mc68hc916y3 Freescale Semiconductor, Inc, mc68hc916y3 Datasheet - Page 162
mc68hc916y3
Manufacturer Part Number
mc68hc916y3
Description
Mc68hc16y3 16 Bit Microcontroller
Manufacturer
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet
1.MC68HC916Y3.pdf
(500 pages)
- Current page: 162 of 500
- Download datasheet (4Mb)
5.7.8 Use of the Three-State Control Pin
5.7.9 Reset Processing Summary
5-54
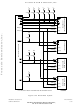
CLKOUT
CYCLES
MOTOROLA
NOTES:
RESET
V
LOCK
VCO
BUS
1. INTERNAL START-UP TIME
2. FIRST INSTRUCTION FETCHED
DD
Asserting the three-state control (TSC) input causes the MCU to put all output drivers
in a disabled, high-impedance state. The signal must remain asserted for approxi-
mately ten clock cycles in order for drivers to change state.
When the internal clock synthesizer is used (MODCLK held high during reset), synthe-
sizer ramp-up time affects how long the ten cycles take. Worst case is approximately
20 milliseconds from TSC assertion.
When an external clock signal is applied (MODCLK held low during reset), pins go to
high-impedance state as soon after TSC assertion as approximately ten clock pulses
have been applied to the EXTAL pin.
To prevent write cycles in progress from being corrupted, a reset is recognized at the
end of a bus cycle, and not at an instruction boundary. Any processing in progress at
the time a reset occurs is aborted. After SCIM2 reset control logic has synchronized
an internal or external reset request, the MSTRST signal is asserted.
The following events take place when MSTRST is asserted.
BUS STATE
UNKNOWN
When TSC assertion takes effect, internal signals are forced to val-
ues that can cause inadvertent mode selection. Once the output driv-
ers change state, the MCU must be powered down and restarted
before normal operation can resume.
2 CLOCKS
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
CONTROL SIGNALS
For More Information On This Product,
THREE-STATED
ADDRESS AND
Figure 5-19 Power-On Reset
512 CLOCKS
Go to: www.freescale.com
10 CLOCKS
NOTE
1
MC68HC16Y3/916Y3
2
USER’S MANUAL
16 POR TIM
Related parts for mc68hc916y3
Image
Part Number
Description
Manufacturer
Datasheet
Request
R
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet: