mcf51ac256a Freescale Semiconductor, Inc, mcf51ac256a Datasheet - Page 292
mcf51ac256a
Manufacturer Part Number
mcf51ac256a
Description
Mcf51ac Flexis
Manufacturer
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet
1.MCF51AC256A.pdf
(566 pages)
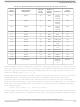
Available stocks
Company
Part Number
Manufacturer
Quantity
Price
Company:
Part Number:
mcf51ac256aCFUE
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor
Quantity:
10 000
Company:
Part Number:
mcf51ac256aCLKE
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor
Quantity:
10 000
Company:
Part Number:
mcf51ac256aCPUE
Manufacturer:
MURATA
Quantity:
1 000
- Current page: 292 of 566
- Download datasheet (4Mb)
Interrupt Controller (CF1_INTC)
13.1.1
Interrupt exception processing includes interrupt recognition, aborting the current instruction execution
stream, storing an 8-byte exception stack frame in the memory, calculation of the appropriate vector, and
passing control to the specified interrupt service routine.
Unless specifically noted otherwise, all ColdFire processors sample for interrupts once during each
instruction’s execution during the first cycle of execution in the OEP. Additionally, all ColdFire processors
use an instruction restart exception model.
The ColdFire processor architecture defines a 3-bit interrupt priority mask field in the processor’s status
register (SR[I]). This field, and the associated hardware, support seven levels of interrupt requests with the
processor providing automatic nesting capabilities. The levels are defined in descending numeric order
with 7 > 6 ... > 1. Level 7 interrupts are treated as non-maskable, edge-sensitive requests while levels 6–1
are maskable, level-sensitive requests. The SR[I] field defines the processor’s current interrupt level. The
processor continuously compares the encoded IRQ level from CF1_INTC against SR[I]. Recall that
interrupt requests are inhibited for all levels less than or equal to the current level, except the edge-sensitive
level 7 request that cannot be masked.
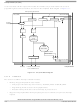
Exception processing for ColdFire processors is streamlined for performance and includes all actions from
detecting the fault condition to the initiation of fetch for the first handler instruction. Exception processing
is comprised of four major steps.
13-2
1. The processor makes an internal copy of the status register (SR) and enters supervisor mode by
2. The processor determines the exception vector number. For all faults except interrupts, the
3. The processor saves the current context by creating an exception stack frame on the system stack.
Exit Instruction from ISR
setting SR[S] and disabling trace mode by clearing SR[T]. The occurrence of an interrupt
exception also forces the master mode (M) bit to clear and the interrupt priority mask (I) to set to
the level of the current interrupt request.
processor performs this calculation based on the exception type. For interrupts, the processor
performs an IACK bus cycle to obtain the vector number from the interrupt controller if
CPUCR[IAE] equals 1. The IACK cycle is mapped to special locations within the interrupt
controller’s IPS address space with the interrupt level encoded in the address. If
CPUCR[IAE] equals 0, the processor uses the vector number supplied by the interrupt controller
at the time the request was signaled (for improved performance).
As a result, exception stack frame is created at a 0-modulo-4 address on top of the system stack
defined by the supervisor stack pointer (SSP). The processor uses an 8-byte stack frame for all
exceptions. It contains the vector number of the exception, the contents of the status register at the
time of the exception, and the program counter (PC) at the time of the exception. The exception
Software IACK
Attribute
Overview
MCF51AC256 ColdFire Integrated Microcontroller Reference Manual, Rev. 5
Table 13-1. Exception Processing Comparison (continued)
No
RTI
HCS08
Yes
RTE
V1 ColdFire
Freescale Semiconductor
Related parts for mcf51ac256a
Image
Part Number
Description
Manufacturer
Datasheet
Request
R
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet: