MM74C922N Fairchild Semiconductor, MM74C922N Datasheet - Page 8
MM74C922N
Manufacturer Part Number
MM74C922N
Description
IC ENCODER 16-KEY 18-DIP
Manufacturer
Fairchild Semiconductor
Series
74Cr
Type
16-Key Encoderr
Specifications of MM74C922N
Circuit
1 x 8:4
Independent Circuits
1
Current - Output High, Low
15mA, 16mA
Voltage Supply Source
Single Supply
Voltage - Supply
3 V ~ 15 V
Operating Temperature
-40°C ~ 85°C
Mounting Type
Through Hole
Package / Case
18-DIP (0.300", 7.62mm)
Lead Free Status / RoHS Status
Lead free / RoHS Compliant
Other names
74C922
74C922N
74C922N
Available stocks
Company
Part Number
Manufacturer
Quantity
Price
Company:
Part Number:
MM74C922N
Manufacturer:
NS
Quantity:
5 510
Company:
Part Number:
MM74C922N
Manufacturer:
FSC
Quantity:
1 300
Part Number:
MM74C922N
Manufacturer:
FAIRCHILD/仙童
Quantity:
20 000
www.fairchildsemi.com
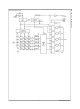
Outputs are in 3-STATE until key is pressed, then data is placed on bus. When key is released, outputs return to 3-STATE.
Theory of Operation
The MM74C922/MM74C923 Keyboard Encoders imple-
ment all the logic necessary to interface a 16 or 20 SPST
key switch matrix to a digital system. The encoder will con-
vert a key switch closer to a 4(MM74C922) or
5(MM74C923) bit nibble. The designer can control both the
keyboard scan rate and the key debounce period by alter-
ing the oscillator capacitor, C
mask capacitor, C
performance can be optimized for many keyboards.
The keyboard encoders connect to a switch matrix that is 4
rows by 4 columns (MM74C922) or 5 rows by 4 columns
(MM74C923). When no keys are depressed, the row inputs
are pulled high by internal pull-ups and the column outputs
sequentially output a logic “0”. These outputs are open
drain and are therefore low for 25% of the time and other-
wise off. The column scan rate is controlled by the oscilla-
tor input, which consists of a Schmitt trigger oscillator, a 2-
bit counter, and a 2–4-bit decoder.
When a key is depressed, key 0, for example, nothing will
happen when the X1 input is off, since Y1 will remain high.
When the X1 column is scanned, X1 goes low and Y1 will
go low. This disables the counter and keeps X1 low. Y1
MSK
. Thus, the MM74C922/MM74C923’s
OSE
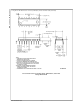
Asynchronous Data Entry Onto Bus (MM74C922)
, and the key bounce
Expansion to 32 Key Encoder (MM74C922)
8
going low also initiates the key bounce circuit timing and
locks out the other Y inputs. The key code to be output is a
combination of the frozen counter value and the decoded Y
inputs. Once the key bounce circuit times out, the data is
latched, and the Data Available (DAV) output goes high.
If, during the key closure the switch bounces, Y1 input will
go high again, restarting the scan and resetting the key
bounce circuitry. The key may bounce several times, but as
soon as the switch stays low for a debounce period, the
closure is assumed valid and the data is latched.
A key may also bounce when it is released. To ensure that
the encoder does not recognize this bounce as another key
closure, the debounce circuit must time out before another
closure is recognized.
The two-key roll-over feature can be illustrated by assum-
ing a key is depressed, and then a second key is
depressed. Since all scanning has stopped, and all other Y
inputs are disabled, the second key is not recognized until
the first key is lifted and the key bounce circuitry has reset.
The output latches feed 3-STATE, which is enabled when
the Output Enable (OE) input is taken low.