CA3130EZ Intersil, CA3130EZ Datasheet - Page 5

CA3130EZ
Manufacturer Part Number
CA3130EZ
Description
IC OP AMP 15MHZ BIMOS 8-DIP
Manufacturer
Intersil
Specifications of CA3130EZ
Amplifier Type
General Purpose
Number Of Circuits
1
Slew Rate
30 V/µs
Gain Bandwidth Product
15MHz
Current - Input Bias
5pA
Voltage - Input Offset
8000µV
Current - Supply
10mA
Current - Output / Channel
45mA
Voltage - Supply, Single/dual (±)
5 V ~ 16 V, ±2.5 V ~ 8 V
Operating Temperature
-55°C ~ 125°C
Mounting Type
Through Hole
Package / Case
8-DIP (0.300", 7.62mm)
Bandwidth
15 MHz
Common Mode Rejection Ratio
90
Current, Input Bias
0.000005 μA
Current, Input Offset
0.5 pA
Current, Output
22 mA
Current, Supply
10 mA
Number Of Amplifiers
Single
Package Type
PDIP-8
Resistance, Input
1.5 Teraohms
Temperature, Operating, Range
-55 to +125 °C
Time, Rise
0.09 μs
Voltage, Gain
320 kV/V
Voltage, Input
-0.5 to 23 V
Voltage, Noise
23000 nV/sqrt Hz
Voltage, Offset
8 mV
Voltage, Output, High
13.3 V
Voltage, Output, Low
0.002 V
Voltage, Supply
5 to 16 V
Lead Free Status / RoHS Status
Lead free / RoHS Compliant
Output Type
-
-3db Bandwidth
-
Lead Free Status / Rohs Status
RoHS Compliant part
Electrostatic Device
Available stocks
Company
Part Number
Manufacturer
Quantity
Price
Company:
Part Number:
CA3130EZ
Manufacturer:
SILICON
Quantity:
19 380
Company:
Part Number:
CA3130EZ
Manufacturer:
INTERSIL
Quantity:
4
Part Number:
CA3130EZ
Manufacturer:
INTERSIL
Quantity:
20 000
NOTES:
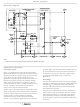
Cascade-connected PMOS transistors Q2, Q4 are the
constant-current source for the input stage. The biasing circuit
for the constant-current source is subsequently described.
The small diodes D
against high-voltage transients, including static electricity
during handling for Q
Second-Stage
Most of the voltage gain in the CA3130 is provided by the
second amplifier stage, consisting of bipolar transistor Q
and its cascade-connected load resistance provided by
PMOS transistors Q
for these PMOS transistors is subsequently described. Miller
Effect compensation (roll-off) is accomplished by simply
connecting a small capacitor between Terminals 1 and 8. A
47pF capacitor provides sufficient compensation for stable
unity-gain operation in most applications.
Bias-Source Circuit
At total supply voltages, somewhat above 8.3V, resistor R
and zener diode Z
the series-connected circuit, consisting of resistor R
D
of resistor R
about 4.5V for PMOS transistors Q
Terminal 7. A potential of about 2.2V is developed across
diode-connected PMOS transistor Q
7 to provide gate bias for PMOS transistors Q
should be noted that Q
both Q
be identical, the approximately 200µA current in Q
establishes a similar current in Q
INPUT
6. Total supply voltage (for indicated voltage gains) = 15V with input
7. Total supply voltage (for indicated voltage gains) = 15V with
1
+
3
2
-
through D
terminals biased so that Terminal 6 potential is +7.5V above
Terminal 4.
output terminal driven to either supply rail.
FIGURE 1. BLOCK DIAGRAM OF THE CA3130 SERIES
2
CA3130
OFFSET
and Q
NULL
5
A
V
≈ 5X
1
1
4
and diode D
, and PMOS transistor Q
3
. Since transistors Q
200µA
(WHEN REQUIRED)
1
BIAS CKT.
COMPENSATION
5
serve to establish a voltage of 8.3V across
3
through D
6
and Q
and Q
1
1.35mA
is “mirror-connected (see Note 8)” to
4
6000X
C
A
provides a gate-bias potential of
5
V
C
7
. The source of bias potentials
.
≈
5
8
provide gate-oxide protection
2
200µA
and Q
4
1
1
8
and Q
, Q
with respect to Terminal
1
2
. A tap at the junction
3
A
, Q
30X
as constant current
V
5
STROBE
8mA
(NOTE 5)
0mA
(NOTE 7)
≈
3
with respect to
2
are designed to
and Q
1
1
, diodes
CA3130, CA3130A
3
OUTPUT
. It
V+
V-
7
6
4
2
11
sources for both the first and second amplifier stages,
respectively.
At total supply voltages somewhat less than 8.3V, zener
diode Z
developed across series-connected R
varies directly with variations in supply voltage.
Consequently, the gate bias for Q
accordance with supply-voltage variations. This variation
results in deterioration of the power-supply-rejection ratio
(PSRR) at total supply voltages below 8.3V. Operation at
total supply voltages below about 4.5V results in seriously
degraded performance.
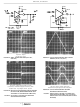
Output Stage
The output stage consists of a drain-loaded inverting
amplifier using CMOS transistors operating in the Class A
mode. When operating into very high resistance loads, the
output can be swung within millivolts of either supply rail.
Because the output stage is a drain-loaded amplifier, its gain
is dependent upon the load impedance. The transfer
characteristics of the output stage for a load returned to the
negative supply rail are shown in Figure 2. Typical op amp
loads are readily driven by the output stage. Because large-
signal excursions are non-linear, requiring feedback for good
waveform reproduction, transient delays may be
encountered. As a voltage follower, the amplifier can achieve
0.01% accuracy levels, including the negative supply rail.
NOTE:
8. For general information on the characteristics of CMOS
FIGURE 2. VOLTAGE TRANSFER CHARACTERISTICS OF
transistor-pairs in linear-circuit applications, see File Number
619, data sheet on CA3600E “CMOS Transistor Array”.
17.5
12.5
7.5
2.5
15
10
5
0
1
0
becomes nonconductive and the potential,
SUPPLY VOLTAGE: V+ = 15, V- = 0V
T
500Ω
A
= 25
1kΩ
CMOS OUTPUT STAGE
2.5
GATE VOLTAGE (TERMINALS 4 AND 8) (V)
o
2kΩ
C
LOAD RESISTANCE = 5kΩ
5
7.5
10
4
, Q
12.5
5
1
, D
and Q
15
1
-D
4
2
17.5
, and Q
, Q
3
varies in
20
1
,
22.5