ATmega88 Atmel Corporation, ATmega88 Datasheet - Page 45

ATmega88
Manufacturer Part Number
ATmega88
Description
Manufacturer
Atmel Corporation
Specifications of ATmega88
Flash (kbytes)
8 Kbytes
Pin Count
32
Max. Operating Frequency
20 MHz
Cpu
8-bit AVR
# Of Touch Channels
12
Hardware Qtouch Acquisition
No
Max I/o Pins
23
Ext Interrupts
24
Usb Speed
No
Usb Interface
No
Spi
2
Twi (i2c)
1
Uart
1
Graphic Lcd
No
Video Decoder
No
Camera Interface
No
Adc Channels
8
Adc Resolution (bits)
10
Adc Speed (ksps)
15
Analog Comparators
1
Resistive Touch Screen
No
Temp. Sensor
No
Crypto Engine
No
Sram (kbytes)
1
Eeprom (bytes)
512
Self Program Memory
YES
Dram Memory
No
Nand Interface
No
Picopower
No
Temp. Range (deg C)
-40 to 85
I/o Supply Class
1.8 to 5.5
Operating Voltage (vcc)
1.8 to 5.5
Fpu
No
Mpu / Mmu
no / no
Timers
3
Output Compare Channels
6
Input Capture Channels
1
Pwm Channels
6
32khz Rtc
Yes
Calibrated Rc Oscillator
Yes
Available stocks
Company
Part Number
Manufacturer
Quantity
Price
Part Number:
ATmega88-15AT
Manufacturer:
ATMEL/爱特梅尔
Quantity:
20 000
Company:
Part Number:
ATmega88-15AT1
Manufacturer:
ATMEL
Quantity:
1 000
Part Number:
ATmega88-15AT1
Manufacturer:
ATMEL/爱特梅尔
Quantity:
20 000
Company:
Part Number:
ATmega88-15ATI
Manufacturer:
ATMEL
Quantity:
5 510
Company:
Part Number:
ATmega88-15ATI
Manufacturer:
LT
Quantity:
5 510
Company:
Part Number:
ATmega88-15AZ
Manufacturer:
ATMEL
Quantity:
2 000
Company:
Part Number:
ATmega88-15AZ
Manufacturer:
ATMEL
Quantity:
120
Part Number:
ATmega88-15AZ
Manufacturer:
ATMEL/爱特梅尔
Quantity:
20 000
Part Number:
ATmega88-20AU
Manufacturer:
ATMEL/爱特梅尔
Quantity:
20 000
11. System control and reset
11.1
11.2
2545T–AVR–05/11
Resetting the AVR
Reset sources
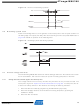
During reset, all I/O registers are set to their initial values, and the program starts execution from
the reset vector. For the Atmel ATmega168, the instruction placed at the reset vector must be a
JMP – absolute jump – instruction to the reset handling routine. For the Atmel ATmega48 and
Atmel ATmega88, the instruction placed at the reset vector must be an RJMP – relative jump –
instruction to the reset handling routine. If the program never enables an interrupt source, the
Interrupt Vectors are not used, and regular program code can be placed at these locations. This
is also the case if the reset vector is in the application section while the interrupt vectors are in
the boot section or vice versa (ATmega88/168 only). The circuit diagram in
46
circuitry.
The I/O ports of the AVR are immediately reset to their initial state when a reset source goes
active. This does not require any clock source to be running.
After all reset sources have gone inactive, a delay counter is invoked, stretching the internal
reset. This allows the power to reach a stable level before normal operation starts. The time-out
period of the delay counter is defined by the user through the SUT and CKSEL Fuses. The dif-
ferent selections for the delay period are presented in
The ATmega48/88/168 has four sources of reset:
• Power-on reset. The MCU is reset when the supply voltage is below the power-on reset
• External reset. The MCU is reset when a low level is present on the RESET pin for longer than
• Watchdog system reset. The MCU is reset when the watchdog timer period expires and the
• Brown-out reset. The MCU is reset when the supply voltage V
threshold (V
the minimum pulse length
watchdog system reset mode is enabled
threshold (V
shows the reset logic.
POT
BOT
)
) and the brown-out detector is enabled
Table 29-3 on page 307
defines the electrical parameters of the reset
“Clock sources” on page
ATmega48/88/168
CC
is below the Brown-out Reset
Figure 11-1 on page
28.
45