MT8VDDT6464AG-335F3 Micron Technology Inc, MT8VDDT6464AG-335F3 Datasheet - Page 8

MT8VDDT6464AG-335F3
Manufacturer Part Number
MT8VDDT6464AG-335F3
Description
MODULE DDR SDRAM 512MB 184-DIMM
Manufacturer
Micron Technology Inc
Datasheet
1.MT8VDDT3264AG-335G6.pdf
(30 pages)
Specifications of MT8VDDT6464AG-335F3
Memory Type
DDR SDRAM
Memory Size
512MB
Speed
333MT/s
Package / Case
184-DIMM
Lead Free Status / RoHS Status
Contains lead / RoHS non-compliant
General Description
MT8VDDT6464A are high-speed CMOS, dynamic ran-
dom-access, 128MB, 256MB, and 512MB memory
modules organized in a x64 configuration. DDR
SDRAM modules use internally configured quad-bank
DDR SDRAM devices.
tecture to achieve high-speed operation. The double
data rate architecture is essentially a 2n-prefetch
architecture with an interface designed to transfer two
data words per clock cycle at the I/O pins. A single
read or write access for the DDR SDRAM module effec-
tively consists of a single 2n-bit wide, one-clock-cycle
data transfer at the internal DRAM core and two corre-
sponding n-bit wide, one-half-clock-cycle data trans-
fers at the I/O pins.
externally, along with data, for use in data capture at
the receiver. DQS is an intermittent strobe transmitted
by the DDR SDRAM during READs and by the memory
controller during WRITEs. DQS is edge-aligned with
data for READs and center-aligned with data for
WRITEs.
ential clocks (CK and CK#); the crossing of CK going
HIGH and CK# going LOW will be referred to as the
positive edge of CK. Commands (address and control
signals) are registered at every positive edge of CK.
Input data is registered on both edges of DQS, and out-
put data is referenced to both edges of DQS, as well as
to both edges of CK.
are burst oriented; accesses start at a selected location
and continue for a programmed number of locations
in a programmed sequence. Accesses begin with the
registration of an ACTIVE command, which is then fol-
lowed by a READ or WRITE command. The address
bits registered coincident with the ACTIVE command
are used to select the device bank and row to be
accessed (BA0, BA1 select device bank; A0–A11 select
device row for the 128MB module, A0–A12 select
device row for the 256MB and 512MB modules). The
address bits registered coincident with the READ or
WRITE command are used to select the device bank
and the starting device column location for the burst
access.
read or write burst lengths of 2, 4, or 8 locations. An
auto precharge function may be enabled to provide a
self-timed row precharge that is initiated at the end of
the burst access.
pdf: 09005aef80867ab3, source: 09005aef80867a99
DD8C16_32_64x64AG.fm - Rev. G 9/04 EN
The
DDR SDRAM modules use a double data rate archi-
A bidirectional data strobe (DQS) is transmitted
DDR SDRAM modules operate from multiple differ-
Read and write accesses to DDR SDRAM modules
DDR SDRAM modules provide for programmable
MT8VDDT1664A,
MT8VDDT3264A,
and
8
SDRAM modules allows for concurrent operation,
thereby providing high effective bandwidth by hiding
row precharge and activation time.
power-saving power-down mode. All inputs are com-
patible with the JEDEC Standard for SSTL_2. All out-
puts are SSTL_2, Class II compatible.
information regarding DDR SDRAM operation, refer to
the 128Mb, 256Mb, or 512Mb DDR SDRAM compo-
nent data sheets.
Serial Presence-Detect Operation
presence-detect (SPD). The SPD function is imple-
mented using a 2,048-bit EEPROM. This nonvolatile
storage device contains 256 bytes. The first 128 bytes
can be programmed by Micron to identify the module
type and various SDRAM organizations and timing
parameters. The remaining 128 bytes of storage are
available for use by the customer. System READ/
WRITE operations between the master (system logic)
and the slave EEPROM device (DIMM) occur via a
standard I
SDA (data) signals, together with SA (2:0), which pro-
vide eight unique DIMM/EEPROM addresses. Write
protect (WP) is tied to ground on the module, perma-
nently disabling hardware write protect.
Mode Register Definition
mode of operation of DDR SDRAM devices. This defi-
nition includes the selection of a burst length, a burst
type, a CAS latency and an operating mode, as shown
in Figure 5, Mode Register Definition Diagram, on
page 9.
MODE REGISTER SET command (with BA0 = 0 and
BA1 = 0) and will retain the stored information until it
is programmed again or the device loses power (except
for bit A8, which is self-clearing).
contents of the memory, provided it is performed cor-
rectly. The mode register must be loaded (reloaded)
when all device banks are idle and no bursts are in
progress, and the controller must wait the specified
time before initiating the subsequent operation. Vio-
lating either of these requirements will result in
unspecified operation.
A3 specifies the type of burst (sequential or inter-
leaved), A4–A6 specify the CAS latency, and A7–A11
(128MB) or A7–A12 (256MB, 512MB) specify the oper-
ating mode.
128MB, 256MB, 512MB (x64, SR)
The pipelined, multibank architecture of DDR
An auto refresh mode is provided, along with a
These DDR SDRAM modules incorporate serial
The mode register is used to define the specific
Reprogramming the mode register will not alter the
Mode register bits A0–A2 specify the burst length,
Micron Technology, Inc., reserves the right to change products or specifications without notice.
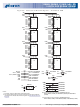
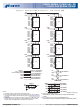
184-PIN DDR SDRAM UDIMM
The mode register is programmed via the
2
C bus using the DIMM’s SCL (clock) and
©2004 Micron Technology. Inc.
For more