FAN9611MX Fairchild Semiconductor, FAN9611MX Datasheet - Page 10

FAN9611MX
Manufacturer Part Number
FAN9611MX
Description
Power Factor Correction ICs Interleaved Dual BCM PFC Controller
Manufacturer
Fairchild Semiconductor
Datasheet
1.FAN9611MX.pdf
(37 pages)
Specifications of FAN9611MX
Switching Frequency
525 KHz
Maximum Operating Temperature
+ 125 C
Mounting Style
SMD/SMT
Package / Case
SOIC-16
Minimum Operating Temperature
- 40 C
Lead Free Status / Rohs Status
Details
Available stocks
Company
Part Number
Manufacturer
Quantity
Price
Part Number:
FAN9611MX
Manufacturer:
FAIRCHILD/仙童
Quantity:
20 000
© 2008 Fairchild Semiconductor Corporation
FAN9611 / FAN9612 • Rev. 1.1.3
When the PWM ramp is made proportional to the input
voltage squared, the system offers other noteworthy
benefits. The first is the input voltage-independent small
signal gain of the closed loop power supply, which
makes compensation of the voltage regulation loop
much easier. The second side benefit is that the output
of the error amplifier becomes directly proportional to
the input power of the converter. This phenomenon is
very significant and it is re-visited in Section 9
describing light-load operation.
5. Starting a PWM Cycle
The principle of boundary conduction mode calls for a
pulse width modulator able to operate with variable
frequency and initiate a switching period whenever the
current in the boost inductor reaches zero. Therefore,
BCM controllers cannot utilize a fixed frequency
oscillator circuit to control the operating frequency.
Instead, a zero current detector is used to sense the
inductor current and turn on the power switch once the
current in the boost inductor reaches zero. This process
is facilitated by an auxiliary winding on the boost
inductor. The voltage waveform of the auxiliary winding
can be used for indirect detection of the zero inductor
current condition of the boost inductor. Therefore it
should be connected to the zero current detect input, as
shown in Figure 11.
The auxiliary winding can also be used to generate bias
for the PFC controller when an independent bias power
supply is not present in the system.
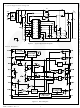
Figure 11. Simple Zero-Current Detection Method
Figure 10. Input-Voltage Feedforward
10
At startup condition and in the unlikely case of missing
zero current detection, the lack of an oscillator would
mean that the converter stops operating. To overcome
these situations, a restart timer is employed to kick start
the controller and provide the first turn-on command, as
shown in Figure 12.
6. Terminating the Conduction Interval
Terminating the conduction period of the boost
transistor in boundary conduction mode controllers is
similar to any other pulse width modulator. During
normal operation, the PWM comparator turns off the
power transistor when the ramp waveform exceeds the
control voltage provided by the error amplifier. In the
FAN9611/12 and in similar voltage-mode PWMs, the
ramp is a linearly rising waveform at one input of the
comparator circuit.
In addition to the PWM comparator, the current limit
circuit and a timer circuit limiting the maximum on-time
of the boost transistor can also terminate the gate drive
pulse of the controller. These functions provide
protection for the power switch against excessive
current stress.
7. Protecting the Power Components
In general, power converters are designed with
adequate margin for reliable operation under all
operating conditions. However, it might be difficult to
predict dangerous conditions under transient or certain
fault situations. Therefore, the FAN9611/12 contains
dedicated protection circuits to monitor the individual
peak currents in the boost inductors and in the power
transistors. Furthermore, the boost output voltage is
sensed by two independent mechanisms to provide
over-voltage protection for the power transistors,
rectifier diodes, and the output energy storage capacitor
of the converter.
Current Limit
Maximum
On-Time
PWM
Figure 13. Conduction Interval Termination
Figure 12. PWM Cycle Start
S
R
D
Q
Q
www.fairchildsemi.com
DRV