FSQ100 Fairchild Semiconductor, FSQ100 Datasheet - Page 10

FSQ100
Manufacturer Part Number
FSQ100
Description
IC SWIT PWM GREEN OVP HV 8DIP
Manufacturer
Fairchild Semiconductor
Datasheet
1.FSQ100.pdf
(12 pages)
Specifications of FSQ100
Output Isolation
Isolated
Frequency Range
61 ~ 73kHz
Voltage - Input
8 ~ 20 V
Voltage - Output
650V
Power (watts)
8W
Operating Temperature
25°C ~ 145°C
Package / Case
8-DIP (0.300", 7.62mm)
Power Switch Family
FSQ100
Power Switch On Resistance
16Ohm
Output Current
475mA
Number Of Outputs
Single
Mounting
Through Hole
Supply Current
1.5mA
Package Type
PDIP W
Operating Temperature (min)
-25C
Operating Temperature (max)
85C
Operating Temperature Classification
Commercial
Pin Count
8
Power Dissipation
1.4W
On Resistance (max)
16 Ohms
Maximum Operating Temperature
+ 85 C
Minimum Operating Temperature
- 25 C
Maximum Power Dissipation
1400 mW
Mounting Style
Through Hole
Lead Free Status / RoHS Status
Lead free / RoHS Compliant
Available stocks
Company
Part Number
Manufacturer
Quantity
Price
Part Number:
FSQ100
Manufacturer:
FAIRCHILD/仙童
Quantity:
20 000
© 2007 Fairchild Semiconductor Corporation
FSQ100 Rev. 1.0.2
Application Tips
1. Methods of Reducing Audible Noise
Switching mode power converters have electronic and
magnetic components that generate audible noise when
the operating frequency is in the range of 20~20,000Hz.
Even though they operate above 20kHz, they can make
noise, depending on the load condition. Designers can
employ several methods to reduce noise.
Glue or Varnish
The most common method involves using glue or
varnish to tighten magnetic components. The motion of
core,
magnetostriction of core can cause the transformer to
produce audible noise. The use of rigid glue and varnish
helps reduce the transformer noise, but can crack the
core. This is because sudden changes in the ambient
temperature cause the core and the glue to expand or
shrink in a different ratio.
Ceramic Capacitor
Using a film capacitor instead of a ceramic capacitor as
a snubber capacitor is another noise-reduction solution.
Some dielectric materials show a piezoelectric effect,
depending on the electric field intensity. Hence, a
snubber capacitor becomes one of the most significant
sources of audible noise. It is possible to use a Zener
clamp circuit instead of an RCD snubber for higher
efficiency as and lower audible noise.
Adjusting Sound Frequency
Moving the fundamental frequency of noise out of
2~4kHz range is the third method. Generally, humans
are more sensitive to noise in the range of 2~4kHz.
When the fundamental frequency of noise is located in
this range, the noise is perceived as louder, although
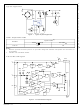
the noise intensity level is identical (refer to Figure 22
Equal Loudness Curves).
When FPS acts in burst mode and the burst operation is
suspected to be a source of noise, this method may be
helpful. If the frequency of burst-mode operation lies in
the range of 2~4 kHz, adjusting the feedback loop can
shift the burst operation frequency. To reduce the burst
operation frequency, increase a feedback gain capacitor
(C
capacitor (C
(R
F
F
), opto-coupler supply resistor (R
), as shown in Figure 23.
bobbin
B
); and decrease a feedback gain resistor
and
coil,
and
the
D
), and feedback
chattering
or
10
2. Reference Materials
AN-4134 — Design Guidelines for Off-line Forward
Converters using FPS™
AN-4137 — Design Guidelines for Off-line Flyback
Converters using FPS™
AN-4138 — Design Considerations for Battery Charger
Using Green Mode Fairchild Power Switch (FPS™)
AN-4140 — Transformer Design Consideration for Off-
line Flyback Converters Using Fairchild Power Switch
(FPS™)
AN-4141 — Troubleshooting and Design Tips for
Fairchild Power Switch (FPS™) Flyback Applications
AN-4147 — Design Guidelines for RCD Snubber of
Flyback
AN-4148 — Audible Noise Reduction Techniques for
FPS™Applications
Figure 23.
Figure 22.
Typical Feedback Network of FPS™
Equal Loudness Curves
www.fairchildsemi.com