EZ80F920120MOD Zilog, EZ80F920120MOD Datasheet - Page 156
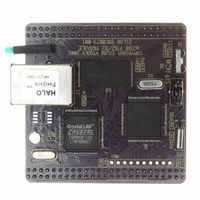
EZ80F920120MOD
Manufacturer Part Number
EZ80F920120MOD
Description
MODULE EZ80F92 512K 20MHZ
Manufacturer
Zilog
Datasheets
1.EZ80F920120MOD.pdf
(269 pages)
2.EZ80F920120MOD.pdf
(4 pages)
3.EZ80F920120MOD.pdf
(2 pages)
Specifications of EZ80F920120MOD
Module/board Type
Development Module
Processor Series
EZ80F92x
Core
eZ80
Data Bus Width
8 bit
Program Memory Type
Flash
Program Memory Size
1 MB
Interface Type
Cable
Maximum Clock Frequency
20 MHz
Operating Supply Voltage
0 V to 3.3 V
Maximum Operating Temperature
+ 70 C
Mounting Style
SMD/SMT
Package / Case
LQFP
Development Tools By Supplier
eZ80F920200ZCOG
Minimum Operating Temperature
0 C
For Use With/related Products
eZ80F92
Lead Free Status / RoHS Status
Contains lead / RoHS non-compliant
Other names
269-3157
EZ80F920120MOD
EZ80F920120MOD
- Current page: 156 of 269
- Download datasheet (4Mb)
Figure 33.I
PS015308-0404
SDA Signal
SCL Signal
Transferring Data
2
C Frame Structure
START Condition
Byte Format
Every character transferred on the SDA line must be a single 8-bit byte. The number of
bytes that can be transmitted per transfer is unrestricted. Each byte must be followed by an
Acknowledge (ACK)
Figure 33. A receiver can hold the SCL line Low to force the transmitter into a wait state.
Data transfer then continues when the receiver is ready for another byte of data and
releases SCL.
Acknowledge
Data transfer with an ACK function is obligatory. The ACK-related clock pulse is gener-
ated by the master. The transmitter releases the SDA line (High) during the ACK clock
pulse. The receiver must pull down the SDA line during the ACK clock pulse so that it
remains stable Low during the High period of this clock pulse. See Figure 34.
A receiver that is addressed is obliged to generate an ACK after each byte is received.
When a slave-receiver doesn't acknowledge the slave address (for example, unable to
receive because it's performing some real-time function), the data line must be left High
by the slave. The master then generates a STOP condition to abort the transfer.
If a slave-receiver acknowledges the slave address, but cannot receive any more data bytes,
the master must abort the transfer. The abort is indicated by the slave generating the Not
Acknowledge (NACK) on the first byte to follow. The slave leaves the data line High and
the master generates the STOP condition.
If a master-receiver is involved in a transfer, it must signal the end of data to the slave-
transmitter by not generating an ACK on the final byte that is clocked out of the slave. The
1. ACK is defined as a general Acknowledge bit. By contrast, the I
represented as AAK, bit 2 of the I
transmit. See
S
MSB
1
I
2
C Control Registers (I2C_CTL = 00CBh)
2
1
. Data is transferred with the most-significant bit (msb) first. See
P R E L I M I N A R Y
Acknowledge from
8
Receiver
2
C Control Register, which identifies which ACK signal to
9
1
Clock Line Held Low By Receiver
on page 158.
Acknowledge from
Receiver
2
ACK
C Acknowledge bit is
9
Product Specification
I2C Serial I/O Interface
eZ80F92/eZ80F93
STOP Condition
P
144
Related parts for EZ80F920120MOD
Image
Part Number
Description
Manufacturer
Datasheet
Request
R

Part Number:
Description:
Communication Controllers, ZILOG INTELLIGENT PERIPHERAL CONTROLLER (ZIP)
Manufacturer:
Zilog, Inc.
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
KIT DEV FOR Z8 ENCORE 16K TO 64K
Manufacturer:
Zilog
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
KIT DEV Z8 ENCORE XP 28-PIN
Manufacturer:
Zilog
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
DEV KIT FOR Z8 ENCORE 8K/4K
Manufacturer:
Zilog
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
KIT DEV Z8 ENCORE XP 28-PIN
Manufacturer:
Zilog
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
DEV KIT FOR Z8 ENCORE 4K TO 8K
Manufacturer:
Zilog
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
CMOS Z8 microcontroller. ROM 16 Kbytes, RAM 256 bytes, speed 16 MHz, 32 lines I/O, 3.0V to 5.5V
Manufacturer:
Zilog, Inc.
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Low-cost microcontroller. 512 bytes ROM, 61 bytes RAM, 8 MHz
Manufacturer:
Zilog, Inc.
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Z8 4K OTP Microcontroller
Manufacturer:
Zilog, Inc.
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
CMOS SUPER8 ROMLESS MCU
Manufacturer:
Zilog, Inc.
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
SL1866 CMOSZ8 OTP Microcontroller
Manufacturer:
Zilog, Inc.
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
SL1866 CMOSZ8 OTP Microcontroller
Manufacturer:
Zilog, Inc.
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
OTP (KB) = 1, RAM = 125, Speed = 12, I/O = 14, 8-bit Timers = 2, Comm Interfaces Other Features = Por, LV Protect, Voltage = 4.5-5.5V
Manufacturer:
Zilog, Inc.
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Zilog, Inc.
Datasheet:










