANAREN
Quantity:
44
Part Number:
isl6312aCRZ-T
Manufacturer:
INTERSIL
Quantity:
20 000
Company:
Part Number:
isl6312aIRZ
Manufacturer:
FINTEK
Quantity:
10
Layout Considerations
MOSFETs switch very fast and efficiently. The speed with
which the current transitions from one device to another
causes voltage spikes across the interconnecting
impedances and parasitic circuit elements. These voltage
spikes can degrade efficiency, radiate noise into the circuit
and lead to device overvoltage stress. Careful component
selection, layout, and placement minimizes these voltage
spikes. Consider, as an example, the turnoff transition of the
upper PWM MOSFET. Prior to turnoff, the upper MOSFET
was carrying channel current. During the turnoff, current
stops flowing in the upper MOSFET and is picked up by the
lower MOSFET. Any inductance in the switched current path
generates a large voltage spike during the switching interval.
Careful component selection, tight layout of the critical
components, and short, wide circuit traces minimize the
magnitude of voltage spikes.
There are two sets of critical components in a DC/DC
converter using a ISL6312A controller. The power
components are the most critical because they switch large
amounts of energy. Next are small signal components that
connect to sensitive nodes or supply critical bypassing
current and signal coupling.
The power components should be placed first, which include
the MOSFETs, input and output capacitors, and the inductors. It
is important to have a symmetrical layout for each power train,
preferably with the controller located equidistant from each.
Symmetrical layout allows heat to be dissipated equally
across all power trains. Equidistant placement of the controller
to the first three power trains it controls through the integrated
drivers helps keep the gate drive traces equally short,
resulting in equal trace impedances and similar drive
capability of all sets of MOSFETs.
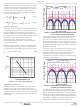
FIGURE 24. NORMALIZED INPUT-CAPACITOR RMS
0.3
0.2
0.1
0
0
I
I
I
L(P-P)
L(P-P)
L(P-P)
CURRENT FOR 2-PHASE CONVERTER
= 0
= 0.5 I
= 0.75 I
0.2
O
O
DUTY CYCLE (V
0.4
32
0.6
IN/
V
O
)
0.8
1.0
ISL6312A
When placing the MOSFETs try to keep the source of the
upper FETs and the drain of the lower FETs as close as
thermally possible. Input Bulk capacitors should be placed
close to the drain of the upper FETs and the source of the lower
FETs. Locate the output inductors and output capacitors
between the MOSFETs and the load. The high-frequency input
and output decoupling capacitors (ceramic) should be placed
as close as practicable to the decoupling target, making use of
the shortest connection paths to any internal planes, such as
vias to GND next or on the capacitor solder pad.
The critical small components include the bypass capacitors
for VCC and PVCC, and many of the components
surrounding the controller including the feedback network
and current sense components. Locate the VCC/PVCC
bypass capacitors as close to the ISL6312A as possible. It is
especially important to locate the components associated
with the feedback circuit close to their respective controller
pins, since they belong to a high-impedance circuit loop,
sensitive to EMI pick-up.
A multi-layer printed circuit board is recommended. Figure 25
shows the connections of the critical components for the
converter. Note that capacitors C
represent numerous physical capacitors. Dedicate one solid
layer, usually the one underneath the component side of the
board, for a ground plane and make all critical component
ground connections with vias to this layer.
Dedicate another solid layer as a power plane and break this
plane into smaller islands of common voltage levels. Keep the
metal runs from the PHASE terminal to output inductors short.
The power plane should support the input power and output
power nodes. Use copper filled polygons on the top and bottom
circuit layers for the phase nodes. Use the remaining printed
circuit layers for small signal wiring.
Routing UGATE, LGATE, and PHASE Traces
Great attention should be paid to routing the UGATE, LGATE,
and PHASE traces since they drive the power train MOSFETs
using short, high current pulses. It is important to size them as
large and as short as possible to reduce their overall
impedance and inductance. They should be sized to carry at
least one ampere of current (0.02” to 0.05”). Going between
layers with vias should also be avoided, but if so, use two vias
for interconnection when possible.
Extra care should be given to the LGATE traces in particular
since keeping their impedance and inductance low helps to
significantly reduce the possibility of shoot-through. It is also
important to route each channels UGATE and PHASE traces
in as close proximity as possible to reduce their inductances.
xxIN
and C
xxOUT
could each
August 1, 2007
FN9290.3