M29W640FT70ZA6E NUMONYX, M29W640FT70ZA6E Datasheet - Page 64

M29W640FT70ZA6E
Manufacturer Part Number
M29W640FT70ZA6E
Description
IC FLASH 64MBIT 70NS 48TFBGA
Manufacturer
NUMONYX
Series
Axcell™r
Datasheet
1.M29W640FB70ZA6E.pdf
(71 pages)
Specifications of M29W640FT70ZA6E
Format - Memory
FLASH
Memory Type
FLASH - Nor
Memory Size
64M (8Mx8, 4Mx16)
Speed
70ns
Interface
Parallel
Voltage - Supply
2.7 V ~ 3.6 V
Operating Temperature
-40°C ~ 85°C
Package / Case
48-TFBGA
Package
48TFBGA
Cell Type
NOR
Density
64 Mb
Architecture
Sectored
Block Organization
Asymmetrical
Location Of Boot Block
Top
Typical Operating Supply Voltage
3|3.3 V
Sector Size
8KByte x 8|64KByte x 127
Timing Type
Asynchronous
Interface Type
Parallel
Lead Free Status / RoHS Status
Lead free / RoHS Compliant
Other names
497-5034
497-5034
497-5034
Available stocks
Company
Part Number
Manufacturer
Quantity
Price
Company:
Part Number:
M29W640FT70ZA6E
Manufacturer:
Micron Technology Inc
Quantity:
10 000
Appendix D
D.1
D.2
Note:
64/71
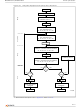
Block protection can be used to prevent any operation from modifying the data stored in the
memory. The blocks are protected in groups, refer to
Table 21
Erase operations within the protected group fail to change the data.
There are three techniques that can be used to control Block Protection, these are the
Programmer technique, the In-System technique and Temporary Unprotection. Temporary
Unprotection is controlled by the Reset/Block Temporary Unprotection pin, RP; this is
described in the Signal Descriptions section.
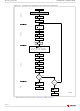
Programmer technique
The Programmer technique uses high (V
cannot be achieved using a standard microprocessor bus, therefore the technique is
recommended only for use in Programming Equipment.
To protect a group of blocks follow the flowchart in
Group Protect
groups first, then all groups can be unprotected at the same time. To unprotect the chip
follow
technique bus operations, BYTE = V
The timing on these flowcharts is critical. Care should be taken to ensure that, where a
pause is specified, it is followed as closely as possible. Do not abort the procedure before
reaching the end. Chip Unprotect can take several seconds and a user message should be
provided to show that the operation is progressing.
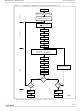
In-System technique
The In-System technique requires a high voltage level on the Reset/Blocks Temporary
Unprotect pin, RP
components on the microprocessor bus, therefore this technique is suitable for use after the
memory has been fitted to the system.
To protect a group of blocks follow the flowchart in
Protect
then all the groups can be unprotected at the same time. To unprotect the chip follow
Figure 19: In-System Equipment Chip Unprotect
The timing on these flowcharts is critical. Care should be taken to ensure that, where a
pause is specified, it is followed as closely as possible. Do not allow the microprocessor to
service interrupts that will upset the timing and do not abort the procedure before reaching
the end. Chip Unprotect can take several seconds and a user message should be provided
to show that the operation is progressing.
RP can be either at V
Extended Block.
Figure 17: Programmer Equipment Chip Unprotect
flowchart. To unprotect the whole chip it is necessary to protect all of the groups first,
and
Block protection
Table 22
flowchart. To unprotect the whole chip it is necessary to protect all of the
(1)
. This can be achieved without violating the maximum ratings of the
IH
for details of the Protection Groups. Once protected, Program and
or at V
ID
when using the In-System Technique to protect the
IH
or V
ID
) voltage levels on some of the bus pins. These
IL
, gives a summary of each operation.
flowchart.
Figure 16: Programmer Equipment
Figure 18: In-System Equipment Group
Appendix A: Block
flowchart.
Table 30: Programmer
addresses,